Explore the basics, workings, and benefits of modified sine wave inverters, and their role in future alternative energy systems.
Understanding Modified Sine Wave Inverters
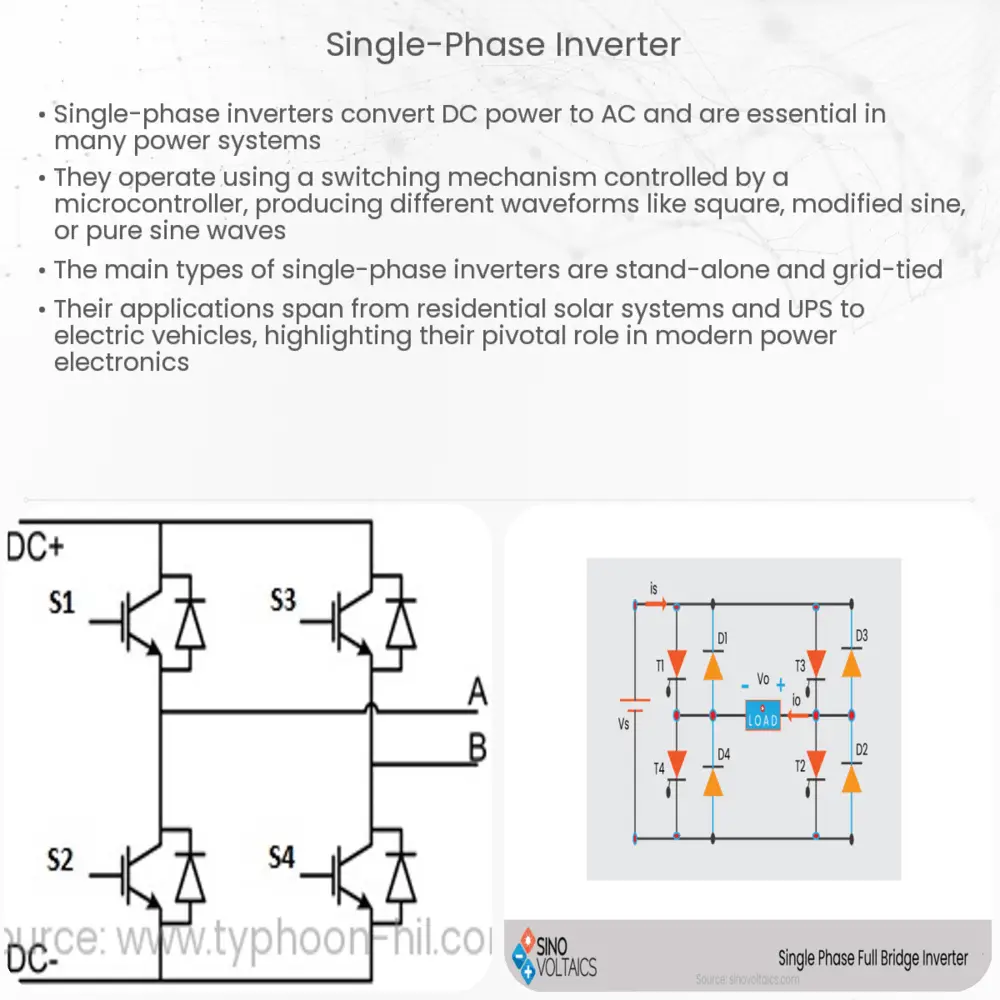
When delving into the world of alternative energy systems, you will often encounter a device called a modified sine wave inverter. The inverter is an integral component of power systems, converting direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) to be used in residential or commercial settings.
Principles of Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Before understanding the nuances of a modified sine wave inverter, it’s essential to know the basics of a sine wave inverter. Sine wave inverters produce an output that is identical to the standard electrical current supplied by utility companies. This type of current is characterized by a smooth, sinusoidal wave.
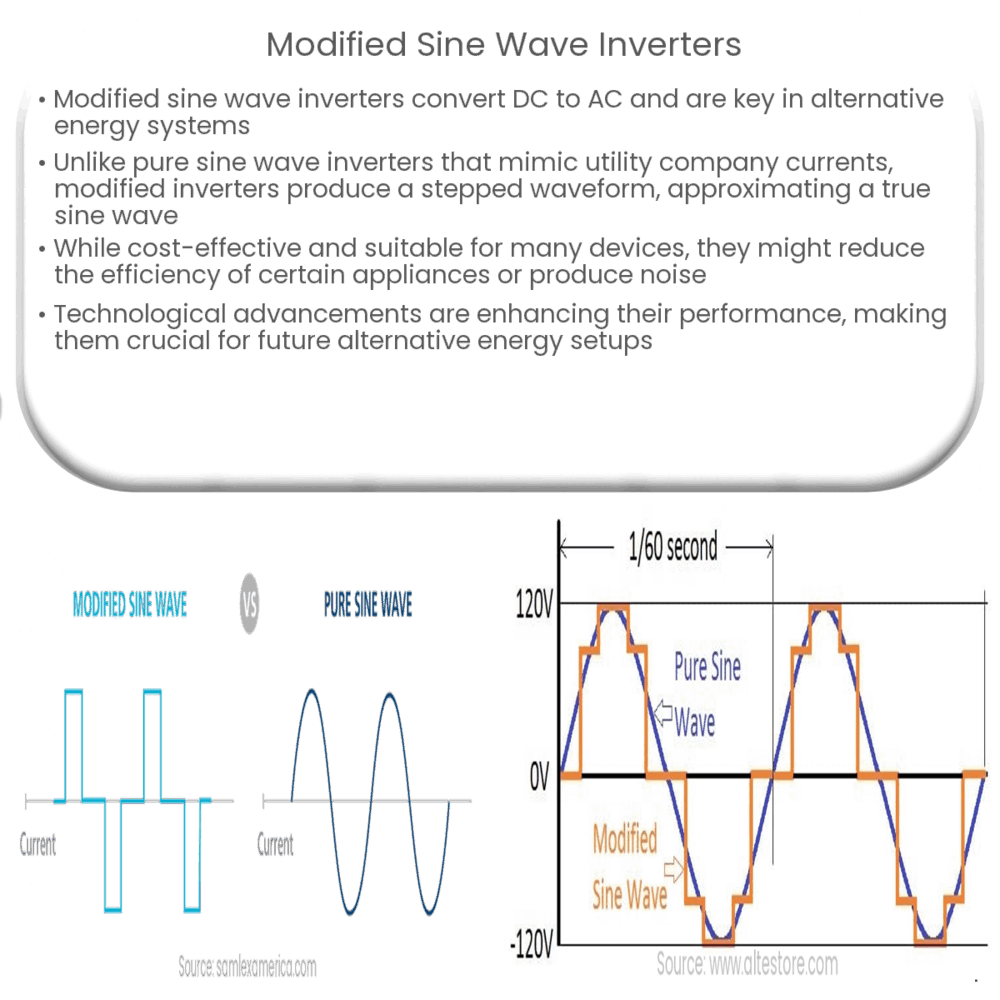
Modified sine wave inverters, on the other hand, produce a different kind of waveform. Instead of a smoothly undulating wave, a modified sine wave looks more like a stepped wave. It switches abruptly between voltage levels rather than gradually transitioning, and the output isn’t pure; it’s an approximation of a true sine wave.
Applications and Limitations of Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Modified sine wave inverters are a popular choice due to their affordability. They are less expensive than pure sine wave inverters, making them a desirable option for many. However, the lower cost does come with certain limitations.
- They may cause some appliances to operate less efficiently, resulting in more power usage or slightly reduced performance.
- Noisy operation is another drawback. Some devices can produce a buzzing sound when powered by a modified sine wave.
- Delicate or sophisticated electronic equipment, such as medical devices or audiovisual systems, may not work correctly or may be damaged over time.
Despite these drawbacks, modified sine wave inverters are suitable for many devices, like simple appliances and tools that do not require precision operation. As such, they are commonly found in RVs, boats, and other off-grid systems where pure sine wave inverters are not necessary or would be cost-prohibitive.
In the next section, we will explore the technical workings of modified sine wave inverters in greater detail.
Technical Workings of Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Modified sine wave inverters operate by generating a waveform that, while not an exact replica of a sine wave, serves a similar purpose. The output is a stepped waveform which alternates between three voltage levels: positive, zero, and negative. This alternation creates a square wave that approximates a sine wave.
The operation of these inverters involves complex electrical engineering principles, yet their essential function boils down to three steps: producing a positive voltage, dropping it to zero voltage, then producing a negative voltage. This cycle repeats to create the waveform. This stepped waveform, while not as smooth as a pure sine wave, is still compatible with most electrical devices.
Choosing a Modified Sine Wave Inverter
If you’re considering a modified sine wave inverter for your energy system, it’s important to keep certain factors in mind. The primary consideration is compatibility. Verify that the devices you plan to power can operate efficiently and safely with a modified sine wave. In addition, consider the inverter’s power rating to ensure it can handle the total electrical load you plan to use.
The Future of Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Advancements in technology are improving the efficiency and effectiveness of modified sine wave inverters. While they may not replace pure sine wave inverters in all applications, their affordability and simplicity make them a viable option for many users. With continuous improvements, we can expect to see these inverters becoming increasingly competitive in terms of performance and efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, modified sine wave inverters serve as a cost-effective alternative to pure sine wave inverters. While they have some limitations in terms of efficiency and compatibility with certain devices, they offer considerable benefits for many applications. Their simple design, coupled with advancements in technology, is set to position them as a significant component of future alternative energy systems. It’s essential to consider your specific power needs, the devices you plan to run, and your budget when choosing between a modified or pure sine wave inverter. This choice will impact the efficiency and reliability of your off-grid power system, potentially leading to significant savings in the long run.