Explore the world of sine wave inverters: their functionality, benefits, applications, key features, and tips on selecting the right model.
Sine Wave Inverters: An In-Depth Analysis
Sine wave inverters, often referred to as “true” or “pure” sine wave inverters, are integral components in many modern power systems. They convert direct current (DC) energy, such as that sourced from solar panels or batteries, into alternating current (AC) energy, the type used in most residential and commercial settings.
Understanding Sine Wave Inverters
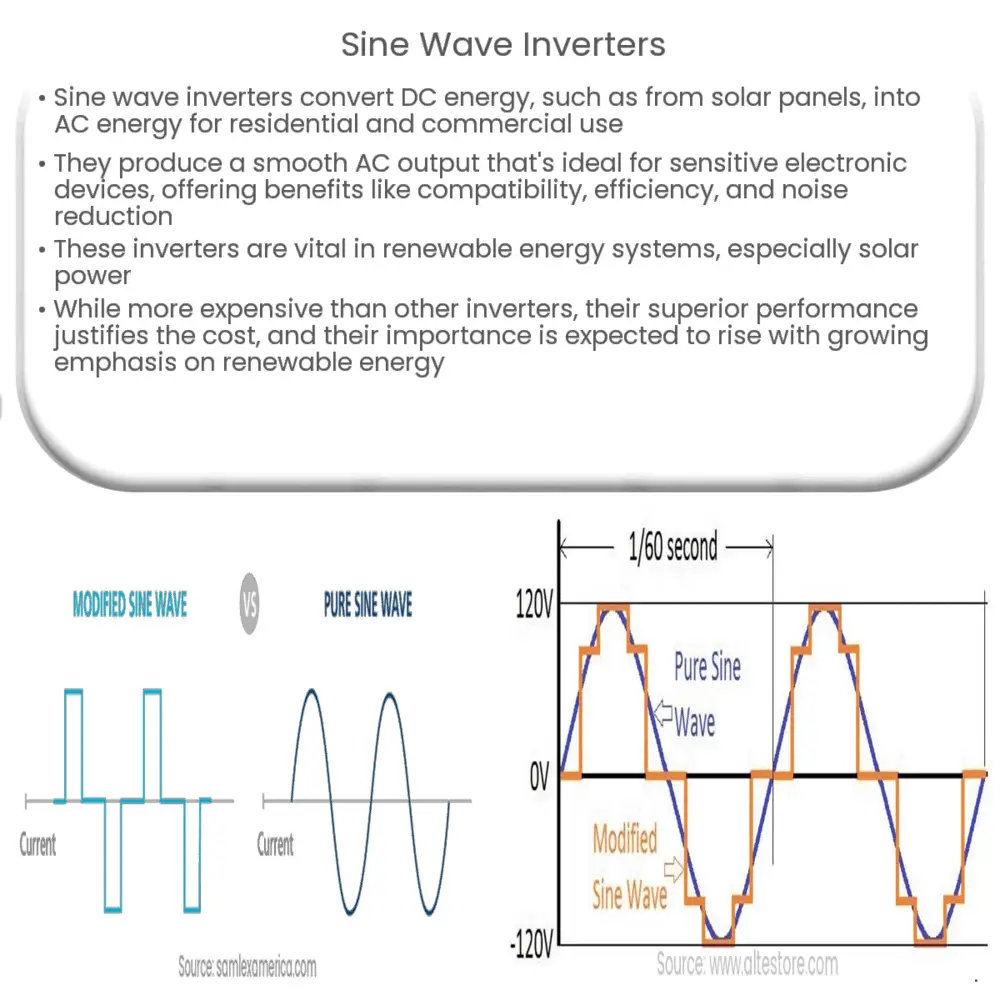
A sine wave inverter operates by transforming a DC input into an AC output that closely mimics the pure sine wave of traditional power grid electricity. This smooth, continuous, and periodically oscillating wave is the ideal form of AC power for running sensitive electronic devices.
- DC Input: The inverter’s operation begins with a DC input, often from a battery or renewable energy source.
- Inversion Process: Through the use of internal electronic components and sophisticated software control, this DC power is converted into AC power.
- AC Output: The end product is an AC power supply that is safe, reliable, and efficient for powering a wide range of appliances and devices.
Benefits of Using Sine Wave Inverters
Sine wave inverters offer several advantages over other types of inverters, like modified sine wave or square wave inverters. Their ability to produce clean, smooth, and uniform power reduces the risk of “electrical noise” which can cause malfunctions or even damage to sensitive equipment.
- Compatibility: A sine wave inverter can power nearly all types of electrical devices without risk of damage or malfunction.
- Efficiency: These inverters can run appliances at their highest efficiency, without producing excess heat or noise.
- Noise Reduction: The pure sine wave output minimizes electrical and auditory noise, making them ideal for environments where silence is critical, such as recording studios or medical facilities.
While sine wave inverters are typically more expensive than their modified or square wave counterparts, the added cost is often justified by their superior performance and broader compatibility.
Applications of Sine Wave Inverters
Sine wave inverters are used in a variety of applications, from residential to commercial and industrial settings. They are particularly popular in renewable energy systems, such as solar power installations, where they convert the DC power generated by solar panels into usable AC power.
Key Features of Sine Wave Inverters
Sine wave inverters come with various features that enhance their performance and ease of use. These features vary depending on the model and manufacturer.
- Battery Charging Capability: Many models have a built-in charger, enabling the inverter to recharge the battery from an AC source when available.
- Power Factor Correction (PFC): PFC enhances the efficiency of power consumption and reduces the energy wasted as heat.
- Low Voltage Protection: This feature shuts down the inverter when the battery voltage drops below a certain level to protect the battery from over-discharge.
The Future of Sine Wave Inverters
With the ever-growing focus on renewable energy sources, the demand for efficient and reliable power conversion technology, such as sine wave inverters, is expected to increase. Advances in inverter technology are also likely to focus on reducing size and cost, improving efficiency, and integrating smart features for improved monitoring and control.
Choosing the Right Sine Wave Inverter
When selecting a sine wave inverter, it’s crucial to consider the power requirements of your appliances and the energy source. A power output rating that matches your total power requirement, coupled with the right input voltage for your DC source, will ensure a reliable and efficient system.
- Power Rating: Inverters come in various power ratings, measured in watts. Ensure the inverter can handle the cumulative wattage of all devices you plan to connect.
- Input Voltage: This must match the voltage of your DC power source. Common values are 12V, 24V, or 48V.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sine wave inverters play a crucial role in converting DC power from sources like batteries or solar panels into the AC power that most of our appliances and devices need. With their high compatibility, efficiency, and noise reduction qualities, they surpass other types of inverters in terms of performance and safety. As we continue to embrace renewable energy, the relevance and demand for sine wave inverters are set to grow. Choosing the right sine wave inverter involves considering your specific power needs and understanding the features that will offer you the most benefit.



