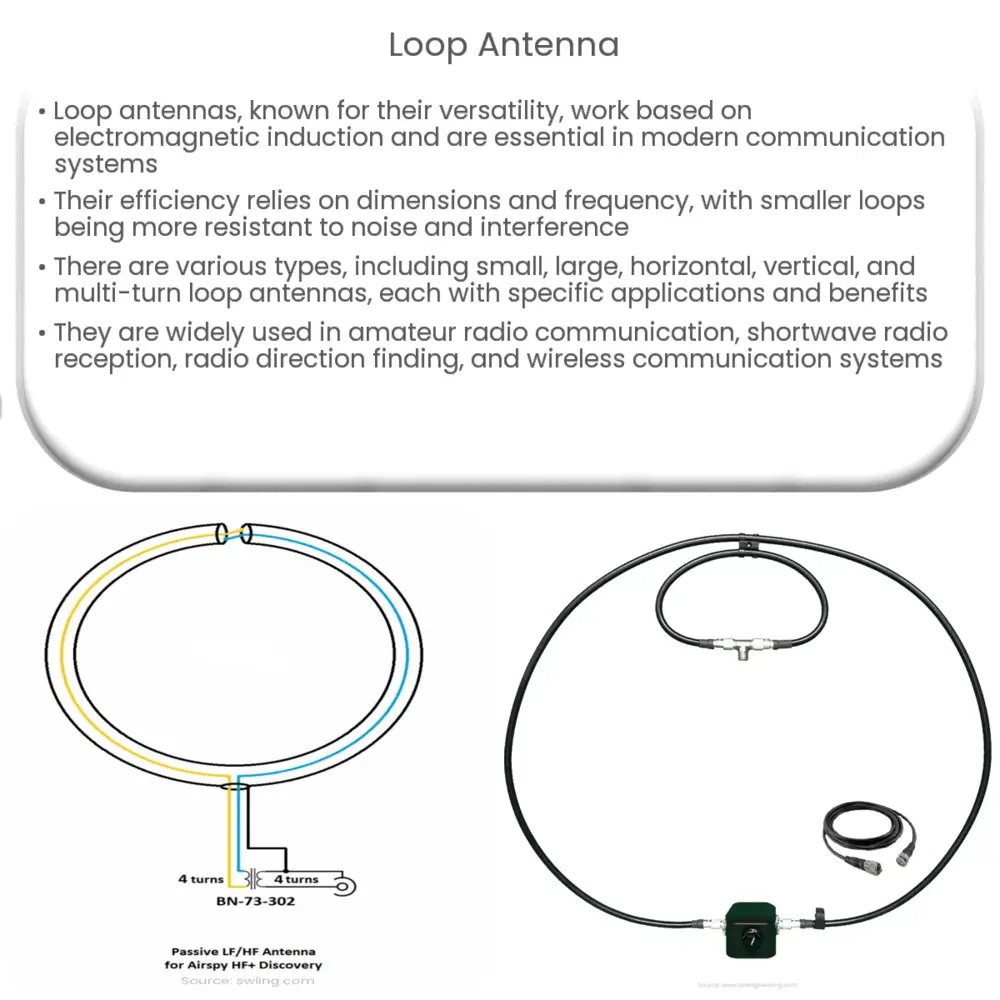
Loop antennas are versatile radio communication devices, known for their compact size, directional properties, and resistance to electrical interference.
Loop Antenna: The Versatile Solution for Radio Communication
Introduction
Loop antennas are a popular choice in the world of radio communication, known for their unique characteristics and versatile applications. This article will delve into the principles behind loop antennas, their various types, and how they are utilized in different situations. By understanding the fundamental concepts and benefits of loop antennas, one can better appreciate their significance in modern communication systems.
Principles of Loop Antennas
A loop antenna is a type of radio antenna that is comprised of a loop or coil of wire, tubing, or other conducting material. The loop can vary in size, shape, and orientation, which all influence the antenna’s performance. In general, loop antennas operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When radio frequency (RF) energy is present, it generates an alternating magnetic field, which in turn induces a current in the loop. This current creates an electric field that radiates the energy as an electromagnetic wave, enabling radio communication.
The efficiency of a loop antenna is largely determined by its dimensions and the frequency of operation. Smaller loops, also known as magnetic loop antennas, are particularly sensitive to the magnetic component of the electromagnetic field. This characteristic makes them less susceptible to electrical noise and interference, which is advantageous for applications such as shortwave radio reception and amateur radio communications.
Types of Loop Antennas
Loop antennas can be classified into several types, depending on factors such as loop size, orientation, and configuration. Some common types include:
Small Loop Antennas
Small loop antennas, also known as magnetic loop antennas, have a circumference that is less than 1/10th of the wavelength of the operating frequency. These antennas are compact, making them suitable for portable applications and installations with limited space. Despite their small size, they can provide good performance in terms of radiation efficiency and gain, especially when tuned with a capacitor.
Large Loop Antennas
Large loop antennas have a circumference greater than 1/10th of the wavelength of the operating frequency. These antennas are typically more efficient and have a higher gain than small loop antennas. They can be employed for various applications, such as long-distance communication, radio direction finding, and radio astronomy.
Horizontal and Vertical Loop Antennas
Loop antennas can be oriented either horizontally or vertically. Horizontal loop antennas, also known as skywave antennas, are commonly used for long-range communication due to their ability to capture signals reflected from the ionosphere. Vertical loop antennas, on the other hand, are more effective at capturing groundwave signals and are often used for short-range communication and direction finding.
Multi-turn Loop Antennas
Multi-turn loop antennas consist of multiple turns of wire or other conducting material, increasing the effective area of the loop. This design results in higher radiation resistance and improved gain compared to single-turn loops. Multi-turn loop antennas are used in various applications, including magnetic field sensing, radio direction finding, and low-frequency communication.
Applications of Loop Antennas
Loop antennas are versatile and can be employed in a wide range of applications, such as:
Amateur Radio Communication
Amateur radio operators, or ham radio enthusiasts, often use loop antennas for their compact size, ease of installation, and immunity to electrical noise. They are particularly beneficial in urban environments where space constraints and interference from electrical sources are common issues.
Shortwave Radio Reception
Loop antennas are an excellent choice for shortwave radio reception due to their directional characteristics and ability to reject interference. Listeners can use loop antennas to improve signal reception and minimize noise from nearby electrical devices and power lines.
Radio Direction Finding
Loop antennas are widely used in radio direction finding (RDF) systems, where their directional properties can help determine the bearing of a radio signal source. RDF is crucial for applications such as search and rescue, military operations, and amateur radio competitions.
Wireless Communication Systems
Loop antennas find applications in wireless communication systems, including RFID systems, wireless sensor networks, and wireless power transfer systems. They offer advantages such as compact size, low cost, and the ability to operate in close proximity to other antennas without causing interference.
Conclusion
Loop antennas are a versatile solution for various radio communication applications, offering unique characteristics that set them apart from other antenna types. Their compact size, directional properties, and ability to reject interference make them an ideal choice for many situations, from amateur radio communication to shortwave radio reception and radio direction finding. By understanding the principles, types, and applications of loop antennas, one can better appreciate their significance and potential benefits in modern communication systems.