Explore the intricacies of linear voltage regulators, their operating principles, advantages, drawbacks, and applications in various electronic circuits.
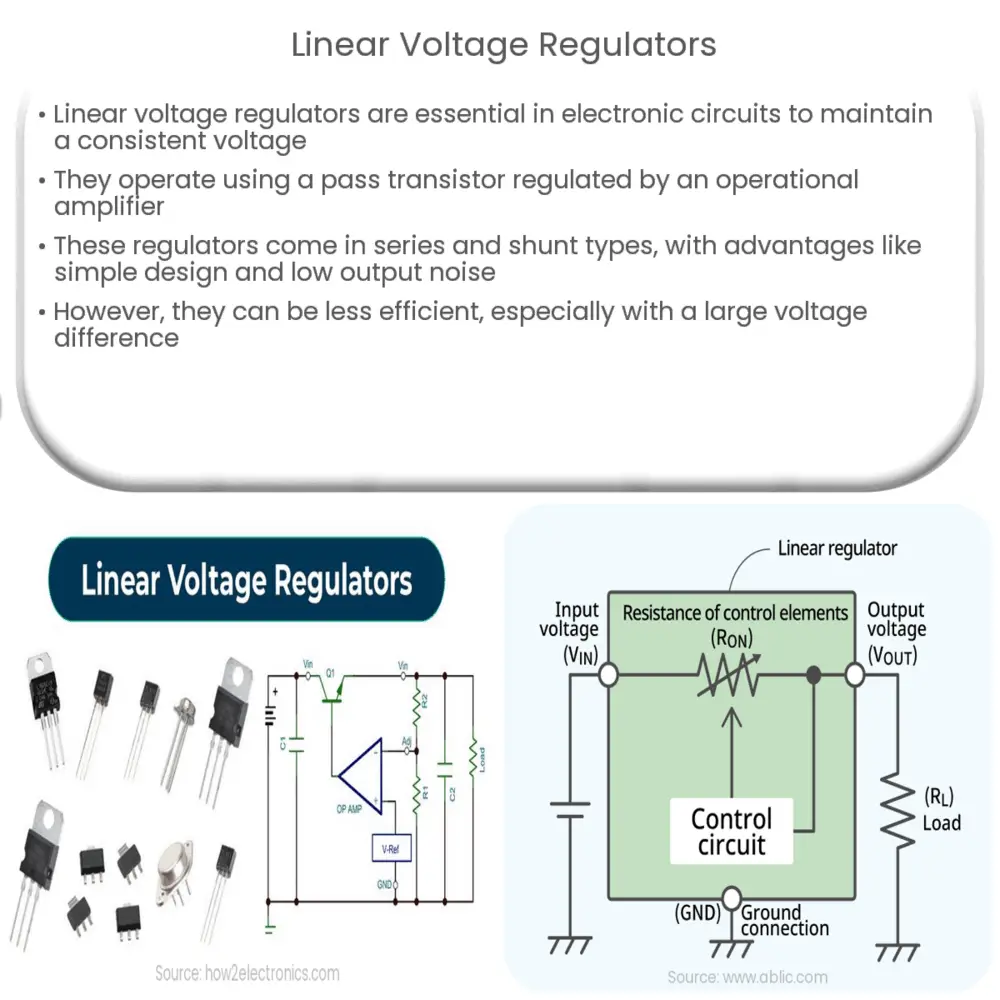
Understanding Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear voltage regulators are vital components in electronic circuits. These specialized devices are designed to maintain a steady voltage level, ensuring that electrical devices function correctly and efficiently. This article will delve into the intricacies of linear voltage regulators, exploring their operating principles, advantages, and potential drawbacks.
Operating Principles
At the heart of a linear voltage regulator is the concept of voltage regulation. As implied by its name, a voltage regulator’s primary function is to maintain a constant output voltage regardless of variations in input voltage or load current. Linear voltage regulators accomplish this task through a simple, yet effective, mechanism.
The core component of a linear voltage regulator is a pass transistor. This component, regulated by an operational amplifier, adjusts its resistance according to the input voltage and load, thereby providing a stable output voltage. When the input voltage or load changes, the operational amplifier adjusts the base current of the pass transistor, ensuring that the output voltage remains constant.
Types of Linear Voltage Regulators
- Series Voltage Regulators: In this type, the regulating element (the transistor) is placed in series with the load. This configuration allows for efficient voltage regulation, especially when dealing with higher load currents.
- Shunt Voltage Regulators: Here, the regulating element is connected in parallel with the load. Shunt regulators can absorb excessive input voltage, protecting the circuit from potential damage. However, they are generally less efficient due to continuous power dissipation.
Advantages of Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear voltage regulators offer several advantages that make them an ideal choice for various applications. These benefits include simplicity of design, low output noise, and excellent line and load regulation.
- Simplicity: Linear voltage regulators have relatively simple designs, making them easier to understand, implement, and troubleshoot. This simplicity often translates into cost-effectiveness, as fewer components are required, reducing the overall circuit cost.
- Low Noise: Due to their linear operation, these regulators produce less output noise compared to their switch-mode counterparts. This low-noise characteristic is particularly beneficial in audio and precision measurement applications where noise can cause significant problems.
Drawbacks of Linear Voltage Regulators
Despite their advantages, it’s important to understand that linear voltage regulators are not without their drawbacks. The primary issue relates to their efficiency, specifically when the difference between the input and output voltage is large.
- Efficiency: Linear regulators operate by dissipating excess power as heat. Therefore, when the difference between the input voltage and the desired output voltage is large, the regulator dissipates a significant amount of power, reducing its overall efficiency.
- Heat Dissipation: As mentioned, linear regulators dissipate excess power as heat, which can potentially cause overheating problems. This issue is particularly significant in applications where power efficiency is crucial or where thermal management is challenging.
Applications of Linear Voltage Regulators
Despite these drawbacks, linear voltage regulators are widely used across various applications due to their simplicity and low-noise operation. Some common use cases include:
- Power Supply Units: Linear voltage regulators are often used in power supply units to provide a stable output voltage, ensuring the reliable operation of electronic devices.
- Battery-Powered Devices: These regulators are also commonly used in battery-operated devices, such as mobile phones and laptops, to maintain a constant voltage level and maximize battery life.
- Audio and Precision Measurement Devices: Due to their low-noise characteristics, linear regulators are a preferred choice for audio equipment and precision measurement devices where noise can interfere with performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, linear voltage regulators play a critical role in electronic circuits, maintaining a steady voltage level and ensuring devices function correctly. While they do have some drawbacks, such as lower efficiency and heat dissipation, their benefits—simplicity of design, low output noise, and excellent line and load regulation—make them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. Understanding these regulators, their workings, advantages, and potential issues, can be immensely beneficial for anyone involved in electronics, whether as a hobbyist, student, or professional.

