Polarization in dielectrics creates an induced electric field that opposes the external field, reducing the net electric field within the material.
Impact of Polarization on Electric Field in Dielectrics
When a dielectric material is subjected to an external electric field, the phenomenon of polarization occurs, affecting the overall behavior of the electric field within the material. This article discusses how polarization influences the electric field in dielectric materials and the consequences of this interaction.
Polarization and Induced Electric Field
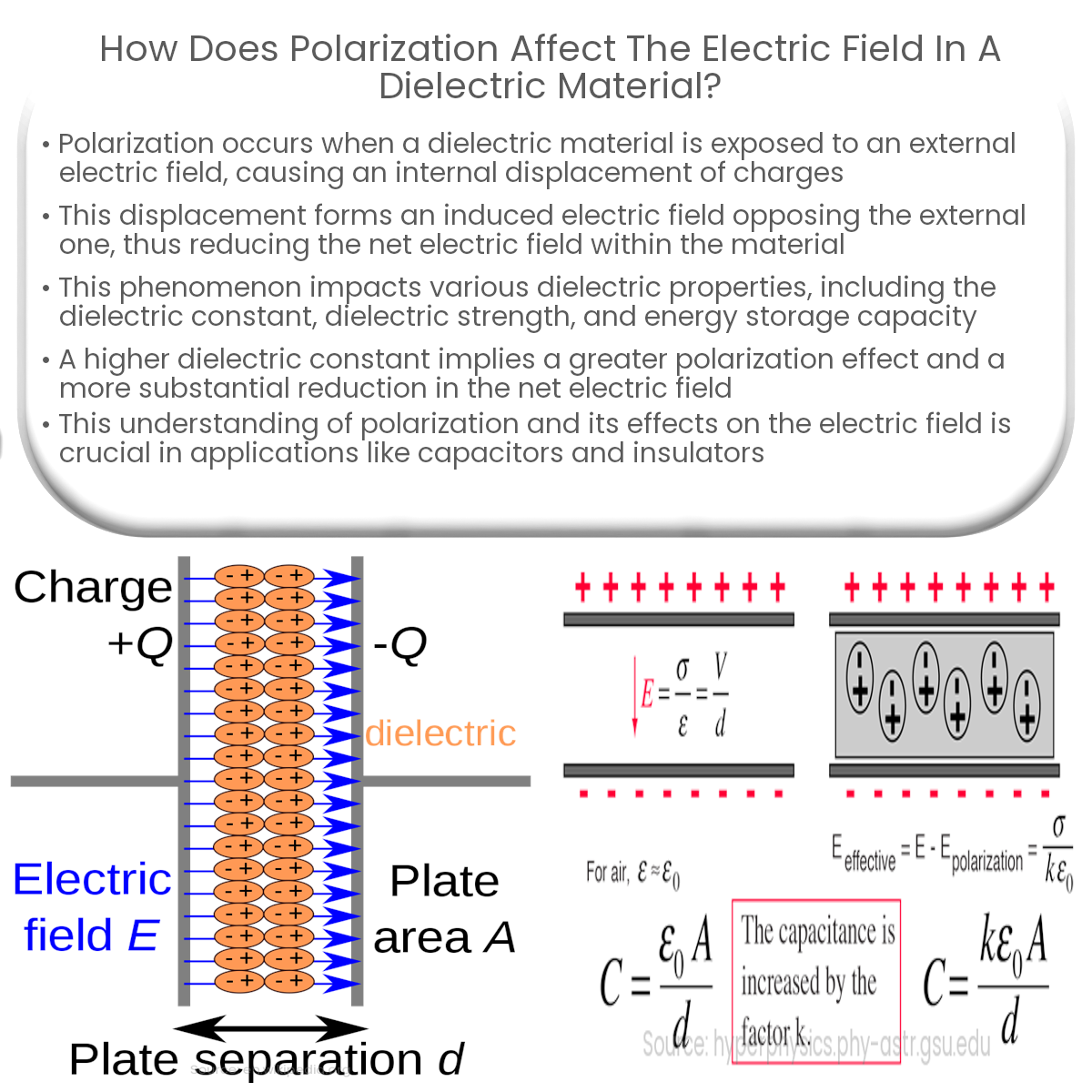
When a dielectric material experiences an external electric field, the charges within the material are displaced, resulting in electric polarization. This displacement leads to the formation of an induced electric field within the dielectric that opposes the external electric field.
Net Electric Field in a Dielectric
The net electric field inside a dielectric material is the vector sum of the external electric field and the induced electric field due to polarization. Since the induced field opposes the external field, the net electric field in the dielectric is reduced compared to the external field. Mathematically, this relationship can be expressed as:
Enet = Eext – Einduced
Consequences of Polarization on Electric Field in Dielectrics
The polarization-induced reduction in the net electric field within dielectric materials has several notable consequences:
- Dielectric Constant: The dielectric constant (relative permittivity) of a material is a measure of its ability to polarize in response to an external electric field. A higher dielectric constant indicates a greater degree of polarization and a more significant reduction in the net electric field.
- Dielectric Strength: The dielectric strength is the maximum electric field a material can withstand without undergoing electrical breakdown. The reduction in the net electric field due to polarization increases the dielectric strength of the material, providing better insulation and protection for electronic components.
- Energy Storage: The reduced net electric field within dielectric materials enables capacitors to store more electrical energy when a dielectric is placed between the capacitor plates. The energy storage capacity is directly related to the dielectric constant of the material.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between polarization and the electric field within dielectric materials is crucial for various applications, such as capacitors and insulators. The polarization-induced reduction in the net electric field has a significant impact on the material’s dielectric properties, ultimately affecting its performance in electronic devices and systems.