In single-phase circuits, calculate PF using PF = P/S or PF = cos(θ). In three-phase circuits, use PF = P_total/S_total or PF = cos(θ).
Calculating the Power Factor of a Circuit
Understanding how to calculate the power factor of a circuit is essential in assessing the efficiency of an electrical system. This article will guide you through the process of calculating the power factor for both single-phase and three-phase circuits.
Single-Phase Circuits
In single-phase circuits, the power factor can be calculated using the following equation:
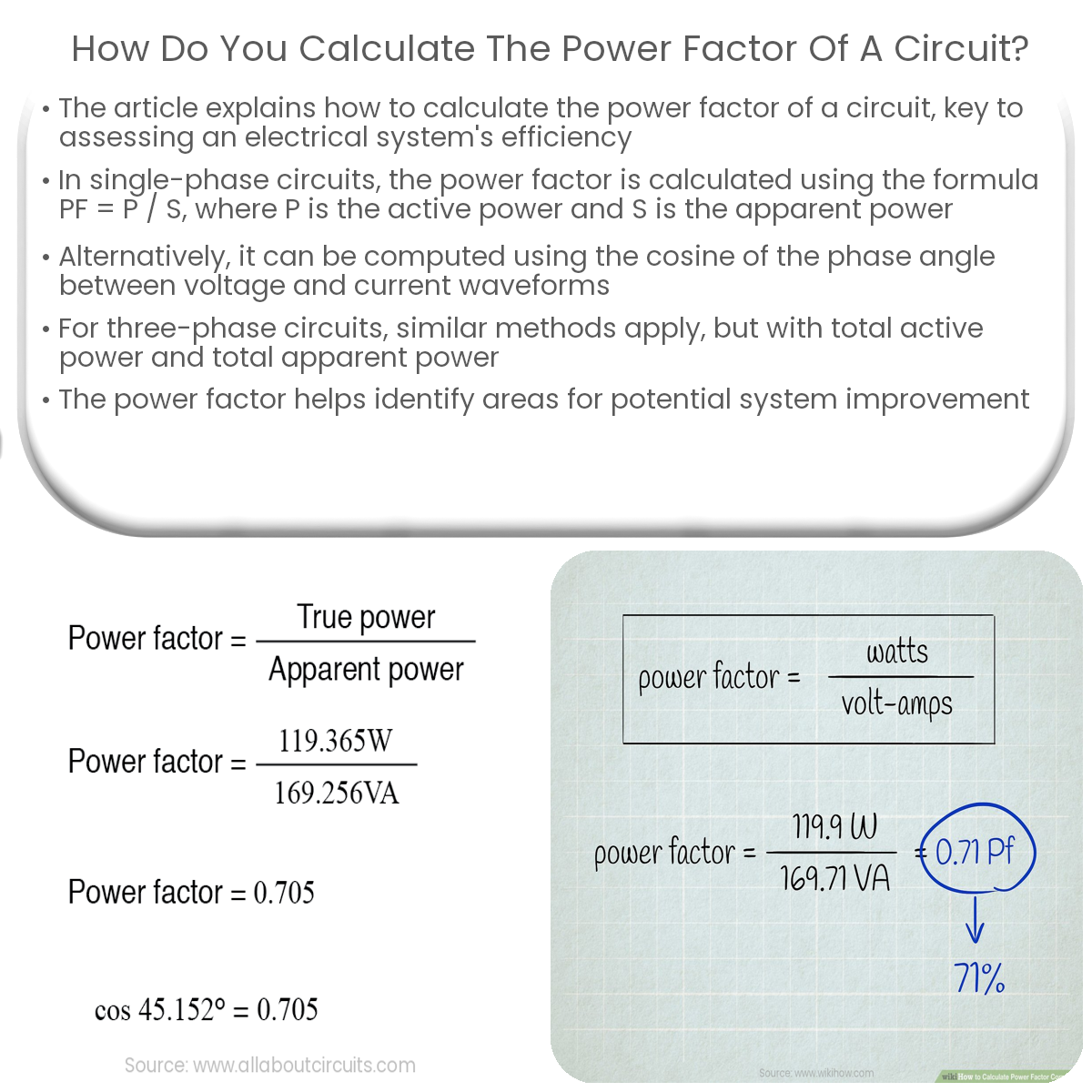
PF = P / S
Where PF is the power factor, P is the active (real) power in watts (W), and S is the apparent power in volt-amperes (VA).
The active power (P) is the power consumed by the resistive components in the circuit, while the apparent power (S) is the product of the voltage (V) and current (I) in the circuit:
S = V × I
Alternatively, you can calculate the power factor using the cosine of the angle between the voltage and current waveforms:
PF = cos(θ)
Where θ is the phase angle between the voltage and current waveforms.
Three-Phase Circuits
In three-phase circuits, the power factor can be calculated using the following equation:
PF = Ptotal / Stotal
Where PF is the power factor, Ptotal is the total active power in watts (W), and Stotal is the total apparent power in volt-amperes (VA).
The total active power (Ptotal) can be calculated as the sum of the active power in each phase, while the total apparent power (Stotal) can be calculated as the square root of the sum of the squares of the apparent power in each phase:
Stotal = √(S12 + S22 + S32)
Where S1, S2, and S3 are the apparent powers in each of the three phases.
As in single-phase circuits, the power factor can also be calculated using the cosine of the angle between the voltage and current waveforms:
PF = cos(θ)
Where θ is the average phase angle between the voltage and current waveforms across the three phases.
Conclusion
Calculating the power factor of a circuit, whether single-phase or three-phase, is essential to assess the efficiency of an electrical system. By measuring the active and apparent power or determining the phase angle between voltage and current waveforms, you can calculate the power factor and identify areas for potential improvement in your electrical system.