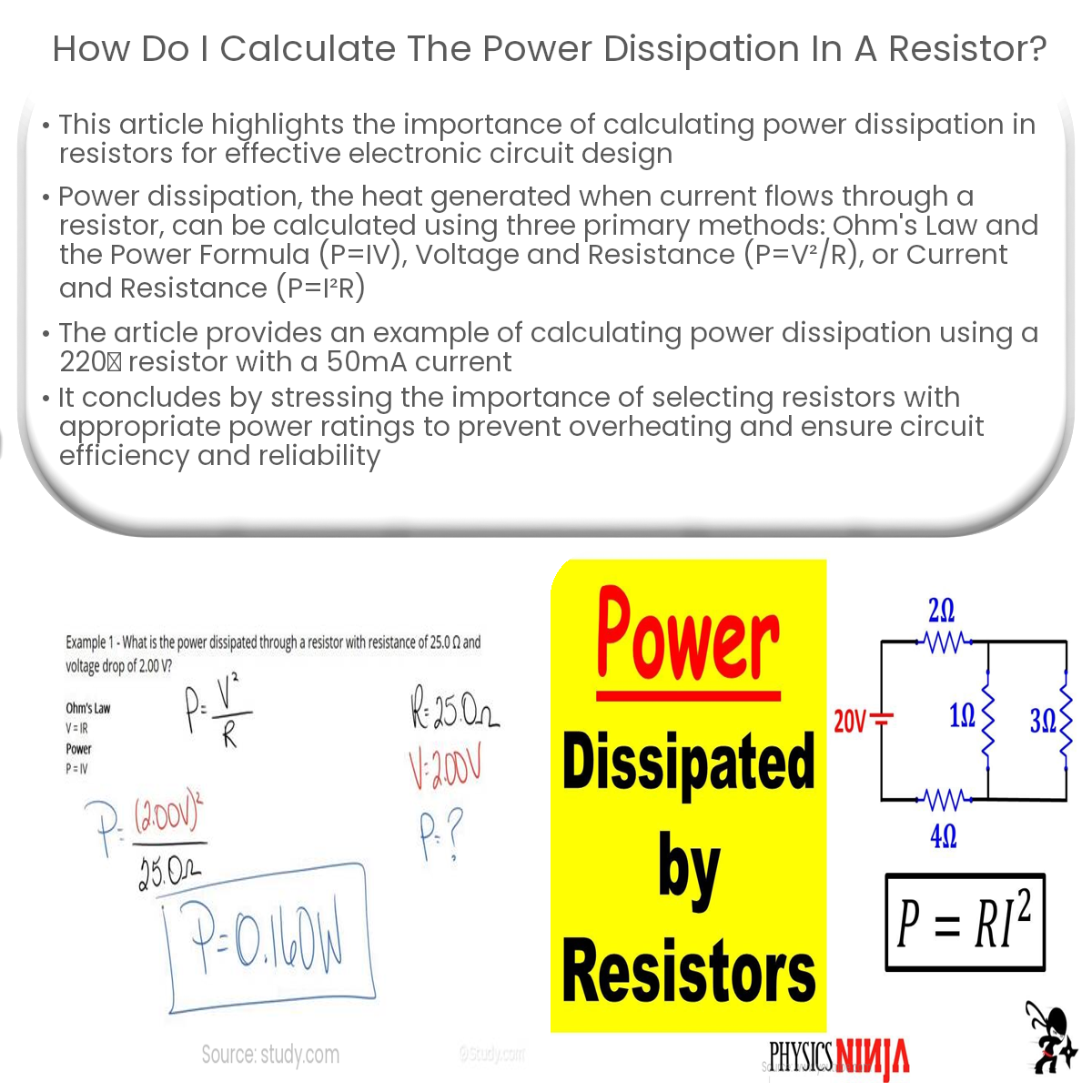
Calculate power dissipation in a resistor using P=IV, P=V²/R, or P=I²R, depending on available information, and choose a resistor with a suitable power rating.
Calculating Power Dissipation in a Resistor
Power dissipation is an essential consideration in electronic circuit design, as it can impact a resistor’s temperature, lifespan, and overall circuit performance. In this article, we’ll discuss how to calculate power dissipation in a resistor.
Understanding Power Dissipation
When current flows through a resistor, some electrical energy is converted into heat. This heat generation is known as power dissipation and is measured in watts (W).
Calculating Power Dissipation
There are three primary methods to calculate power dissipation in a resistor, depending on the available information:
- Using Ohm’s Law and the Power Formula (P = IV): If you know the current (I) flowing through the resistor and the voltage (V) across it, you can calculate power dissipation using the formula P = IV.
- Using Voltage and Resistance (P = V2/R): If you have the voltage across the resistor (V) and the resistor’s value (R), you can calculate power dissipation using the formula P = V2/R.
- Using Current and Resistance (P = I2R): If you know the current flowing through the resistor (I) and the resistor’s value (R), you can calculate power dissipation using the formula P = I2R.
Example Calculation
Suppose we have a 220Ω resistor with 50 mA of current flowing through it. We’ll use the third method (P = I2R) to calculate power dissipation:
P = I2R = (0.050 A)2 × 220Ω = 0.0025 A2 × 220Ω = 0.55 W
The power dissipation in the resistor is 0.55 watts.
Choosing the Right Resistor
It’s crucial to select a resistor with a power rating that can handle the calculated power dissipation. For example, if the power dissipation is 0.55 W, a resistor with a power rating of 1 W or higher would be a safe choice. Providing a margin of safety helps prevent overheating and potential damage to the resistor and surrounding components.
Conclusion
Calculating power dissipation in a resistor is essential for ensuring proper circuit operation and component longevity. By using the appropriate formulas and selecting resistors with suitable power ratings, you can design efficient and reliable circuits.