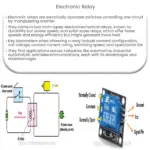
What is an H-bridge?
An H-bridge is an electronic circuit that is used to control the direction of current flow in a motor or other load. It is called an H-bridge because its shape resembles the letter “H” when drawn on a diagram. The H-bridge circuit is typically used with a DC motor, but it can also be used with other types of loads, such as solenoids, relays, or even LED arrays.
The H-bridge circuit consists of four switches that are arranged in a specific pattern. The switches are usually transistors, but they can also be MOSFETs or other types of electronic switches. By turning the switches on and off in the correct sequence, the H-bridge can control the direction of current flow and the speed of the load.
Basic circuitry of an H-bridge
The basic H-bridge circuit is made up of four switches, arranged in a specific pattern. The switches are usually labeled as Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4. The load, such as a motor, is connected to the center of the H-bridge circuit, where the switches meet.
When Q1 and Q4 are turned on, current flows from the positive terminal of the power supply, through the load, and back to the negative terminal. This is called “forward” direction. When Q2 and Q3 are turned on, current flows in the opposite direction. This is called “reverse” direction. By turning the switches on and off in the correct sequence, the H-bridge can control the speed and direction of the load.
Applications of H-bridge in robotics
The H-bridge circuit is commonly used in robotics, where it is used to control the movement of motors that drive wheels or other mechanical components. In addition to controlling the direction and speed of the motors, the H-bridge can also be used to apply braking force, or to stop the motor completely.
The H-bridge circuit is also used in other types of robotic applications, such as controlling the position of robotic arms or grippers. In these applications, the H-bridge can be used to control the movement of the motors that drive the various joints or segments of the robot.
Example of H-bridge used in motor control
One of the most common applications of the H-bridge is in motor control. Here’s an example of how an H-bridge can be used to control the speed and direction of a DC motor:
- When Q1 and Q4 are turned on, current flows from the positive terminal of the power supply, through the motor, and back to the negative terminal. This causes the motor to spin in one direction.
- When Q2 and Q3 are turned on, current flows in the opposite direction, causing the motor to spin in the opposite direction.
- By varying the amount of time that each switch is on, the H-bridge can control the speed of the motor. For example, if Q1 and Q4 are turned on for a longer time than Q2 and Q3, the motor will spin faster in the forward direction.
- If Q2 and Q3 are turned on for a longer time than Q1 and Q4, the motor will spin faster in the reverse direction.
In conclusion, the H-bridge is a versatile electronic circuit that is widely used in robotics and other applications that require precise control of the direction and speed of a motor or other load. By understanding the basic circuitry of an H-bridge and its applications, engineers and hobbyists can design and build their own robots and motor control systems.