Explore the world of relays in electrical engineering: their types, operation, applications, advantages, and challenges.

Understanding Relays: The Unsung Heroes of Electrical Engineering
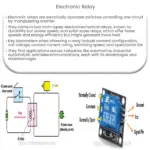
Relays are an integral part of the world of electrical engineering. These small yet powerful devices play a vital role in controlling the functionality of numerous electronic systems and appliances we use daily. The fundamental purpose of a relay is to control a high voltage circuit with a low power signal.
Relays are typically used in applications where it is necessary to control a circuit by a separate low-power signal, or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. This is achieved through a design that involves an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch.
Types of Relays
Relays come in various forms, each designed to fulfill specific needs. The three main types of relays are:
- Electromechanical Relays: These are the most common type of relays. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic attraction. When a current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that pulls a lever and changes the switch position.
- Solid State Relays: Unlike electromechanical relays, solid state relays have no moving parts. They use semiconductor properties to perform their switching function. Because of their design, they offer advantages such as longer life and faster switching speeds than electromechanical relays.
- Hybrid Relays: These relays combine the best of electromechanical and solid-state relays. They offer the reliability of electromechanical relays and the speed of solid-state relays.
How Relays Work
A relay operates through a relatively simple principle. When a low voltage is applied to the coil, the current flowing through it creates an electromagnetic field. This magnetic field attracts a metal lever, which is spring-loaded. The movement of this lever either makes or breaks a connection with a fixed contact. In effect, this operation allows a small current to control a much larger one.
Relays, therefore, offer a method of control that is safe, reliable, and highly effective. They are a testament to the power of electromagnetism and its practical applications.
Applications of Relays
Relays are employed in a vast range of applications due to their versatility and reliability. Here are a few key areas where they are commonly used:
- Automotive Systems: Cars and other vehicles often use relays to control high current circuits. Examples include headlight and ignition circuits, where the relay allows the switch to carry a much smaller current than the device it controls.
- Industrial Applications: In industrial environments, relays are used extensively in control systems. They help manage the operation of heavy machinery by providing safe and efficient control of high current circuits.
- Home Appliances: Everyday appliances like washing machines and refrigerators also use relays. They help in controlling the power to the motors and heaters in these devices.
- Telecommunication Systems: In telecommunication and data processing systems, relays aid in signal transmission and data exchange, contributing to efficient communication.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Relays
Like any other component, relays have their advantages and disadvantages, which need to be considered when choosing them for specific applications.
- Advantages: Relays provide good isolation between the control and output circuit, which is essential for safety. They can also handle high voltage and current loads, making them suitable for controlling heavy machinery and industrial applications.
- Disadvantages: Electromechanical relays, despite their robustness, can be susceptible to physical wear and tear due to the mechanical movement involved. Solid-state relays, while being more durable, can generate more heat and require careful heat management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, relays are indispensable components in many electrical and electronic systems, serving as the bridge between control signals and high-powered operations. Despite some challenges, the versatility and efficiency of relays make them a go-to choice for engineers in diverse fields. As technology continues to advance, it’s exciting to think about the future innovations that will further enhance the capabilities of these unsung heroes of electrical engineering.