An Electric Double-Layer Capacitor (EDLC) is a high-power energy storage device that excels in rapid charge-discharge and durability.
Introduction to Electric Double-Layer Capacitor (EDLC)
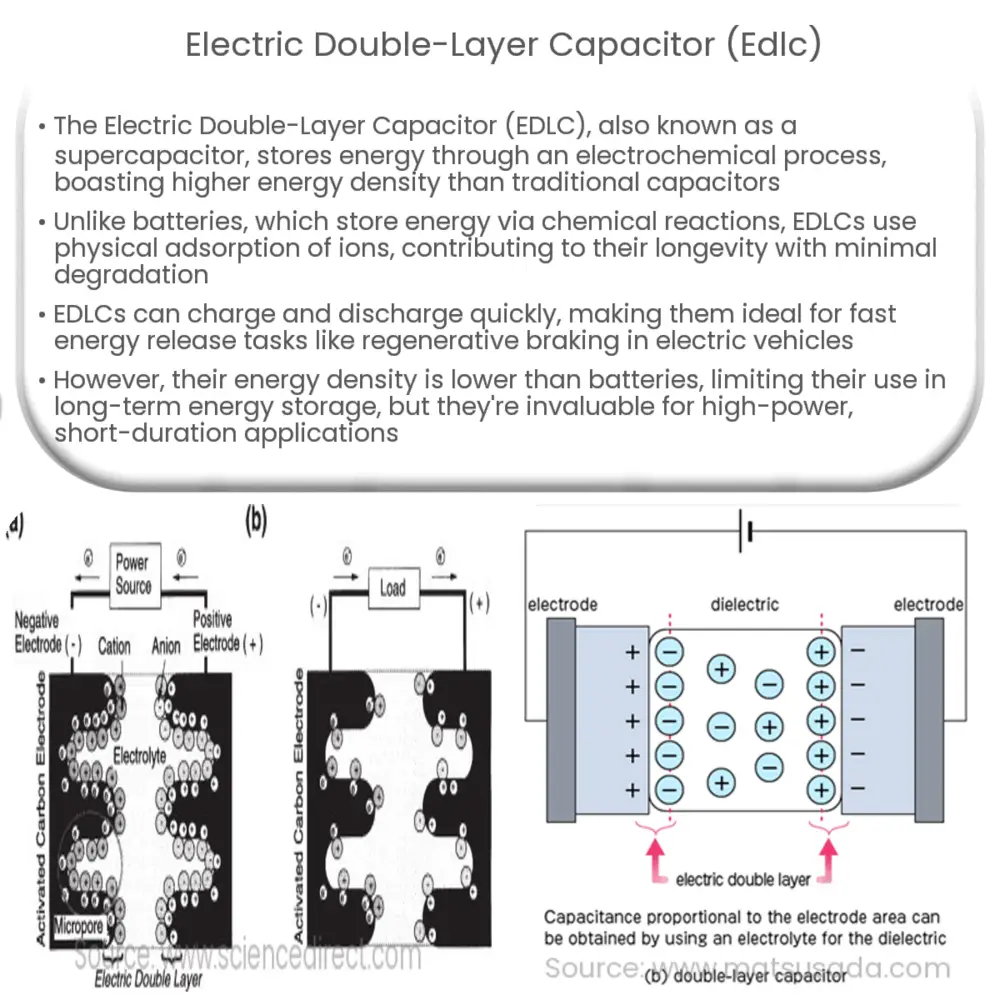
The Electric Double-Layer Capacitor (EDLC), also commonly referred to as a supercapacitor or ultracapacitor, is a type of energy storage device. Unlike traditional capacitors that utilize the electrostatic field formed between conductive plates, EDLCs store energy by means of an electrochemical process, which allows them to possess a much higher energy density.
EDLCs consist of two electrodes immersed in an electrolyte, separated by a porous membrane that acts as a separator. The electrodes are typically made from a high surface area activated carbon material, while the electrolyte can be either aqueous or organic-based. When a voltage is applied across the electrodes, ions from the electrolyte move towards the electrodes of opposite charge, forming a “double layer” of charge at the electrode/electrolyte interface, hence the term “Electric Double-Layer Capacitor.
Working Mechanism of EDLCs
The operation of an EDLC is centered on the physical adsorption and desorption of ions at the electrode/electrolyte interface. When a potential difference is applied across the electrodes, positive and negative ions from the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrodes of opposite charge, creating a double layer of charges. This accumulation of charges at the interface results in energy storage.
In an EDLC, no chemical reaction takes place. This is a distinguishing feature from batteries where energy storage involves redox reactions. The physical nature of the charge storage in EDLCs contributes to their long cycle life, as there is minimal material degradation over time.
The amount of energy that an EDLC can store is largely determined by the surface area of the electrode material and the thickness of the electric double layer. Therefore, materials with high surface area, such as activated carbon, are often used as electrode materials. These materials provide a large number of sites for ion adsorption, enabling the storage of a significant amount of charge.
The separator in an EDLC is crucial as it prevents the short-circuiting of the electrodes while allowing for the movement of ions. It is typically made from a porous material that is permeable to ions but not to the electrode particles.
In the next part of the article, we will dive into the advantages, limitations, and applications of Electric Double-Layer Capacitors.
Advantages of Electric Double-Layer Capacitors
One of the primary advantages of EDLCs is their ability to charge and discharge rapidly. Due to the physical nature of energy storage in EDLCs, they can handle significantly higher charge and discharge rates compared to batteries without undergoing considerable degradation. This makes them particularly suitable for applications that require quick energy release, such as in regenerative braking systems in electric vehicles.
Another key benefit of EDLCs is their impressive cycle life. While typical batteries may endure thousands of charge-discharge cycles before their capacity begins to degrade, EDLCs can withstand millions of cycles. This high durability stems from the absence of chemical reactions during charge storage, which minimizes wear and tear on the device.
Furthermore, EDLCs perform well in a wide temperature range, making them suitable for use in extreme environments where traditional batteries might fail.
Limitations and Applications of EDLCs
Despite their advantages, EDLCs do have certain limitations. The most notable is their relatively low energy density when compared to batteries. This means that for the same volume or weight, a battery can store more energy than an EDLC. As a result, while EDLCs can deliver high power quickly, they can’t store as much total energy, making them unsuitable as a standalone power source for long-term energy supply.
However, these characteristics make EDLCs ideal for specific applications where high power delivery or energy recovery over short periods is required. For instance, in electric vehicles, EDLCs are often used in conjunction with batteries. The EDLC can provide the high power necessary for acceleration or recover energy during braking, while the battery provides the steady long-term energy supply for cruising.
Other applications include power backup in case of power interruptions, energy storage in renewable energy systems, and power supply for portable electronics. In these applications, the combination of quick charge-discharge capability, high cycle life, and performance over a wide temperature range makes the EDLC a valuable component in modern energy storage solutions.
In conclusion, while EDLCs may not replace batteries in all applications due to their lower energy density, their unique properties make them an essential element in a broad range of high-power, rapid-response applications. As technology advances, we can expect to see further enhancements in the performance of EDLCs, broadening their scope of application.

