30-second summary
Lithium Metal Battery
Lithium-based primary cells are non-rechargeable batteries that have metallic lithium as an anode. These types of batteries are also referred to as lithium-metal batteries.
Primary lithium batteries have the lowest self-discharge rate hence the longest available shelf time, up to 10 years, and in temperatures up to 70.
The most common cells are summarized below:
- Lithium-Manganese Dioxide Cell.
- Lithium Iron Disulphide Cell.
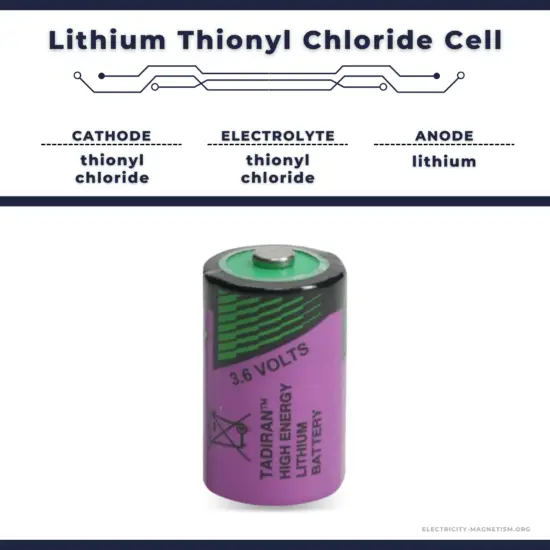
- Lithium Thionyl Chloride Cell.
- Lithium Air Cell.
Overall reaction (Li/MnO2 cells):
Li(s) + MnIVO2(s) ⇌ MnIIIO2(Li+) [E° = +3.19 V]
Lithium Thionyl Chloride Cell
Lithium-based primary cells are batteries that have metallic lithium as an anode. These types of batteries are also referred to as lithium-metal batteries. Note that disposable primary lithium batteries must be distinguished from secondary lithium-ion or lithium-polymer, which are rechargeable batteries. Lithium-ion batteries do not contain metallic lithium.
Lithium thionyl chloride or Li-SoCl2 are primary cell batteries of a wet type. In this case, electrolyte based on sulfonated thionyl chloride serves as the positive electrode. The main difference between this and other lithium battery types is that this type cannot be recharged once discharged. Thionyl chloride, a very corrosive and toxic chemical, serves not only as the electrolyte solvent but also as the cathode material. The electrolyte is typically lithium tetrachloroaluminate. The overall discharge reaction is as follows:
4 Li + 2 SOCl2 → 4 LiCl + 1⁄8 S8 + SO2
These non-rechargeable batteries have many advantages over other forms of lithium batteries, such as a high energy density, a wide operational temperature range, and long storage and operational lifespans. However, their high cost, non-rechargeability, and safety concerns have limited their use. The contents of the batteries are highly toxic and require special disposal procedures.
Types of Lithium Metal Batteries
The most common cells are summarized below:
- Lithium-Manganese Dioxide Cell. This cell uses lithium foil as the anode and manganese dioxide as the cathode. The electrolyte is a separator sheet impregnated with electrolytic salts. The overall cell voltage is 3 volts. It is the most common non-rechargeable lithium cell commonly used in button cells like CR2032.
- Lithium Iron Disulphide Cell. Cylindrical lithium iron disulfide batteries (LiFeS2) use lithium for the anode, iron disulfide for the cathode, and a lithium salt in an organic solvent blend as the electrolyte. Designed to be a drop-in replacement for Zinc-carbon or alkaline batteries, the cell voltage is 1.5 volts. They are often called “voltage-compatible” lithium cells. They have a higher energy density than the cells they replace and are tailored to high current applications. They are also produced in the AA battery format.
- Lithium Thionyl Chloride Cell. This type of cell has the highest energy density of all lithium-type cells and has a service life of 15 to 20 years.
- Lithium Air Cell. Similar to zinc-air cells, they have a very high theoretical energy density. The anode, a metallic lithium foil pressed into a nickel mesh current collector, is electrochemically coupled to an unlimited supply of atmospheric oxygen through an air cathode.
Disposable primary lithium batteries must be distinguished from secondary lithium-ion or lithium-polymer, which are rechargeable batteries.

