Explore the role of digital multiplexers in electronics and communications, their structure, types, applications, advantages, and drawbacks.
Introduction to Digital Multiplexers
Digital Multiplexers, commonly referred to as Mux, play an instrumental role in the field of digital electronics and communications. A multiplexer is essentially a data selector, a device that selects between multiple input signals and forwards the selected input into a single line.
The Fundamental Operation of Multiplexers
At the most basic level, a multiplexer operates as a high-speed switch directed by the select lines. The number of the select lines is determined by the number of the input signals. For instance, a 2-to-1 multiplexer would need one select line, while a 4-to-1 multiplexer requires two select lines. The select lines decide which input to forward to the output. The purpose of multiplexers is to perform high-speed switching and they are used extensively in data routing and digital communication networks.
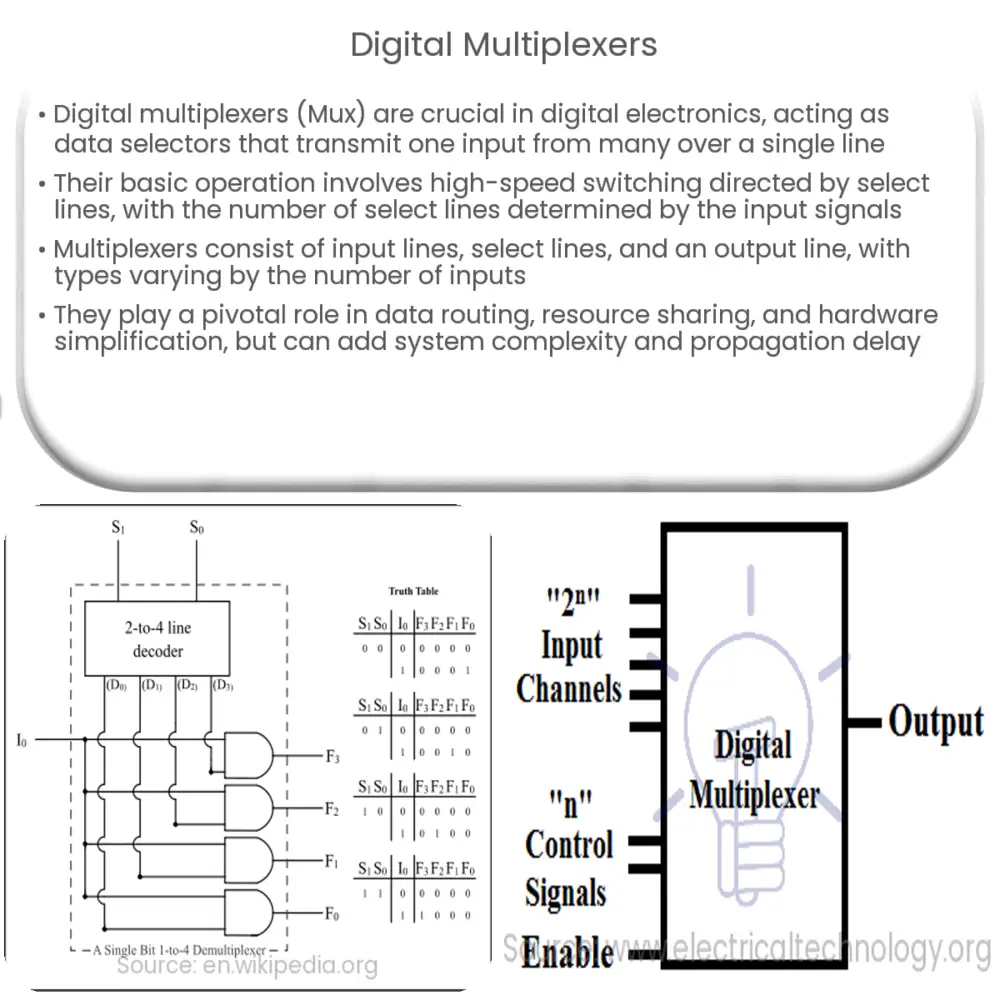
The Structure of Multiplexers
A typical multiplexer is made up of three main components: input lines, select lines, and an output line. The multiplexer’s operation is governed by a set of selection rules determined by the select lines. For instance, if there are 3 select lines, the multiplexer can accommodate 8 (23) inputs.
- Input Lines: The multiplexer takes multiple inputs which are usually binary in nature.
- Select Lines: These are essentially control signals that determine which input should be forwarded to the output line.
- Output Line: There’s only a single output line which carries the selected input signal.
Types of Multiplexers
Multiplexers can be categorized based on the number of inputs they can process. The most commonly used types of multiplexers in digital circuits include 2-to-1, 4-to-1, 8-to-1, and 16-to-1. As the number of input lines increases, the number of select lines increases correspondingly.
Despite their various types, all multiplexers function based on the same fundamental principle of selecting one from many inputs and transmitting it over a single line. The application of multiplexers spans across multiple fields in electronics and telecommunication industry such as in the construction of processors, memory units, and data routing systems.
Application of Multiplexers
The application of digital multiplexers is extensive and spans across a wide array of fields within electronics and digital communications. They are crucial for the development of digital computing systems and are involved in several key operations:
- Data Routing: Mux are utilized in the transmission and routing of data within a network. By choosing the required input line based on the selection line, Mux helps route data packets from multiple sources over a single line.
- Resource Sharing: In digital communication, multiplexers enable multiple devices to share a single resource, such as a transmission line, thereby reducing the overall cost of the system.
- Hardware Simplification: The use of multiplexers can also lead to simplification of hardware design. They are used in building functions that can reduce the number of gates required in a design.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Multiplexers
Like any digital device, multiplexers have their advantages and limitations. On one hand, they allow efficient data management and resource sharing, and on the other hand, they add a layer of complexity to the system and can introduce a propagation delay.
- Advantages: Multiplexers enable efficient use of the bandwidth by allowing multiple signals to be sent over a single data line. They also simplify hardware design by reducing the number of gates needed.
- Disadvantages: Despite their benefits, multiplexers can add a level of complexity to system designs, and their use can introduce a propagation delay, which is the delay between an input changing and the output responding to this change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital multiplexers are essential components of digital circuits, serving as high-speed switches that allow the selection and transmission of one input signal among many over a single line. They play a critical role in data routing, resource sharing, and hardware simplification, thereby being vital to the efficiency and performance of a wide array of digital systems. However, like any device, they come with their set of challenges, including system complexity and propagation delay, which need to be taken into consideration during system design. Nevertheless, the importance and utility of multiplexers in today’s digital world remain undeniable.




