A bridge rectifier is an electronic component that efficiently converts AC voltage into stable DC voltage for use in various devices and systems.
Introduction to Bridge Rectifiers
A bridge rectifier is a crucial electronic component that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This conversion is essential for powering various electronic devices and systems that require a stable and constant DC voltage. In this article, we will explore the principles behind bridge rectifiers, their applications, and the benefits they offer.
Basic Principles of Bridge Rectifiers
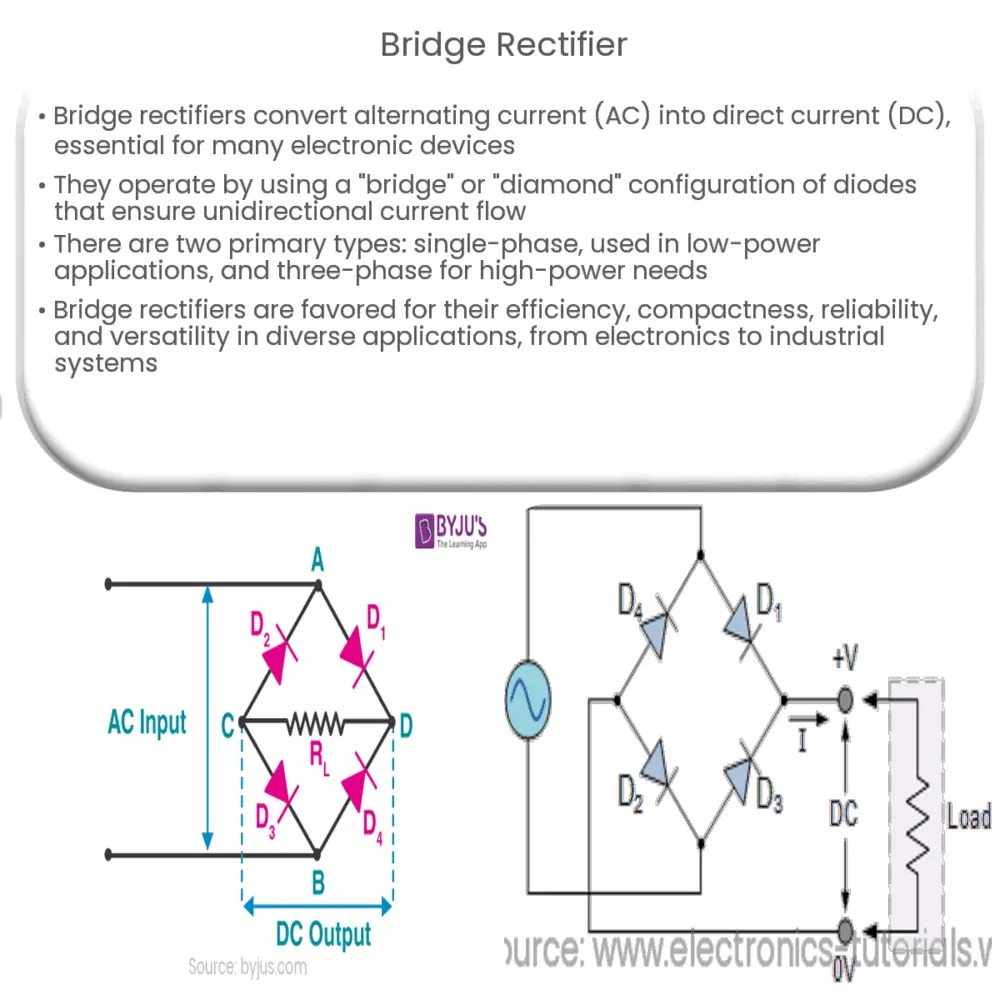
The primary function of a bridge rectifier is to convert AC voltage, which periodically changes its polarity, into a unidirectional voltage, or DC. The process of converting AC to DC is known as rectification. Bridge rectifiers consist of four diodes connected in a specific configuration called a “bridge” or a “diamond” arrangement.
During the positive half cycle of the AC input, two of the diodes become forward-biased and conduct current, while the other two are reverse-biased and do not conduct. This allows the current to flow in one direction, creating a positive output voltage. During the negative half cycle, the roles of the diodes are reversed, with the previously reverse-biased diodes becoming forward-biased and conducting current. This results in the negative input voltage being converted into positive output voltage. The output waveform, after being passed through a smoothing capacitor, closely resembles a continuous DC voltage.
Types of Bridge Rectifiers
There are two main types of bridge rectifiers: single-phase and three-phase. The choice between these two types depends on the application and the required output voltage.
Single-phase Bridge Rectifiers
Single-phase bridge rectifiers are used for converting single-phase AC voltage into DC voltage. They are the most common type of bridge rectifier and are widely used in low-power applications, such as power supplies for electronic devices and battery chargers. A single-phase bridge rectifier consists of four diodes connected in a bridge configuration.
Three-phase Bridge Rectifiers
Three-phase bridge rectifiers are designed for converting three-phase AC voltage into DC voltage. They are used in higher-power applications, such as industrial motor drives, electric vehicle charging stations, and high-power DC transmission lines. A three-phase bridge rectifier consists of six diodes connected in a similar bridge configuration as the single-phase bridge rectifier, but with each diode pair connected to a separate phase of the AC input.
Applications of Bridge Rectifiers
Bridge rectifiers are widely used in various applications, including:
- Power supplies for electronic devices, such as computers, TVs, and audio systems
- Battery chargers for devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles
- Industrial motor drives, where constant DC voltage is required to control the speed and torque of electric motors
- Renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power installations, which require stable DC voltage for power storage and conversion
Benefits of Bridge Rectifiers
Bridge rectifiers offer several benefits that make them a popular choice for various applications. Some of the advantages include:
- Efficiency: Bridge rectifiers are highly efficient in converting AC voltage to DC voltage. They have minimal power loss due to the low voltage drop across the diodes, resulting in less energy waste and lower operating costs.
- Compactness: Compared to other rectifier configurations, such as center-tapped and full-wave rectifiers, bridge rectifiers are more compact and require fewer components. This makes them an ideal choice for applications with space constraints or tight budgets.
- Reliability: Bridge rectifiers have a simple design, which makes them highly reliable and easy to maintain. With fewer components to fail, they have a longer service life and lower maintenance costs.
- Versatility: Bridge rectifiers can be easily adapted to different voltage levels and power requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from low-power electronics to high-power industrial systems.
Choosing the Right Bridge Rectifier
When selecting a bridge rectifier for a specific application, there are several factors to consider:
- Input voltage: Choose a bridge rectifier with a suitable input voltage range that matches the AC voltage source in your application.
- Output voltage and current: Ensure that the bridge rectifier can handle the required output voltage and current levels for your application, taking into account any possible fluctuations or variations in the input voltage.
- Thermal management: Bridge rectifiers can generate heat during operation, so it is essential to consider the thermal management requirements of your application, including heat sinks, cooling fans, or other cooling solutions.
- Physical size and mounting: Select a bridge rectifier that fits within the available space in your application and has suitable mounting options to ensure secure installation and proper heat dissipation.
Conclusion
Bridge rectifiers play a critical role in converting AC voltage to DC voltage, enabling the operation of various electronic devices and systems. Understanding the principles, applications, and benefits of bridge rectifiers is essential for selecting the right component for your specific needs. By considering factors such as input and output voltage, thermal management, and physical size, you can ensure that your bridge rectifier will provide reliable and efficient performance in your application.



