Explore the workings, benefits, challenges, and future of biogas generators as a sustainable solution for renewable energy and waste management.
Understanding Biogas Generators
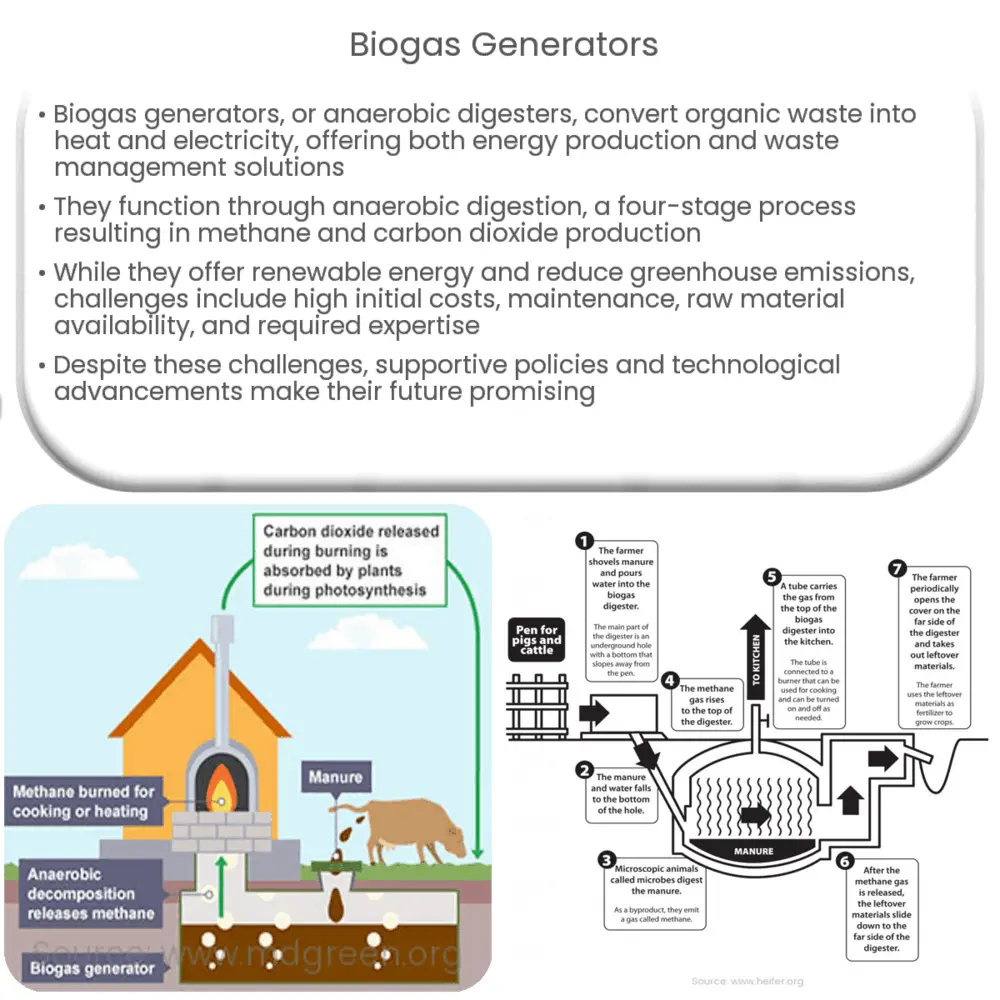
Biogas generators, also referred to as anaerobic digesters, are growing in popularity as an alternative source of energy. They provide a sustainable solution to energy problems, especially in rural areas. The operational principle of these generators revolves around the conversion of organic waste into a form of gas that can be used as a source of heat and electricity. Biogas generators serve a dual purpose, in terms of energy production and waste management.
How Does a Biogas Generator Work?
Biogas generators rely on the process of anaerobic digestion, which occurs when organic matter is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen. This process generates a biogas, primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide, which can then be burned to produce heat or electricity. Let’s delve deeper into the operational stages of a biogas generator:
- Hydrolysis: In this first stage, complex organic materials are broken down into simpler sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids.
- Acidogenesis: The simpler compounds are then converted into volatile fatty acids, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and ammonia by acidogenic bacteria.
- Acetogenesis: During this phase, the remaining products are converted into acetic acid, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen.
- Methanogenesis: Finally, the end products of the previous stage are converted into methane, carbon dioxide, and water by methanogens.
Components of a Biogas Generator
Understanding the parts of a biogas generator is essential to fully appreciate how they operate. Key components include:
- The Digestion Chamber: This is where the anaerobic digestion process takes place. The chamber is sealed off from oxygen to create the necessary anaerobic conditions.
- The Input and Output: Organic waste (input) is introduced into the digestion chamber, and after processing, residue (output) is removed for use as fertilizer.
- The Gas Storage: This is where the biogas produced is stored before being channeled to the point of use.
The advantages of biogas generators are multi-faceted, ranging from providing a reliable source of renewable energy to improving waste management and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, like all energy systems, they also come with certain challenges and limitations, which will be explored in the following section.
Challenges and Limitations of Biogas Generators
While biogas generators provide numerous benefits, they are not without their share of challenges and limitations. Some of the primary issues include:
- Initial Investment Costs: The construction and setup of biogas generators can be expensive, making them a significant initial investment.
- Maintenance: They require regular and careful maintenance to ensure efficient gas production. This can also incur additional costs.
- Raw Material Availability: Consistent availability of organic waste materials, such as livestock manure or food waste, is crucial for uninterrupted operation.
- Technical Expertise: The operation and maintenance of biogas generators require a certain level of technical expertise, which may be a barrier in some regions.
Future of Biogas Generators
Despite these challenges, the future of biogas generators appears promising. Continuous technological advancements are mitigating some of the limitations, making them more efficient and accessible. Moreover, with the growing global emphasis on reducing carbon emissions and promoting renewable energy sources, biogas generators are increasingly viewed as a viable option to meet energy needs while promoting environmental sustainability.
The Role of Policy in Promoting Biogas Generators
Government policy plays a crucial role in promoting the adoption of biogas generators. Policies that incentivize renewable energy use, offer financial support for initial setup costs, or provide training for proper operation and maintenance can significantly encourage the deployment of these systems. Such initiatives are already taking shape in various parts of the world, contributing to a greener and more sustainable energy landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biogas generators present a remarkable alternative to conventional energy sources. They offer an innovative solution to waste management problems and contribute significantly to the mitigation of climate change. Although they are not without challenges, ongoing technological advancements and supportive policies continue to improve their feasibility and accessibility. The increasing global emphasis on renewable energy sources, coupled with the need for sustainable waste management, positions biogas generators as a key component in our sustainable energy future.




