Asynchronous DC-DC converters are efficient, cost-effective voltage regulators, used in electronics like portable devices, power supplies, and renewable energy systems.
Asynchronous DC-DC Converter: An Overview
Introduction
DC-DC converters play a pivotal role in modern electronics, providing the necessary voltage regulation and power conversion for various applications. Asynchronous DC-DC converters, also known as buck converters, are a popular choice for their simplicity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This article will delve into the fundamentals of asynchronous DC-DC converters, their advantages, drawbacks, and potential applications.
Asynchronous DC-DC Converter Basics
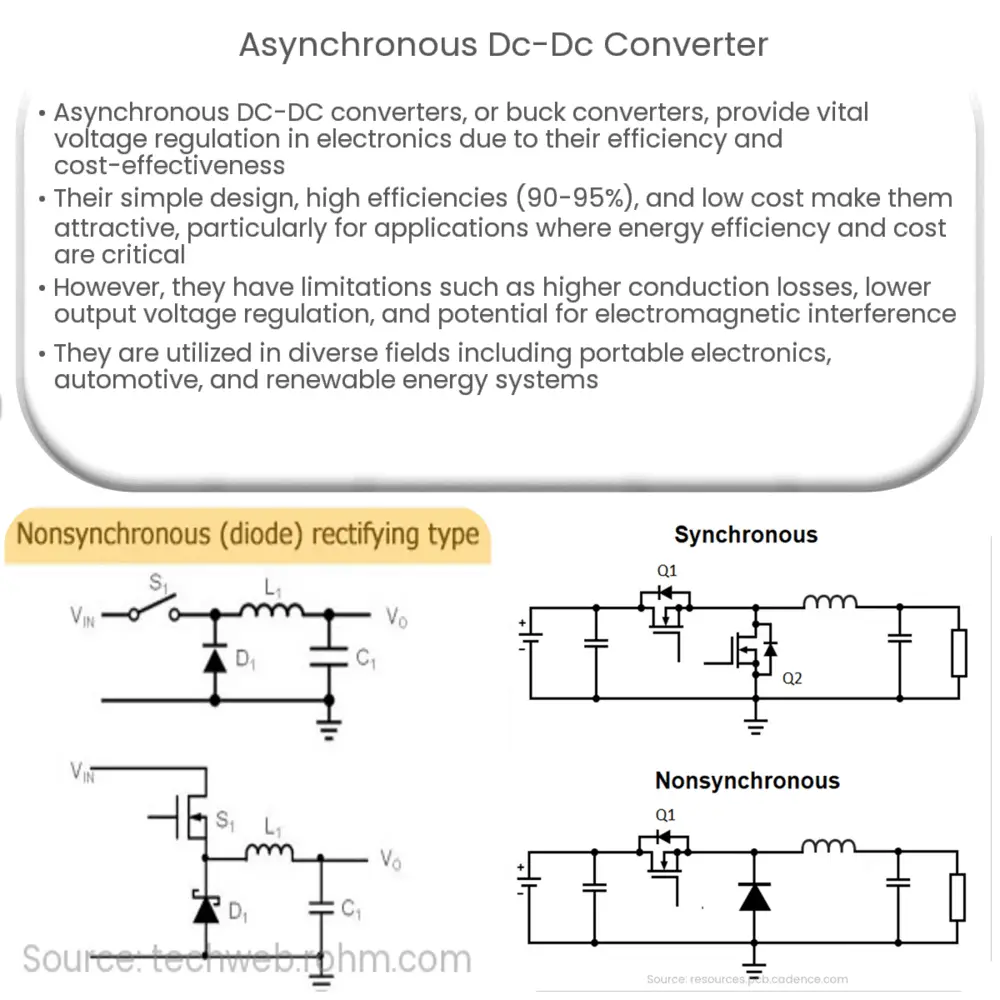
An asynchronous DC-DC converter is a type of switching power supply that converts a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage. It consists of an input capacitor, an inductor, a diode, and a switching transistor. The transistor switches on and off at a high frequency, typically in the range of tens of kilohertz to a few megahertz, depending on the application requirements.
When the transistor is on, the input voltage is applied across the inductor, causing the current to ramp up and energy to be stored. When the transistor is off, the stored energy in the inductor is released to the output capacitor, providing the desired output voltage. The diode serves as a path for the inductor current to flow when the transistor is off, preventing a sudden drop in the output voltage. By adjusting the duty cycle – the ratio of the transistor’s on-time to the total switching period – the output voltage can be controlled.
Advantages of Asynchronous DC-DC Converters
There are several benefits to using asynchronous DC-DC converters, including:
- Efficiency: Asynchronous converters can achieve high efficiencies, typically in the range of 90-95%, depending on the input and output voltage levels and load conditions. This makes them suitable for applications where energy efficiency is crucial, such as battery-powered devices and renewable energy systems.
- Low Cost: Due to their simplicity, asynchronous converters have fewer components compared to other types of converters, making them more cost-effective. The absence of a synchronous rectifier reduces the overall cost, making these converters an attractive option for budget-conscious applications.
- Design Simplicity: Asynchronous converters are relatively simple to design and implement, allowing engineers to create compact and straightforward solutions for various power conversion needs. This simplicity also makes them suitable for beginners looking to learn about power electronics.
Drawbacks of Asynchronous DC-DC Converters
Despite their advantages, asynchronous DC-DC converters do have some limitations:
- Higher Conduction Losses: The use of a diode instead of a synchronous rectifier in the design leads to higher conduction losses. This is due to the forward voltage drop across the diode, which results in power loss and reduced efficiency, particularly at high output currents.
- Lower Output Voltage Regulation: Asynchronous converters typically have a lower output voltage regulation compared to synchronous converters. This means that the output voltage may vary more significantly with changes in load current or input voltage, which can be undesirable in some applications.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): The high-frequency switching operation of asynchronous converters can generate EMI, which may interfere with the operation of nearby electronic devices. Appropriate EMI filtering and shielding techniques are required to mitigate these effects.
Applications of Asynchronous DC-DC Converters
Asynchronous DC-DC converters find use in a variety of applications, including:
- Portable Electronic Devices: Due to their high efficiency and low cost, asynchronous converters are often used in battery-powered devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, where power consumption and cost are critical factors.
- Power Supplies: Asynchronous converters can be used in power supply units for various electronic devices, such as computers, servers, and networking equipment, providing stable and efficient voltage regulation.
- Automotive Electronics: In automotive systems, asynchronous converters help regulate voltages for different subsystems, such as lighting, infotainment, and engine control modules.
- Industrial Equipment: Asynchronous converters are used in industrial machinery and equipment for voltage regulation and power management, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Asynchronous converters are employed in solar and wind energy systems to regulate and convert the generated power into usable voltages for various loads or grid connections.
Conclusion
Asynchronous DC-DC converters are an essential component in modern electronics, offering simplicity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for a wide range of applications. Despite some drawbacks, their benefits make them a popular choice for voltage regulation and power conversion needs. By understanding the principles, advantages, and limitations of asynchronous DC-DC converters, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting and designing power solutions for various applications.

