Explore the fascinating world of accelerometers, their types, working principles, and diverse applications in technology, industry, and healthcare.
Introduction to Accelerometers
Accelerometers are critical components in modern technology, often overlooked despite their ubiquity in devices we use every day. These tiny, sensitive devices measure acceleration – the rate of change of velocity – and detect changes in orientation or movement, offering a plethora of uses in various fields.
Working Principle of Accelerometers
At their core, accelerometers work by measuring disruptions in their own rest state, or equilibrium. This is typically achieved by a tiny mass suspended inside the device. When the accelerometer moves or accelerates, this internal mass is displaced from its equilibrium position, and the degree of this displacement is used to determine the level of acceleration.
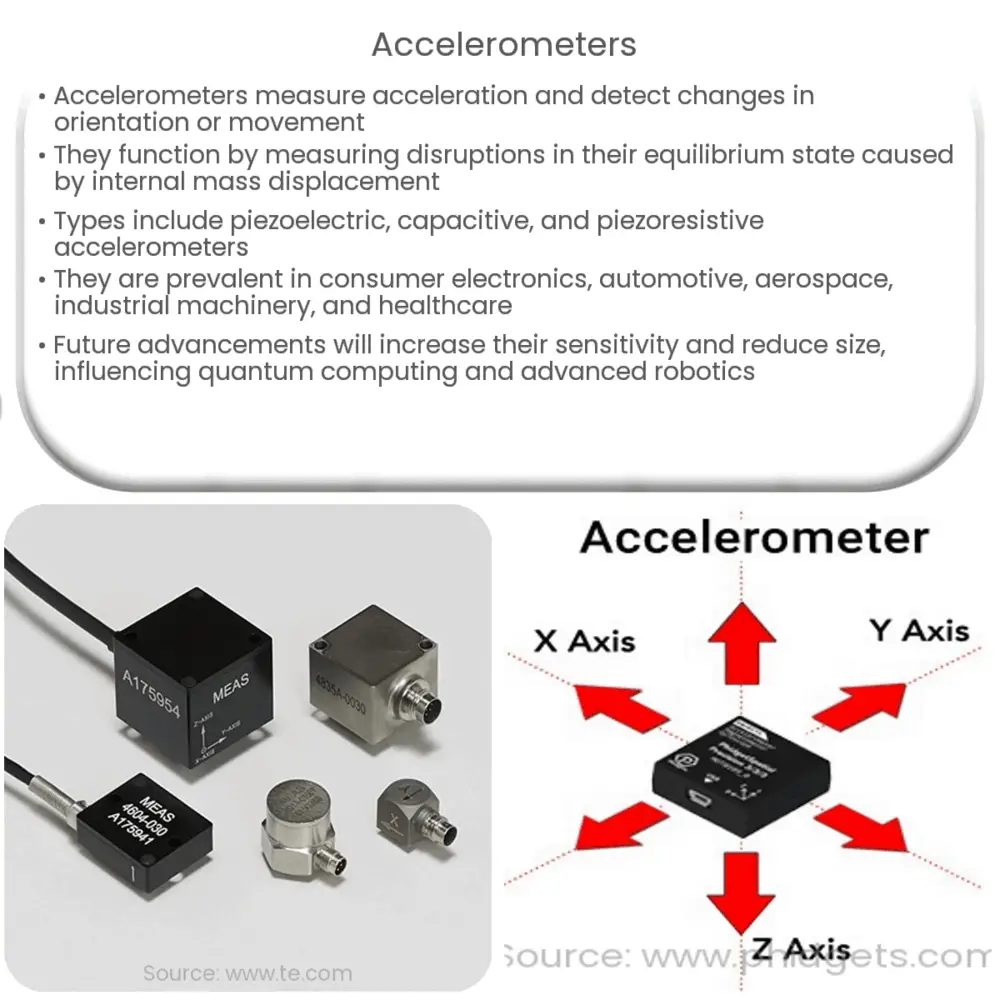
Types of Accelerometers
Applications of Accelerometers
Accelerometers find numerous applications in various fields, thanks to their ability to detect motion and orientation.
Accelerometers in Industry and Healthcare
Not limited to consumer electronics and vehicles, accelerometers also play a significant role in industrial and healthcare settings.
Future of Accelerometers
As technology advances, so too does the potential applications of accelerometers. Future accelerometers will likely become even more sensitive, smaller, and energy-efficient. This could pave the way for their use in areas like quantum computing research and advanced robotics. Furthermore, as part of the broader Internet of Things (IoT), accelerometers will likely play a crucial role in enabling smarter, more responsive environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, accelerometers are a crucial piece of technology, critical to a wide variety of applications in various fields. Whether in your smartphone, car, or medical device, these small but mighty devices provide essential data on movement and orientation. As they continue to improve in sensitivity and decrease in size, we can expect to see them become increasingly integral to the technology of the future.

