A 7-segment display decoder translates input signals into control signals for driving 7-segment displays, simplifying numeric data representation.
Understanding the 7-Segment Display Decoder
A 7-segment display is a widely used electronic device that can represent numerical digits and some alphabetic characters. It is often found in applications such as digital clocks, calculators, and various measurement devices. The 7-segment display consists of seven LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) arranged in a specific pattern, and by illuminating different combinations of these LEDs, various digits and characters can be displayed. In this article, we will discuss the 7-segment display decoder, which is an essential component for driving a 7-segment display.
Overview of the 7-Segment Display
The 7-segment display is named after its seven individual segments, labeled A through G. Each segment is an LED that can be turned on or off independently. By selectively illuminating these segments, it is possible to create the visual representation of any number from 0 to 9 and some letters of the alphabet. For instance, to display the digit ‘3’, segments A, B, C, D, and G would be turned on, while segments E and F would be turned off.
There are two main types of 7-segment displays: common anode and common cathode. In a common anode display, all the LED anodes are connected together, while in a common cathode display, all the LED cathodes are connected together. The choice between these two types depends on the specific application and the driving circuitry.
What is a 7-Segment Display Decoder?
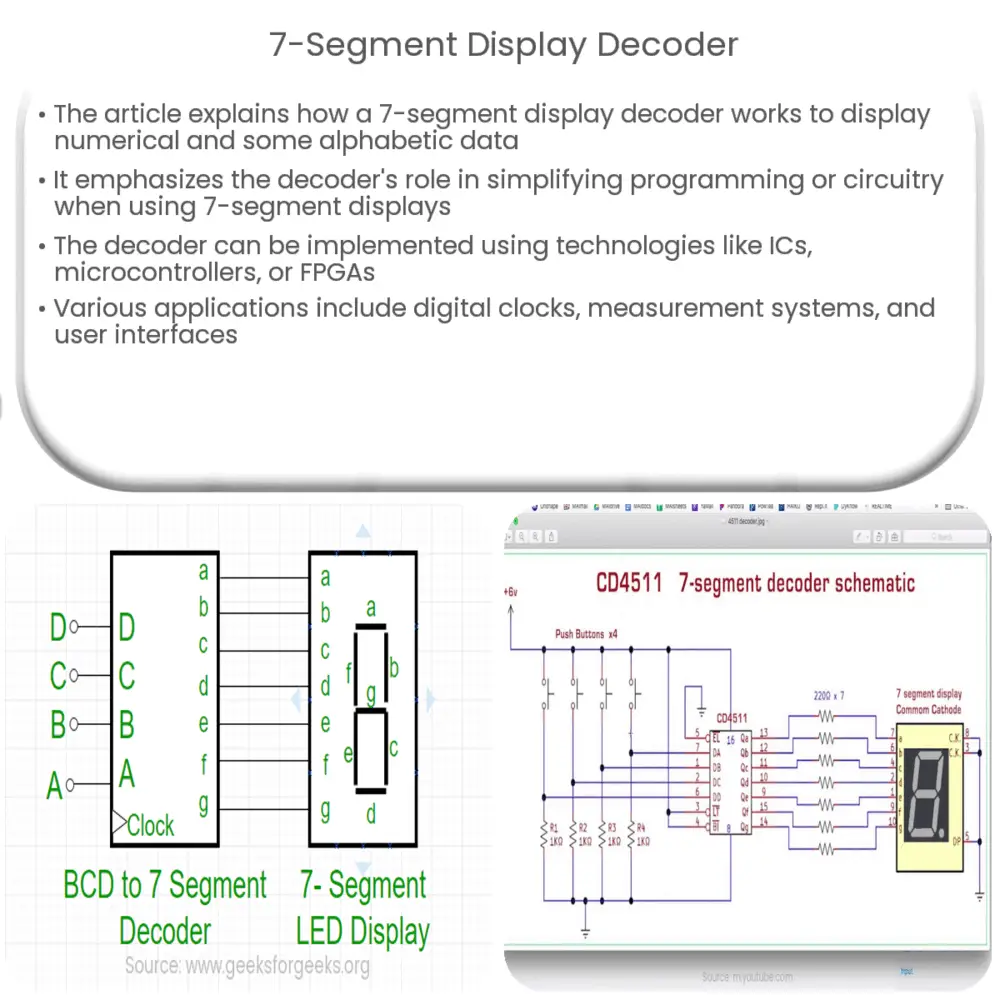
A 7-segment display decoder is an electronic component that translates a binary-coded decimal (BCD) or other input signal into the appropriate control signals for driving a 7-segment display. It is essentially a circuit that interprets the input data and outputs the correct combination of signals to light up the corresponding segments of the display. This eliminates the need for complex programming or circuitry when working with 7-segment displays.
Decoders can be implemented using various technologies, such as integrated circuits (ICs), microcontrollers, or field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). Some of the most popular IC-based decoders for 7-segment displays include the 74LS47 and the CD4511.
How Does a 7-Segment Display Decoder Work?
The primary function of a 7-segment display decoder is to convert the input data into the appropriate signals that can drive the display. To achieve this, the decoder analyzes the input data and maps it to a specific combination of segment control signals. This mapping process can be implemented using combinational logic circuits, such as AND, OR, and NOT gates, or through lookup tables (LUTs) in digital devices like microcontrollers and FPGAs.
For example, consider a BCD to 7-segment display decoder. The BCD input consists of four binary digits, representing a decimal number between 0 and 9. The decoder’s task is to convert this BCD input into the appropriate segment control signals. This can be achieved by designing a combinational logic circuit that generates the correct combination of signals for each BCD input, or by using a lookup table that maps each BCD value to the corresponding segment control signals.
Implementing a 7-Segment Display Decoder with a Microcontroller
Microcontrollers offer a versatile and cost-effective solution for implementing 7-segment display decoders. With built-in digital I/O pins and programming capabilities, a microcontroller can be programmed to function as a 7-segment display decoder by defining a lookup table and using conditional statements or loops to drive the display. Popular microcontroller platforms such as Arduino, PIC, and MSP430 can be easily programmed to work with 7-segment displays.
To implement a 7-segment display decoder with a microcontroller, follow these steps:
- Connect the 7-segment display to the microcontroller’s digital I/O pins. Ensure that the common anode or common cathode connections are properly made, depending on the display type.
- Define a lookup table that maps the input data to the corresponding segment control signals. This can be done using an array or similar data structure.
- Write a function that takes the input data, looks up the corresponding segment control signals from the lookup table, and sets the microcontroller’s digital I/O pins accordingly to drive the display.
- Include the display driving function in the main program loop or as part of an interrupt-driven routine, depending on the application requirements.
Using a 7-Segment Display Decoder in Projects
7-segment display decoders are an essential component in numerous electronic projects, ranging from simple digital clocks and timers to more complex measurement systems and user interfaces. By incorporating a 7-segment display decoder into your project, you can easily present numerical data to users without the need for complex programming or additional circuitry.
Some potential applications for 7-segment display decoders include:
- Digital clocks and timers
- Temperature and humidity monitors
- Voltmeters and ammeters
- Frequency counters
- Scoreboards and game displays
Conclusion
7-segment display decoders play a crucial role in driving 7-segment displays, allowing for the easy representation of numerical and some alphabetic data. With a variety of implementation options, such as integrated circuits, microcontrollers, or FPGAs, 7-segment display decoders can be tailored to suit the specific requirements of any project. By understanding the basics of 7-segment displays and their associated decoders, you can build sophisticated electronic devices and enhance the user experience of your projects.

