Explore the versatile 555 timer, its operating modes, key components, and myriad applications in electronics design.
Introduction to 555 Timers
The 555 timer is an integral component in the world of electronics. It is a versatile, simple, and efficient integrated circuit (IC) used in a variety of applications. It is often utilized in timers, pulse generation, oscillator applications, and much more. Named for the original design’s three 5kΩ resistors, the 555 timer is a classic in IC design.
Working Principles of 555 Timers
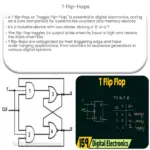
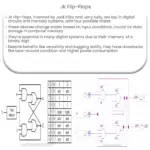
The 555 timer functions as a flip-flop circuit, an elementary form of memory storage in digital systems. It has three main operating modes: Monostable, Bistable, and Astable. Let’s explore these modes in detail.
Monostable Mode: In this mode, the 555 timer acts as a “one-shot” pulse generator. The output pulse ends after a time period determined by the RC network, which includes a resistor and a capacitor.
Bistable Mode: In bistable mode, the 555 timer acts as a flip-flop. Two external triggers can cause it to switch between two states.
Astable Mode: In this mode, the 555 timer oscillates between two states, providing a square wave output. The timing is defined by two resistors and one capacitor.
Components of a 555 Timer
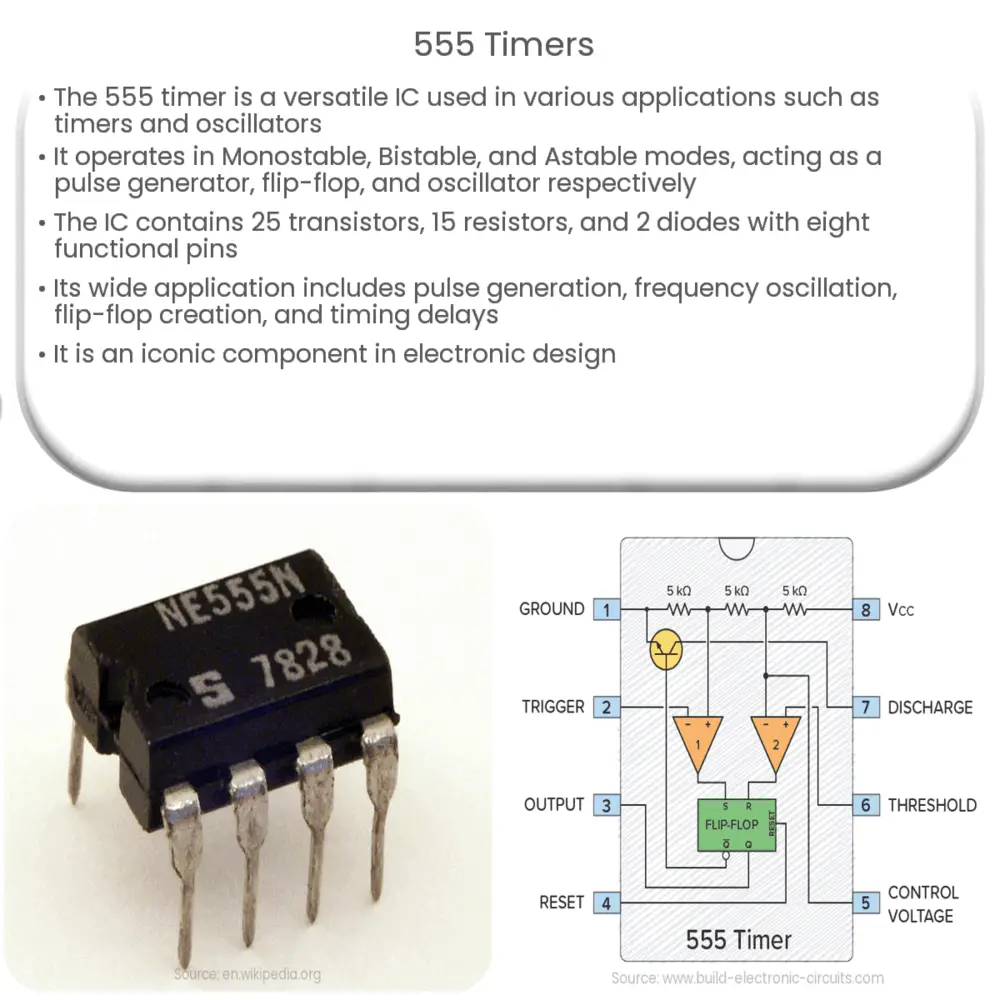
A 555 timer IC contains 25 transistors, 15 resistors, and 2 diodes. The eight pins on the 555 timer each perform unique functions. The following describes the key pins and their functions:
Ground (Pin 1): This pin is connected to the negative terminal (0V) of the power supply.
Trigger (Pin 2): This pin triggers the timing operation when its voltage falls below 1/3 of the supply voltage.
Output (Pin 3): This is the output pin. It can source or sink up to 200 mA of current.
Reset (Pin 4): This pin resets the timing operation when it is connected to the ground.
Control Voltage (Pin 5): This pin controls the timing of the operation by bypassing the 2/3 Vcc voltage level of the voltage-divider network through an external capacitor.
Threshold (Pin 6): The threshold pin resets the timing operation when its voltage exceeds 2/3 of the supply voltage.
Discharge (Pin 7): This pin is connected to ground through an external capacitor and is responsible for discharging that capacitor every time the output switches state.
Vcc (Pin 8): This pin is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, which can vary from +4.5 volts to +15 volts.
Applications of 555 Timers
The flexibility of the 555 timer allows for a multitude of applications. These include, but are not limited to:
Pulse Generation: The 555 timer is frequently used to generate pulses of specific durations, typically in monostable mode.
Oscillators: In astable mode, the 555 timer can act as an oscillator, creating a square wave output at a specific frequency.
Flip-Flop: By using the bistable mode, a 555 timer can create a simple flip-flop, an essential component in digital memory circuits.
Timing Delays: One of the most common applications for a 555 timer is to create a delay before an action occurs, such as turning a device on after a certain period.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 555 timer is an iconic integrated circuit and a workhorse of the electronics world. It’s a versatile and flexible chip that can be found in many electronic devices. From simple timing applications to more complex digital memory circuits, the 555 timer’s robust functionality has stood the test of time, and it continues to be an essential component in many electronic design projects. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional electronics engineer, understanding the 555 timer is fundamental to understanding the broader landscape of electronics design.