Explore the five most common types of electric relays: Electromagnetic, Solid State, Thermal, Reed, and Hybrid. Understand their functions for optimal system performance.
The Five Most Common Types of Electric Relays
An electric relay is an essential component in electrical systems. It allows a low power circuit to control a much higher power circuit, acting as a sort of electrical switch. There are several types of electric relays, each serving a unique purpose. The five most common are the Electromagnetic Relay, Solid State Relay, Thermal Relay, Reed Relay, and Hybrid Relay.
1. Electromagnetic Relay
The Electromagnetic Relay operates based on the principles of electromagnetism. When an electrical current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that actuates the switch, enabling current flow in another circuit. Its main advantage is its isolation ability, as the circuit that activates the relay is electrically separate from the circuit being controlled.
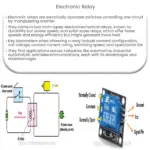
2. Solid State Relay
Solid State Relays (SSRs) are devoid of moving parts, relying on semiconductor properties for their operation. SSRs switch on and off much faster than electromagnetic relays and are noiseless. Moreover, they are more resistant to shock and vibration, making them suitable for numerous industrial applications.
3. Thermal Relay
A Thermal Relay is primarily used for overload protection in electrical motors. It works based on the thermal effect of electric current. In the event of an overload, the heat generated causes a bimetallic strip to bend, activating the relay and breaking the circuit. This protects the motor from damage.
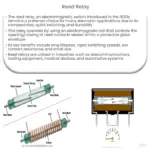
4. Reed Relay
Reed Relays consist of a pair of magnetic strips (reeds) enclosed in a glass tube. When a magnetic field is applied to the coil, the reeds move and make or break the circuit. They offer advantages like a compact size and fast operation but are limited by their low switching current capacities.
5. Hybrid Relay
Hybrid Relays combine the benefits of electromagnetic and solid-state relays. They typically employ solid-state components for input and an electromagnetic relay for output. This results in a relay with fast switching times, durability, and good electrical isolation.
Understanding the properties and functions of these common types of electric relays helps in their appropriate selection, thereby optimizing electrical system performance and safety.