Explore the world of Zero Current Switching (ZCS) converters: their working principle, types, advantages, limitations, and future prospects.
Understanding Zero Current Switching (ZCS) Converters
Zero Current Switching (ZCS) converters are a pivotal element in modern power electronics, enabling the efficient conversion of electrical energy while minimizing losses associated with switching devices. The term “Zero Current Switching” refers to the strategy of switching the power semiconductor device at zero current conditions, reducing switching losses and improving system efficiency.
Working Principle of ZCS Converters
The fundamental operation of ZCS converters is rooted in the nature of inductive loads. In such systems, the current through the inductor cannot change instantaneously. When the switching device in a ZCS converter turns off, it does so at the instant when the current flowing through it becomes zero. This operation reduces the power dissipation across the switching devices and enhances the overall efficiency of the system.
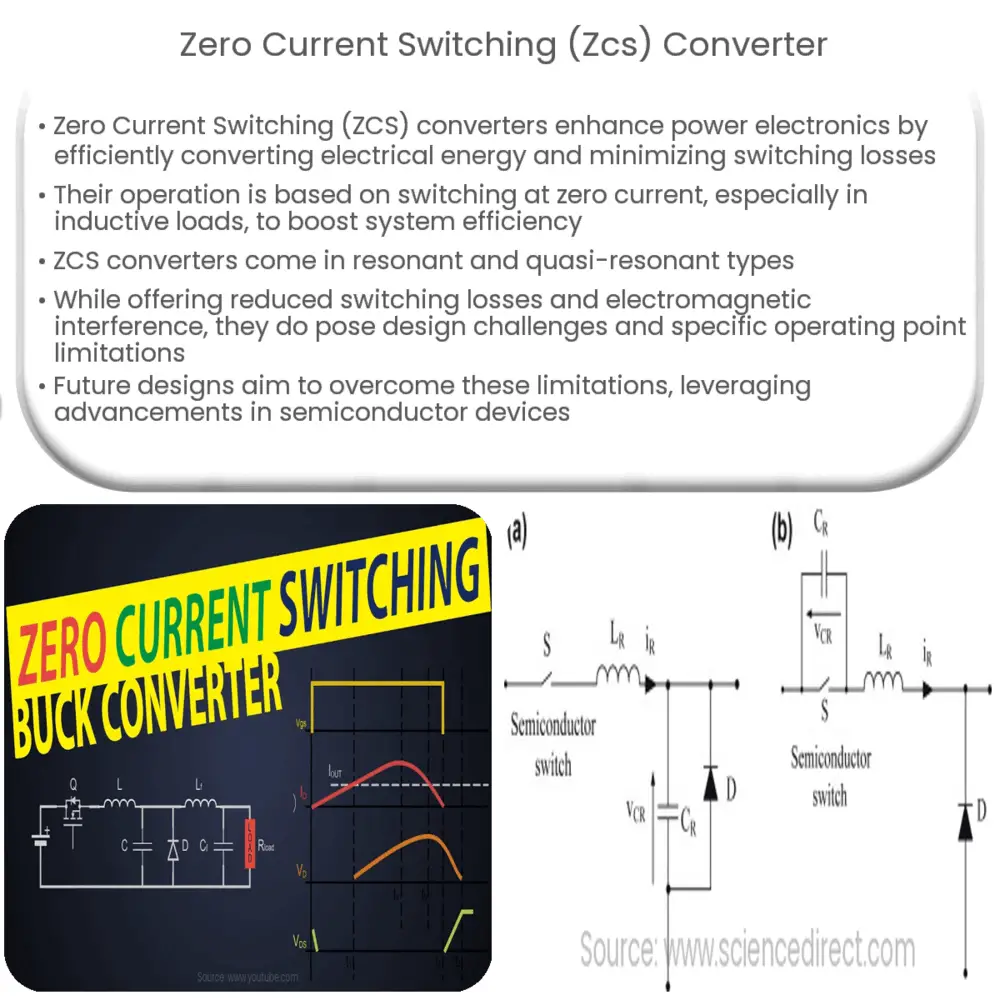
Types of ZCS Converters
- Resonant ZCS converters: These converters incorporate resonant circuits, which create a natural zero-current condition at the switching instances. The resonant circuit consists of an inductor and capacitor that make the current flow sinusoidal. Thus, the current naturally becomes zero at specific times, allowing the switch to turn off with minimal losses.
- Quasi-resonant ZCS converters: Unlike the resonant ZCS converters, quasi-resonant converters don’t create a resonant condition throughout the entire operation. However, they still manage to turn the switching devices off at zero current conditions, reducing switching losses.
Advantages and Applications of ZCS Converters
ZCS converters offer numerous advantages, leading to their widespread use in various applications. They significantly reduce switching losses, extending the life of the power semiconductor devices and increasing the overall efficiency of power conversion systems. Moreover, ZCS converters generate less electromagnetic interference (EMI), thus improving the reliability of electronic systems.
Given their high efficiency and reduced EMI, ZCS converters are extensively used in a wide array of applications, including telecommunications equipment, computer power supplies, electric vehicle chargers, and renewable energy systems.
Key Design Considerations for ZCS Converters
While designing ZCS converters, certain key factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance. The design process should take into account the parameters like the resonant frequency of the resonant circuit, the characteristics of the switching device, and the load requirements. In addition, the designer must also consider the trade-off between the efficiency and the complexity of the design.
Challenges and Limitations of ZCS Converters
Despite their benefits, ZCS converters are not without their limitations. One of the primary challenges is that the zero current switching condition can only be achieved at specific operating points. This means that the ZCS condition may not be maintained under all load conditions, leading to increased switching losses.
In addition, the use of resonant circuits in ZCS converters adds complexity to the design, making them more difficult to design and manufacture compared to traditional converters. Also, these circuits can generate high peak currents, which may lead to increased stress on the components and potentially reduce their lifespan.
Future Directions in ZCS Converter Design
The future of ZCS converters lies in overcoming their limitations and further enhancing their performance. Recent advancements in power semiconductor devices and control strategies offer promising opportunities in this direction. For instance, wide bandgap semiconductor devices can potentially improve the performance of ZCS converters by enabling operation at higher frequencies and temperatures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Zero Current Switching (ZCS) converters play an indispensable role in power electronics, providing high-efficiency power conversion with reduced switching losses. Despite their challenges and limitations, ZCS converters remain a promising technology in the face of growing demand for energy-efficient and reliable power conversion systems. As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in the design and performance of ZCS converters, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable power electronics in the future.

