The temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) quantifies the change in a material’s electrical resistance per degree Celsius, crucial for component selection and thermal management.
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance: A Key Parameter
The temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) is an essential parameter that characterizes the change in electrical resistance of a material with respect to temperature. It is crucial for understanding the performance and behavior of electrical components and devices, especially those operating in varying temperature environments. This article discusses the concept of the temperature coefficient of resistance and its significance in the field of electrical engineering.
Defining Temperature Coefficient of Resistance
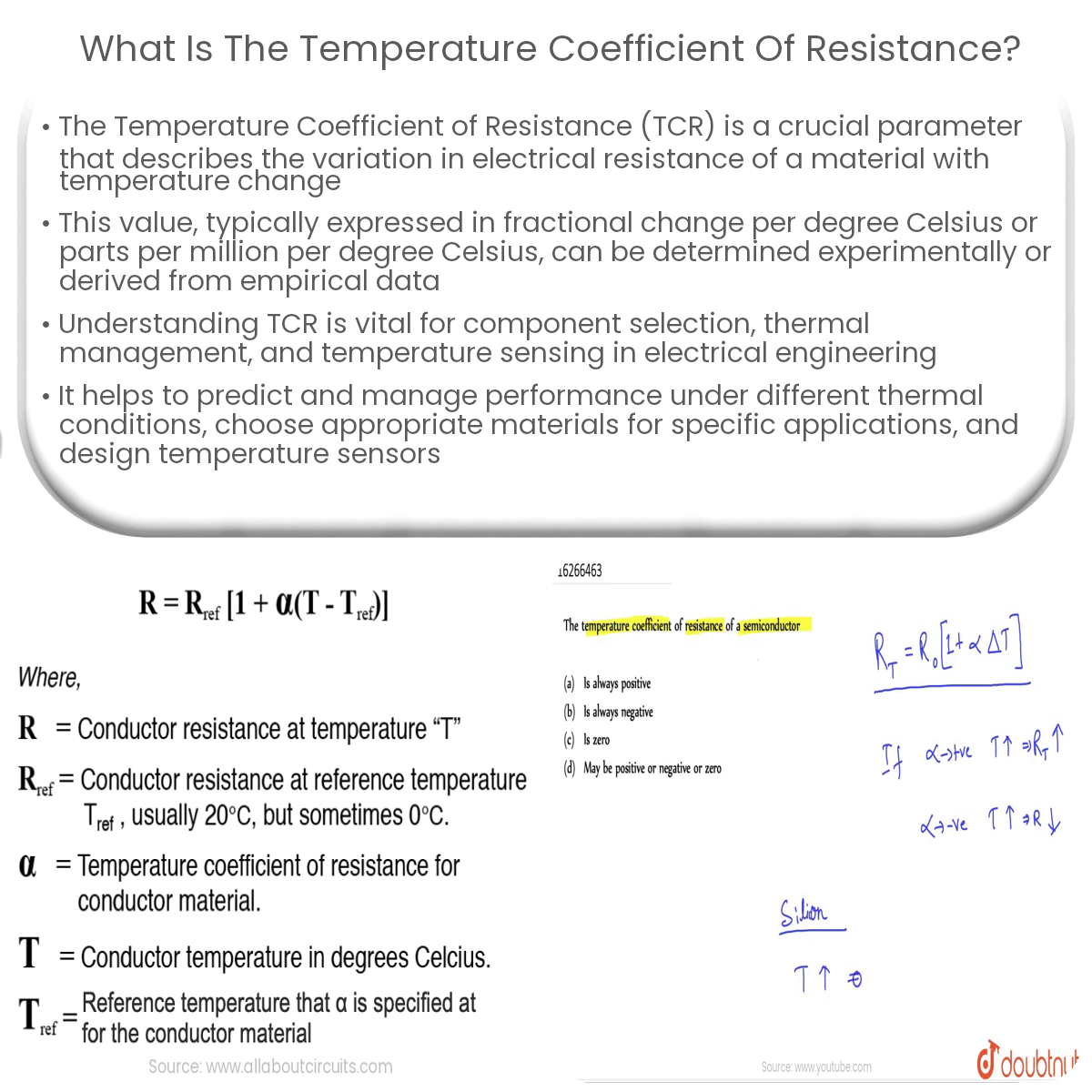
The temperature coefficient of resistance (α) is a parameter that quantifies the relative change in electrical resistance of a material per degree Celsius (°C). It is typically expressed in units of fractional change per degree Celsius (°C⁻¹) or parts per million per degree Celsius (ppm/°C). The TCR indicates how the resistance of a material changes as the temperature varies, which is essential for predicting and managing the performance of electrical components and devices under different thermal conditions.
Calculating the Temperature Coefficient of Resistance
The TCR can be determined experimentally or derived from empirical data. To calculate the TCR, the resistance of a material is measured at two different temperatures (usually at a reference temperature, T0, and another temperature, T). The TCR is then calculated using the following formula:
α = (RT – R0) / (R0(T – T0))
Where α is the temperature coefficient of resistance, RT is the resistance at temperature T, R0 is the resistance at the reference temperature T0, and T and T0 are the two temperatures in degrees Celsius.
Significance and Applications
The temperature coefficient of resistance is significant in various aspects of electrical engineering:
- Component selection: Understanding the TCR of materials is crucial for selecting appropriate components for specific applications, ensuring reliable and consistent performance under varying temperature conditions.
- Thermal management: Knowledge of the TCR helps in designing effective thermal management strategies for electrical circuits and devices, preventing temperature-induced performance issues and component failures.
- Temperature sensing: The TCR is a key parameter for designing temperature sensors, such as resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) and thermistors, which exploit the temperature-dependent resistance of materials to measure temperature.
In conclusion, the temperature coefficient of resistance is a critical parameter that characterizes the change in electrical resistance of a material with respect to temperature. Understanding the TCR is essential for predicting and managing the performance of electrical components and devices, selecting appropriate materials for specific applications, and designing temperature sensors. As a result, the TCR is an important concept in the field of electrical engineering.