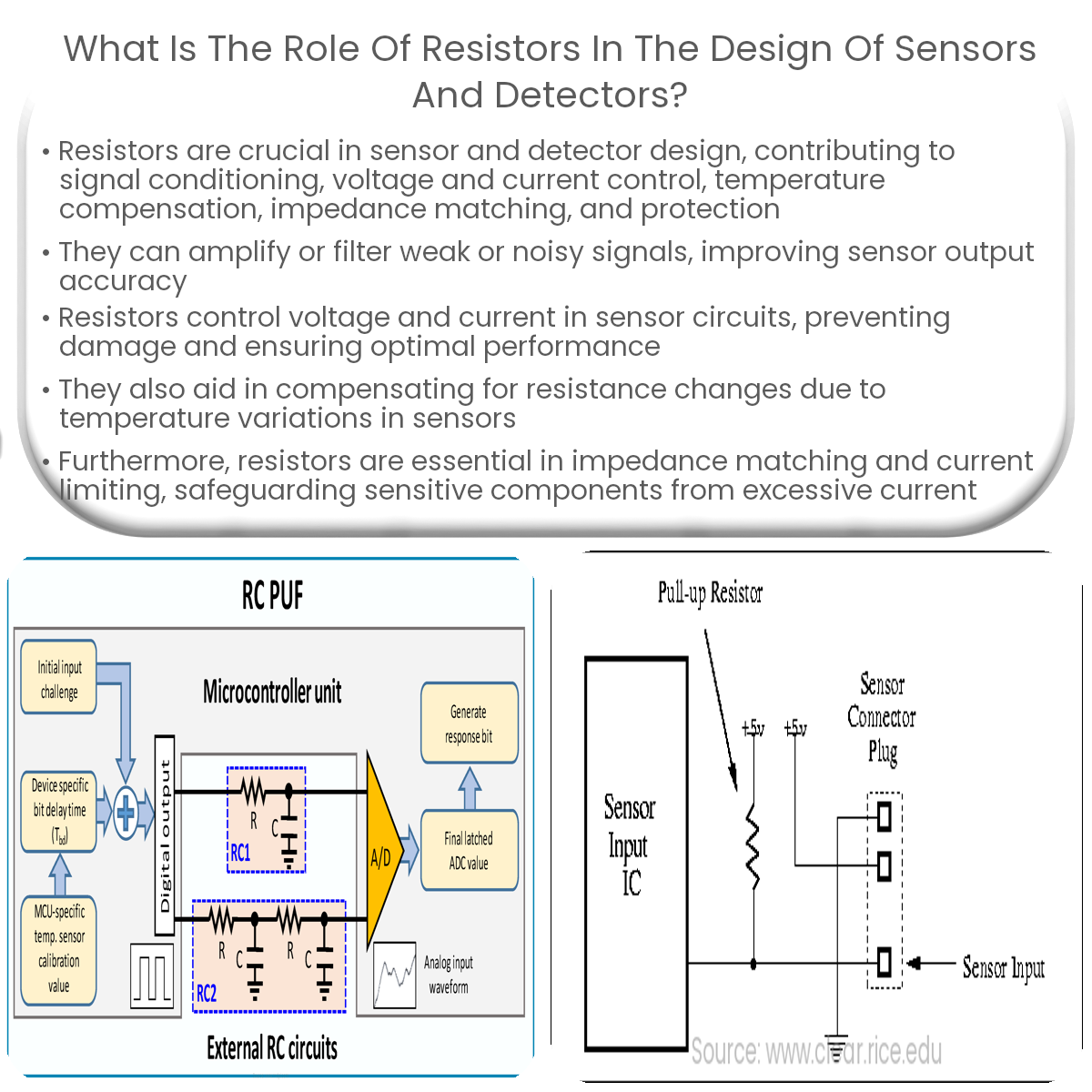
Resistors play a crucial role in sensor design, including signal conditioning, voltage control, temperature compensation, impedance matching, and protection.
Role of Resistors in Sensor and Detector Design
Resistors play a critical role in the design of sensors and detectors. They help in signal conditioning, voltage and current control, as well as maintaining the stability of the sensor circuit. In this article, we’ll explore the various ways resistors contribute to the functionality and performance of sensors and detectors.
Signal Conditioning
Sensors often produce weak or noisy signals that need to be amplified or filtered before being processed. Resistors can be used in conjunction with operational amplifiers and capacitors to create filters and amplifiers. These circuits help improve the signal-to-noise ratio, ensuring that the sensor’s output is accurate and reliable.
Voltage and Current Control
Resistors are crucial for controlling voltage and current levels in sensor circuits. By designing the appropriate resistor network, engineers can ensure that the sensor receives the proper voltage and current levels for optimal performance. This can help prevent damage to the sensor and maintain its accuracy and longevity.
Temperature Compensation
Many sensors, such as thermistors and RTDs, change their resistance with temperature. By using resistors with known temperature coefficients, engineers can design circuits that compensate for these changes and provide accurate measurements regardless of temperature fluctuations. This is particularly important in environments with significant temperature variations.
Impedance Matching
Impedance matching is essential for maximizing signal transfer between a sensor and its associated circuitry. Resistors can be used to create impedance-matching networks that ensure the sensor’s output impedance matches the input impedance of the next stage in the circuit. This minimizes signal loss and improves overall system performance.
Current Limiting and Protection
Resistors can also act as current limiters and protect sensitive components in sensor circuits from damage due to excessive current. By adding a resistor in series with the sensor element, the current can be limited to a safe level, preventing overheating and damage to the sensor or other components.
Conclusion
In summary, resistors play a vital role in the design of sensors and detectors. They contribute to signal conditioning, voltage and current control, temperature compensation, impedance matching, and protection. Understanding the importance of resistors and their applications in sensor design enables engineers to create reliable, accurate, and robust sensing systems for a wide range of applications.