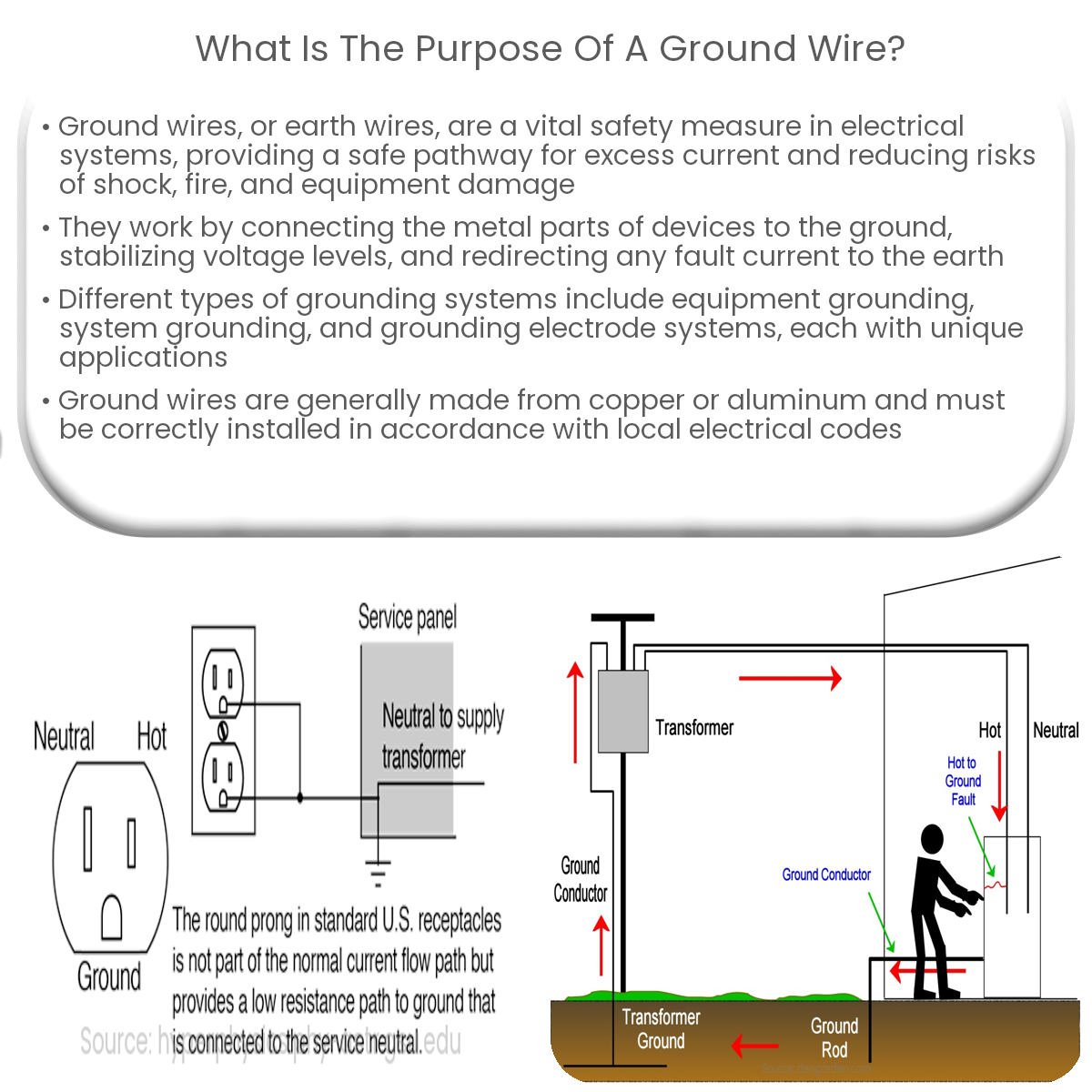
A ground wire provides a safe path for excess current, protecting users from electric shock, preventing equipment damage, and minimizing fire hazards.
Introduction to Ground Wires
A ground wire, also known as an earth wire or protective earth, is an essential safety component in electrical systems. Its purpose is to provide a safe pathway for excess current to flow in the event of a fault or short circuit, reducing the risk of electrical shock, fires, and damage to electrical components.
Role of Ground Wires in Electrical Systems
Ground wires are an important part of an electrical system’s safety measures. They help to:
- Prevent electrical shock
- Protect electrical equipment from damage
- Minimize fire hazards
- Stabilize voltage levels
By connecting the metal parts of electrical devices to the ground, any leakage current or fault current is safely redirected to the earth, protecting the user from electrical shock. The ground wire also provides a stable reference point for voltage levels, ensuring a consistent and reliable supply of power.
Types of Grounding Systems
There are several types of grounding systems, with the most common being:
- Equipment Grounding: This type of grounding connects the metal parts of electrical equipment to the ground to protect users from electric shock.
- System Grounding: In this case, one conductor of the electrical supply system is connected to the ground to stabilize voltage levels and protect the system from lightning and other high-voltage disturbances.
- Grounding Electrode System: This is a network of conductors, electrodes, and connections that establishes a direct connection between an electrical system and the earth. It is typically used for larger installations like buildings and industrial facilities.
Ground Wire Materials and Installation
Ground wires are typically made from copper or aluminum due to their excellent conductivity properties. They must be properly sized according to the current-carrying capacity of the electrical system and installed following local electrical codes and regulations.
Ground wires are connected to the grounding terminal of electrical devices or to a grounding busbar in an electrical panel. In most residential and commercial applications, the ground wire is then connected to a grounding electrode, such as a metal rod driven into the earth or a metal water pipe, to establish a direct connection to the ground.
Conclusion
Ground wires play a crucial role in maintaining the safety and stability of electrical systems. By providing a safe path for fault currents and stabilizing voltage levels, they protect users from electrical shock, prevent damage to electrical equipment, and minimize fire hazards.