Inductive wireless power transfer systems are designed to transmit electrical energy from one device to another without the need for physical connections, such as cables or cords.
Understanding Inductive Wireless Power Transfer Systems
Inductive wireless power transfer systems are designed to transmit electrical energy from one device to another without the need for physical connections, such as cables or cords. This technology is becoming increasingly popular, enabling devices like smartphones, electric toothbrushes, and even electric vehicles to charge wirelessly. In this article, we’ll explore the basic principle of operation of an inductive wireless power transfer system.
Inductive Coupling
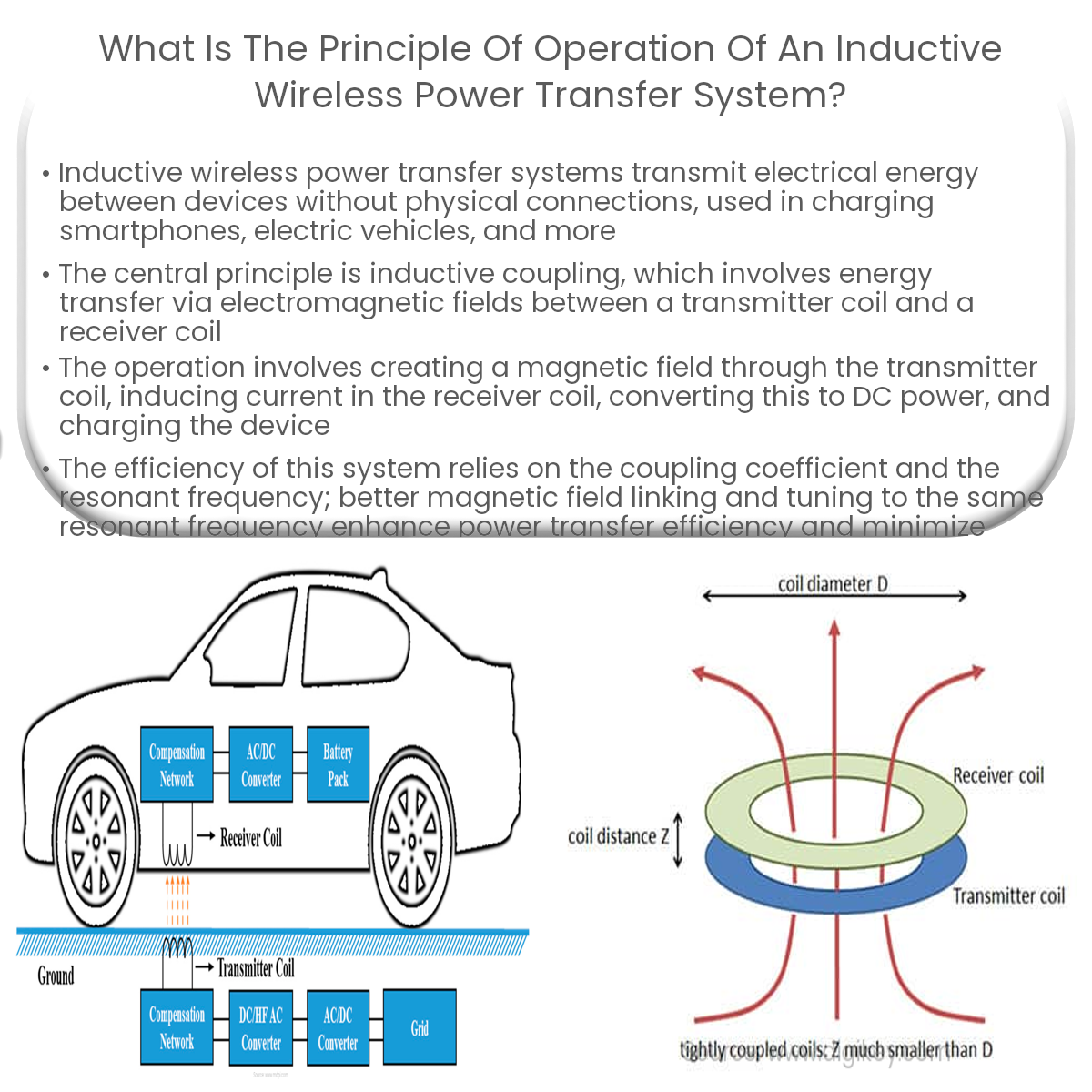
The core principle behind inductive power transfer is inductive coupling, which is a method of transferring energy through electromagnetic fields. This involves two coils of wire – a transmitter coil and a receiver coil – that are placed in close proximity to each other. The transmitter coil is connected to an alternating current (AC) power source, while the receiver coil is connected to the device that needs to be charged.
How Does It Work?
- Generating a magnetic field: When the AC power source is turned on, an alternating current flows through the transmitter coil, creating a time-varying magnetic field around it.
- Inducing a current in the receiver coil: The magnetic field generated by the transmitter coil cuts through the turns of the receiver coil, inducing an electromotive force (EMF) in it. This phenomenon is governed by Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
- Converting the induced EMF to DC power: The induced EMF in the receiver coil is an alternating voltage. To charge a device like a smartphone, this AC voltage needs to be converted to direct current (DC). This is done using a rectifier, which is typically a part of the charging circuit within the receiving device.
- Charging the device: Once the induced EMF has been converted to DC power, it can be used to charge the device’s battery, providing a wireless power transfer.
Efficiency and Resonant Frequency
The efficiency of an inductive wireless power transfer system is primarily determined by two factors: the coupling coefficient (k) and the resonant frequency. The coupling coefficient is a measure of how well the magnetic field generated by the transmitter coil links with the receiver coil. A higher k-value indicates better coupling, leading to greater power transfer efficiency.
Resonant frequency plays a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency of the system. When both the transmitter and receiver coils are tuned to the same resonant frequency, energy transfer is optimized, and power losses are minimized. This phenomenon is known as resonant inductive coupling.
Conclusion
In summary, inductive wireless power transfer systems rely on the principle of inductive coupling to transmit energy from one coil to another without physical connections. By understanding the basic operation of these systems, we can appreciate the convenience and potential of wireless power transfer in our everyday lives.