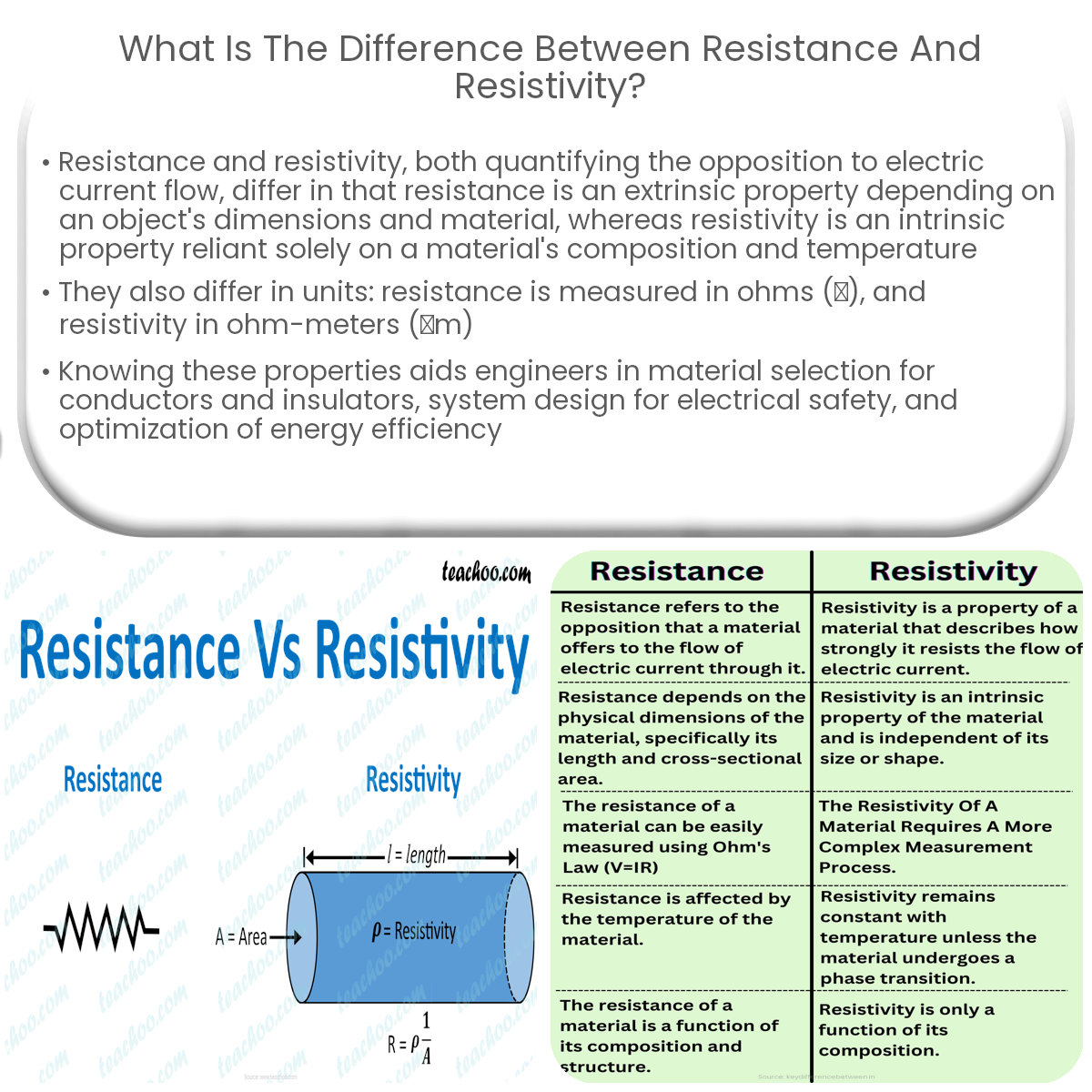
Resistance is an object’s opposition to electric current, depending on its material and dimensions, while resistivity is an intrinsic property of a material.
Resistance vs. Resistivity: Understanding the Difference
Resistance and resistivity are two related concepts in the field of electrical engineering that describe the opposition of a material or an object to the flow of electric current. This article will explain the differences between resistance and resistivity, their respective units, and how they are used in various applications.
Resistance
Resistance, denoted by the symbol R, is a property of an object, such as a wire, that quantifies its opposition to the flow of electric current. It depends on the object’s material, dimensions, and temperature. The unit of resistance is the ohm (Ω). The resistance of an object is calculated using Ohm’s law:
R = ρ (L / A)
Where:
- R is the resistance;
- ρ (rho) is the resistivity of the material;
- L is the length of the object; and
- A is the cross-sectional area of the object.
Resistivity
Resistivity, denoted by the Greek letter rho (ρ), is an intrinsic property of a material that describes its ability to resist the flow of electric current. It is independent of the object’s shape or size and is only affected by the material’s composition and temperature. The unit of resistivity is the ohm-meter (Ωm).
Key Differences between Resistance and Resistivity
While both resistance and resistivity are related to the opposition of electric current flow, there are several key differences between the two:
- Property Type: Resistance is an extrinsic property that depends on an object’s dimensions and material, while resistivity is an intrinsic property, depending only on the material’s composition and temperature.
- Units: Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω), whereas resistivity is measured in ohm-meters (Ωm).
- Formula: Resistance is calculated using Ohm’s law (R = ρ(L/A)), while resistivity is a constant for a given material and temperature.
Applications of Resistance and Resistivity
Understanding the concepts of resistance and resistivity is crucial in various electrical applications:
- Material Selection: Knowing the resistivity of materials helps engineers select appropriate conductors and insulators for different applications, such as wires, connectors, and circuit boards.
- System Design: Calculating the resistance of components is vital for designing efficient and safe electrical systems, ensuring that components can handle the required current without overheating or causing electrical fires.
- Energy Efficiency: By understanding the relationship between resistance and resistivity, engineers can minimize energy losses in electrical systems, increasing overall efficiency.
In conclusion, resistance and resistivity are two distinct concepts that describe the opposition to electric current flow. Resistance is an extrinsic property that depends on an object’s dimensions and material, while resistivity is an intrinsic property of a material. Understanding these differences is essential for the selection of materials and the design of safe and efficient electrical systems.