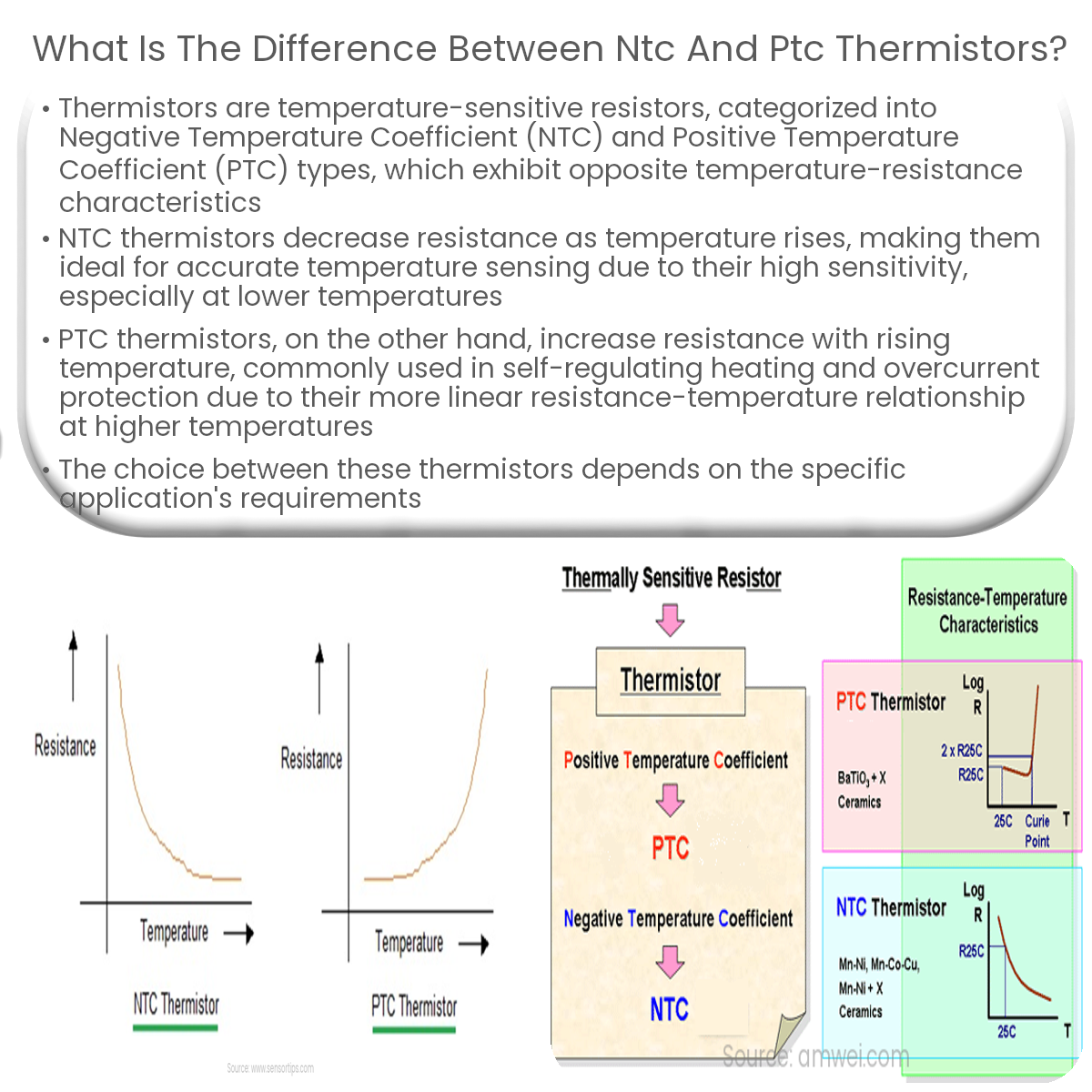
NTC thermistors have negative temperature coefficients, decreasing resistance with increasing temperature. PTC thermistors have positive coefficients, increasing resistance with rising temperature.
NTC and PTC Thermistors: Understanding the Differences
Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors that exhibit a change in electrical resistance with temperature variations. There are two main types of thermistors: Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) and Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC). This article will discuss the key differences between NTC and PTC thermistors.
Temperature Coefficient
The fundamental difference between NTC and PTC thermistors lies in their temperature coefficient:
- NTC Thermistors: These thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient, which means their resistance decreases as temperature increases.
- PTC Thermistors: These thermistors have a positive temperature coefficient, meaning their resistance increases as temperature increases.
Applications
NTC and PTC thermistors have different applications due to their distinct temperature-resistance characteristics:
- NTC Thermistors: They are commonly used for temperature sensing, measurement, and control applications, where high sensitivity and accuracy are required. Examples include temperature sensors in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and medical devices.
- PTC Thermistors: They are typically used as self-regulating heating elements or overcurrent protection devices. PTC thermistors are often found in applications like heaters, motor protection, and circuit protection.
Sensitivity and Linearity
NTC and PTC thermistors have different sensitivity and linearity profiles:
- NTC Thermistors: They offer high sensitivity, especially at lower temperatures, enabling precise temperature measurements. However, they have a non-linear resistance-temperature relationship, which requires linearization for accurate readings over a wide temperature range.
- PTC Thermistors: They have lower sensitivity compared to NTC thermistors, and their resistance-temperature relationship tends to be more linear, particularly at higher temperatures.
Stability and Response Time
There are differences in stability and response time between NTC and PTC thermistors:
- NTC Thermistors: They exhibit long-term stability and fast response times, making them suitable for applications requiring quick and consistent temperature measurements.
- PTC Thermistors: Their stability and response time can vary depending on the specific material used and the application. In general, PTC thermistors have slower response times compared to NTC thermistors.
Conclusion
NTC and PTC thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors with opposite temperature-resistance characteristics. NTC thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient and are commonly used for temperature sensing, while PTC thermistors have a positive temperature coefficient and are used in self-regulating heating elements and overcurrent protection. Understanding the differences between these two types of thermistors is essential for selecting the appropriate device for a specific application.