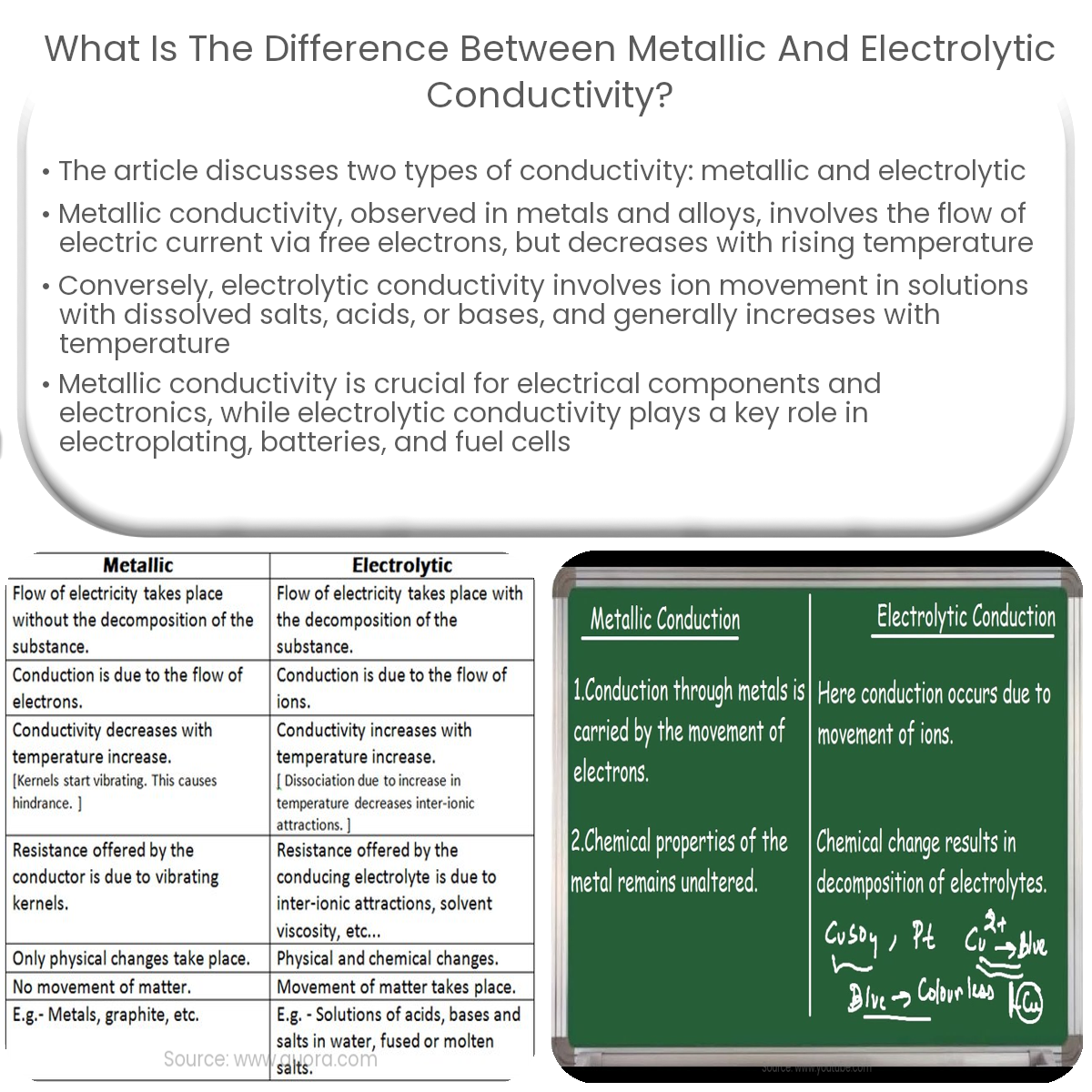
Metallic conductivity involves free electrons in metals, while electrolytic conductivity relies on ion movement in solutions containing dissolved ions.
Metallic Conductivity
Metallic conductivity refers to the ability of metals to conduct electricity. This conductivity occurs due to the presence of free electrons in the metallic lattice structure. These free electrons, also known as conduction electrons, are free to move and form an “electron sea” that is responsible for the flow of electric current.
Electrolytic Conductivity
Electrolytic conductivity, on the other hand, is the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. In this case, the conduction of electricity is facilitated by the movement of ions present in the solution. When a solution contains dissolved salts, acids, or bases, these substances dissociate into their respective ions, which can then carry electric charge through the solution.
Key Differences
- Conduction Mechanism: In metallic conductivity, the conduction of electricity is due to the movement of free electrons, while in electrolytic conductivity, it is due to the movement of ions in a solution.
- Materials: Metallic conductivity is observed in metals and metal alloys, while electrolytic conductivity is observed in solutions containing dissolved ions from salts, acids, or bases.
- Temperature Dependence: Metallic conductivity generally decreases with an increase in temperature, as the increased thermal vibrations of the lattice impede the movement of electrons. In contrast, electrolytic conductivity typically increases with temperature, as higher temperatures result in increased ion mobility.
- Electrical Resistance: Metals usually have low electrical resistance due to the presence of a large number of free electrons. Electrolytic solutions, however, can have a wide range of resistances, depending on the concentration and type of ions present in the solution.
Applications
Metallic conductivity is crucial in the design and manufacturing of electrical components, such as wires, connectors, and printed circuit boards, as well as in various electronic devices. Electrolytic conductivity, on the other hand, is important in applications such as electroplating, batteries, and fuel cells, where the movement of ions is an essential aspect of the process.