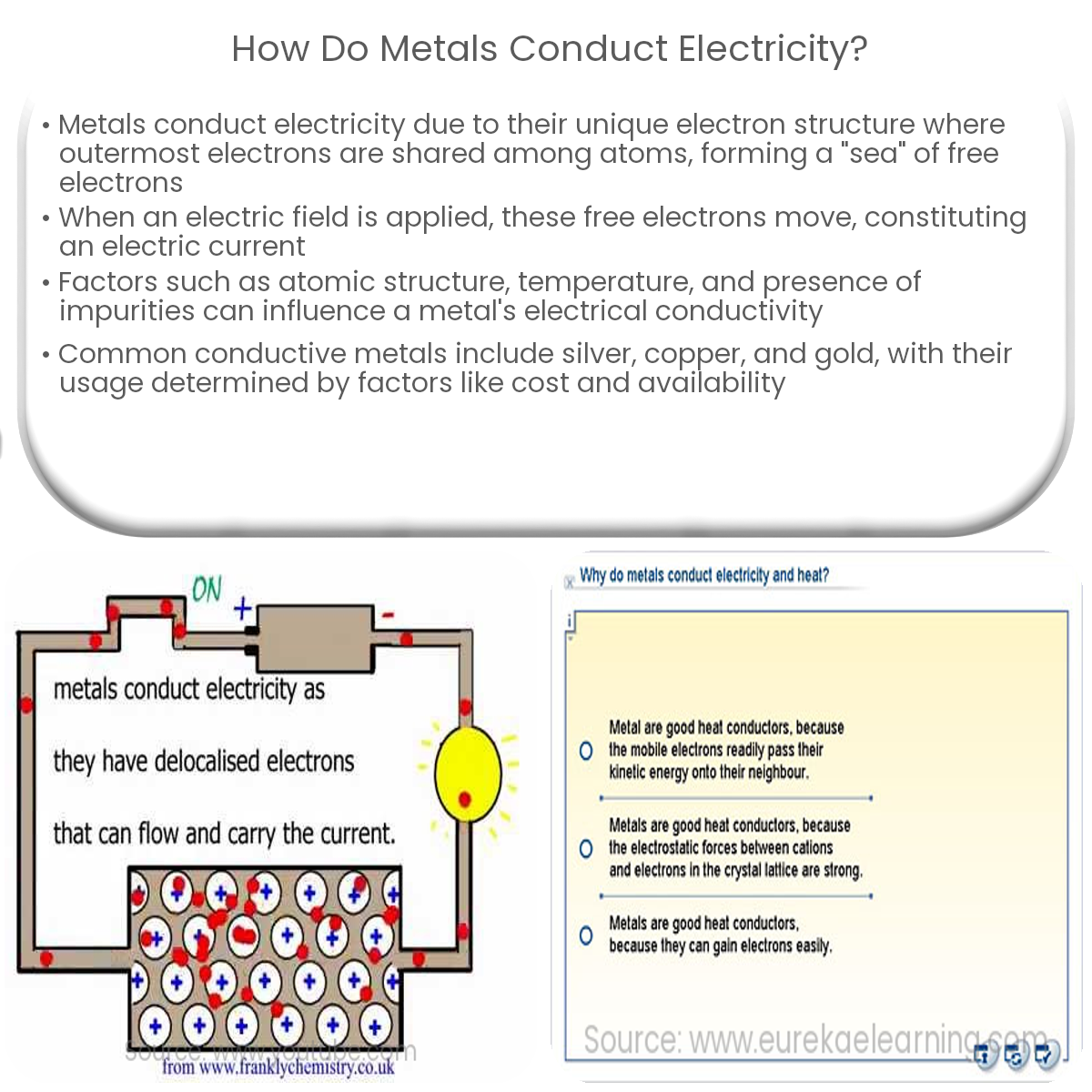
Metals conduct electricity due to their lattice structure and the presence of free, delocalized electrons that move when an electric field is applied.
How Do Metals Conduct Electricity?
Metals are excellent conductors of electricity due to the unique structure of their electrons. The atoms in metals are arranged in a lattice structure, with the outermost electrons being shared among many atoms. These free electrons, also known as conduction electrons, are responsible for the high electrical conductivity of metals.
Electron Sea Model
The electron sea model, also known as the free electron model, is a concept used to explain how metals conduct electricity. According to this model, metal atoms release their outermost electrons into a “sea” of free electrons that are mobile and delocalized. This sea of electrons surrounds a lattice of positively charged metal ions.
Free Electron Movement
When an electric field is applied across a metal, the free electrons are influenced by the force of the field, causing them to move in the direction of the electric field. This movement of electrons constitutes an electric current. The ease with which these electrons can move through the lattice is directly related to the metal’s electrical conductivity.
Factors Influencing Electrical Conductivity
Several factors can influence the electrical conductivity of metals, such as:
- Atomic structure: Metals with fewer valence electrons (outermost electrons) generally have higher electrical conductivity because they can more easily release their electrons into the electron sea.
- Temperature: As the temperature increases, the vibrations of the metal ions in the lattice also increase. This increased vibration can impede the movement of free electrons, resulting in a decrease in electrical conductivity.
- Impurities: The presence of impurities in a metal can interfere with the movement of free electrons, reducing the metal’s electrical conductivity. This is why highly purified metals, such as copper and aluminum, are used for electrical applications.
Common Conductive Metals
Some of the most common metals with high electrical conductivity include:
- Silver: Silver has the highest electrical conductivity of all elements, making it an excellent conductor. However, due to its high cost, it is not commonly used for large-scale electrical applications.
- Copper: Copper is the second-best conductor of electricity and is widely used in electrical wiring and electronic devices due to its affordability and availability.
- Gold: Gold is an excellent conductor, but its high cost restricts its use to specialized applications, such as corrosion-resistant coatings and connectors in high-end electronics.
In summary, metals conduct electricity due to their electron structure and the presence of free electrons within the lattice. The movement of these electrons in response to an electric field generates an electric current, allowing metals to efficiently conduct electricity.