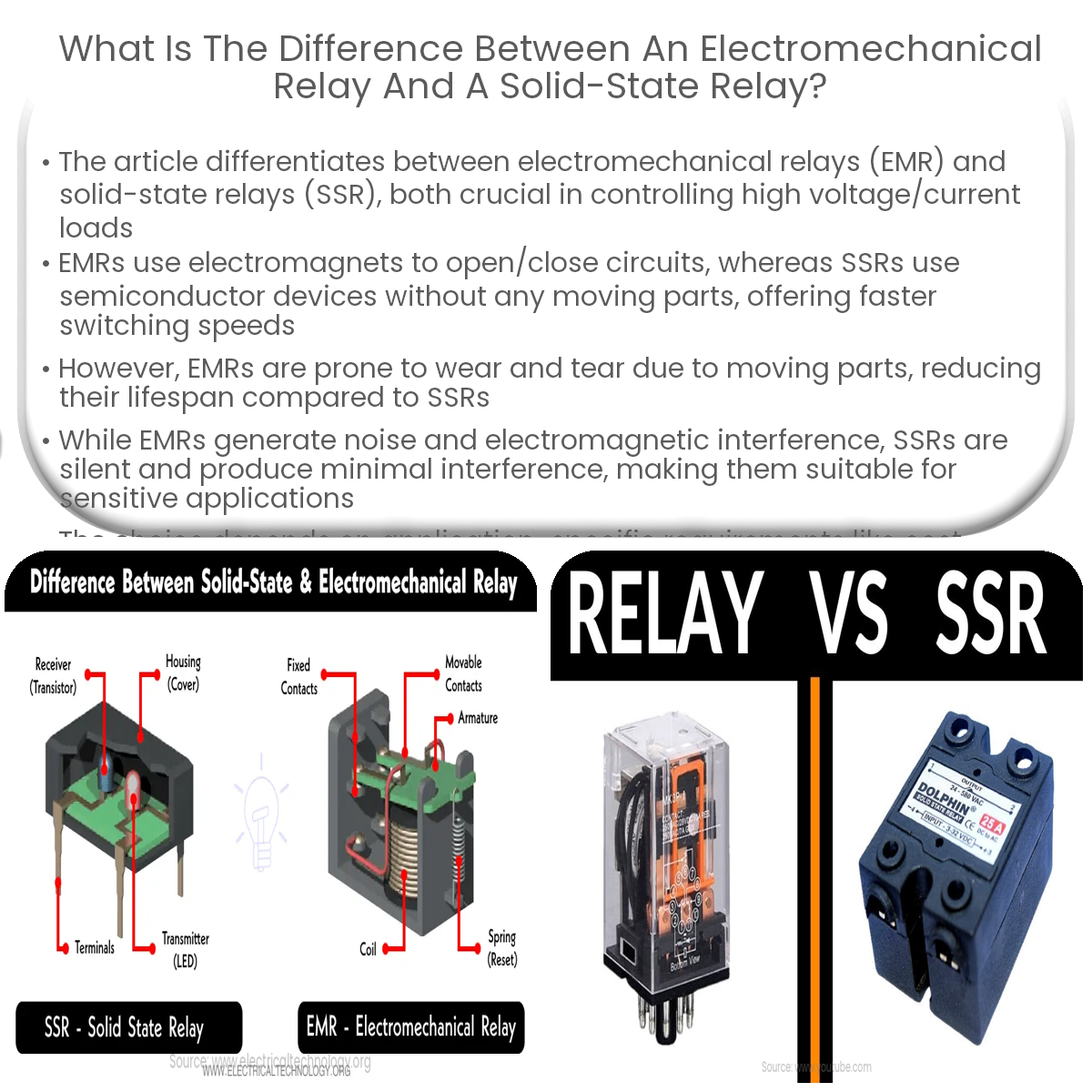
EMRs have moving parts, slower switching, shorter life span, and generate noise. SSRs have no moving parts, faster switching, longer life, and less noise.
Electromechanical Relay vs Solid-State Relay
Relays are essential components in electronic circuits, used to control high voltage or high current loads with a low voltage or low current signal. There are two main types of relays: electromechanical relays (EMR) and solid-state relays (SSR). In this article, we will discuss the key differences between these two types of relays.
Construction
An electromechanical relay is a switch that uses an electromagnet to open or close a circuit. When a current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that attracts a metal armature, causing it to move and change the state of the contacts.
A solid-state relay, on the other hand, is an electronic switch with no moving parts. It uses semiconductor devices, such as thyristors, triacs, or MOSFETs, to control the flow of current.
Switching Speed
Electromechanical relays have relatively slow switching speeds, typically ranging from milliseconds to tens of milliseconds, due to the physical movement of the contacts.
Solid-state relays have much faster switching speeds, typically in the microsecond to millisecond range, because they use electronic components instead of mechanical parts.
Life Span and Reliability
As electromechanical relays have moving parts, they are subject to wear and tear, which can lead to contact degradation and eventually, failure. Their life span is generally rated in the range of millions of operations.
Since solid-state relays have no moving parts, they are less susceptible to wear and tear. Their life span is typically much longer, often exceeding billions of operations, depending on the specific application and conditions.
Noise and EMI
Electromechanical relays generate audible clicking sounds when switching and can also produce electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to the physical movement of the contacts.
Solid-state relays are virtually silent during operation and produce little to no EMI, making them more suitable for sensitive applications and environments where noise or interference is a concern.
Conclusion
In summary, electromechanical and solid-state relays have distinct differences in construction, switching speed, life span, and noise generation. The choice between these two types of relays will depend on the specific requirements and constraints of the application, such as cost, switching speed, life span, and noise tolerance.