Fuses are one-time-use devices that melt when overloaded, while circuit breakers are reusable and trip to interrupt excess current flow.
What is the Difference Between a Fuse and a Circuit Breaker?
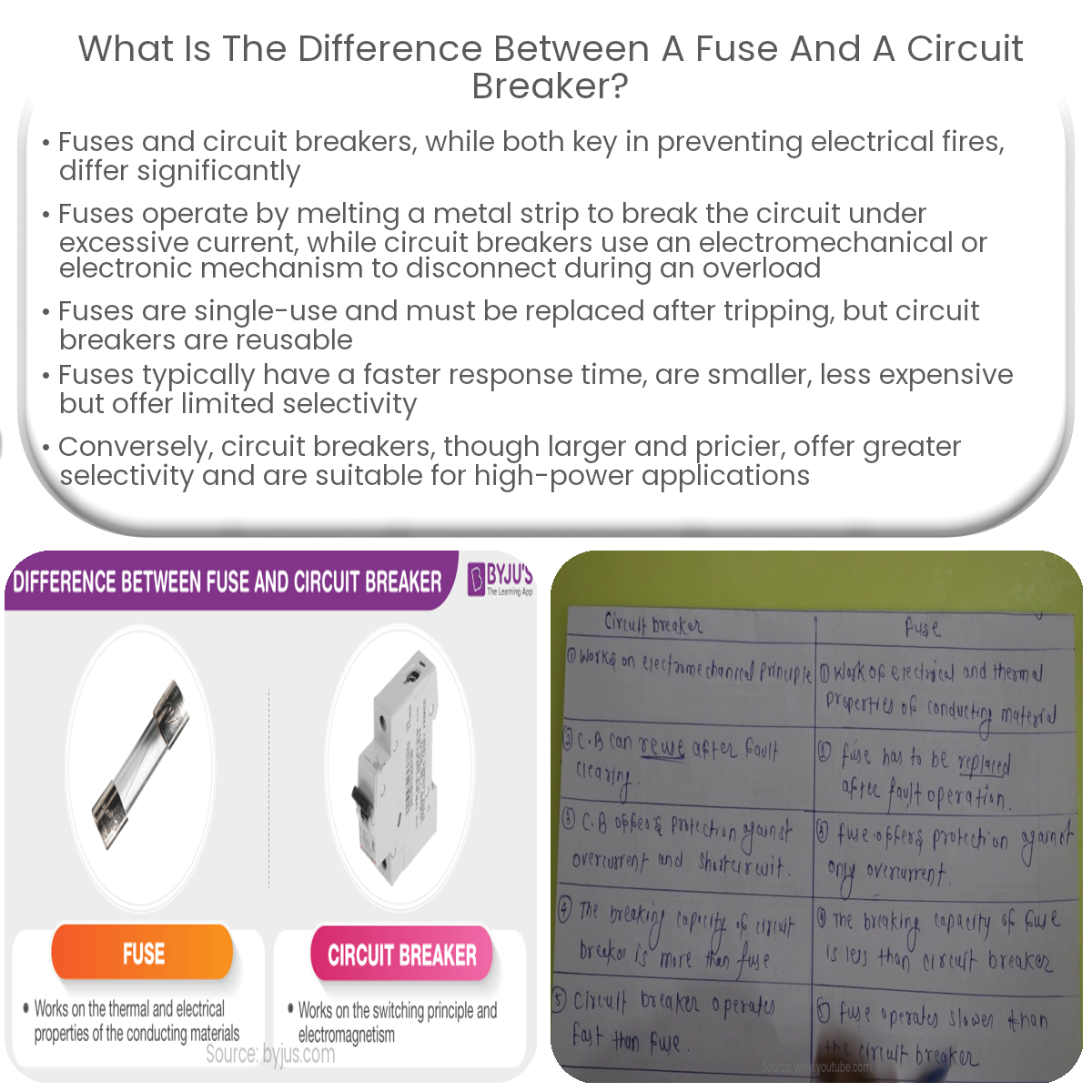
Fuses and circuit breakers are both essential electrical safety devices designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by excess current. However, they operate on different principles and have distinct advantages and disadvantages. This article will discuss the primary differences between fuses and circuit breakers.
How Fuses Work
A fuse is a simple, one-time-use device that contains a thin wire or metal strip called the fusible element. When the current in the circuit exceeds the fuse’s rated capacity, the excess heat generated causes the fusible element to melt, thereby breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. Once a fuse has blown, it must be replaced with a new one to restore power to the circuit.
How Circuit Breakers Work
A circuit breaker is a reusable device that automatically interrupts the flow of electricity when it detects a fault, such as an overload, short circuit, or ground fault. Circuit breakers come in various types, including thermal, magnetic, and thermal-magnetic. When the current in the circuit exceeds the breaker’s rated capacity, the breaker trips and disconnects the power supply to the affected circuit. To restore power, the issue causing the fault must be resolved, and the circuit breaker can be manually reset to the ‘ON’ position.
Key Differences Between Fuses and Circuit Breakers
- Reset vs. Replacement: Circuit breakers are reusable and can be reset after tripping, while fuses must be replaced once they have blown.
- Response Time: Fuses generally respond faster to overcurrent situations than circuit breakers, providing better protection for sensitive electronic devices.
- Cost: Fuses are generally less expensive than circuit breakers but need to be replaced after each fault, potentially leading to higher long-term costs.
- Size: Circuit breakers are usually larger than fuses, making them less suitable for some space-constrained applications.
- Indication: Circuit breakers provide a clear visual indication of the tripped state, while it may not be as obvious when a fuse has blown.
Choosing Between Fuses and Circuit Breakers
The choice between fuses and circuit breakers depends on the specific application and requirements. Fuses may be more suitable for sensitive electronics due to their faster response time, while circuit breakers are often preferred for their reusability and convenience in residential and commercial settings.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between fuses and circuit breakers is essential for selecting the appropriate electrical safety device for your needs. By considering factors such as resetability, response time, cost, and size, you can make an informed decision that will help protect your electrical system and ensure a safe operating environment.