The capacitance of a cylindrical capacitor depends on the dielectric material, dimensions, and spacing between its conductors, affecting its performance.
Capacitance of a Cylindrical Capacitor
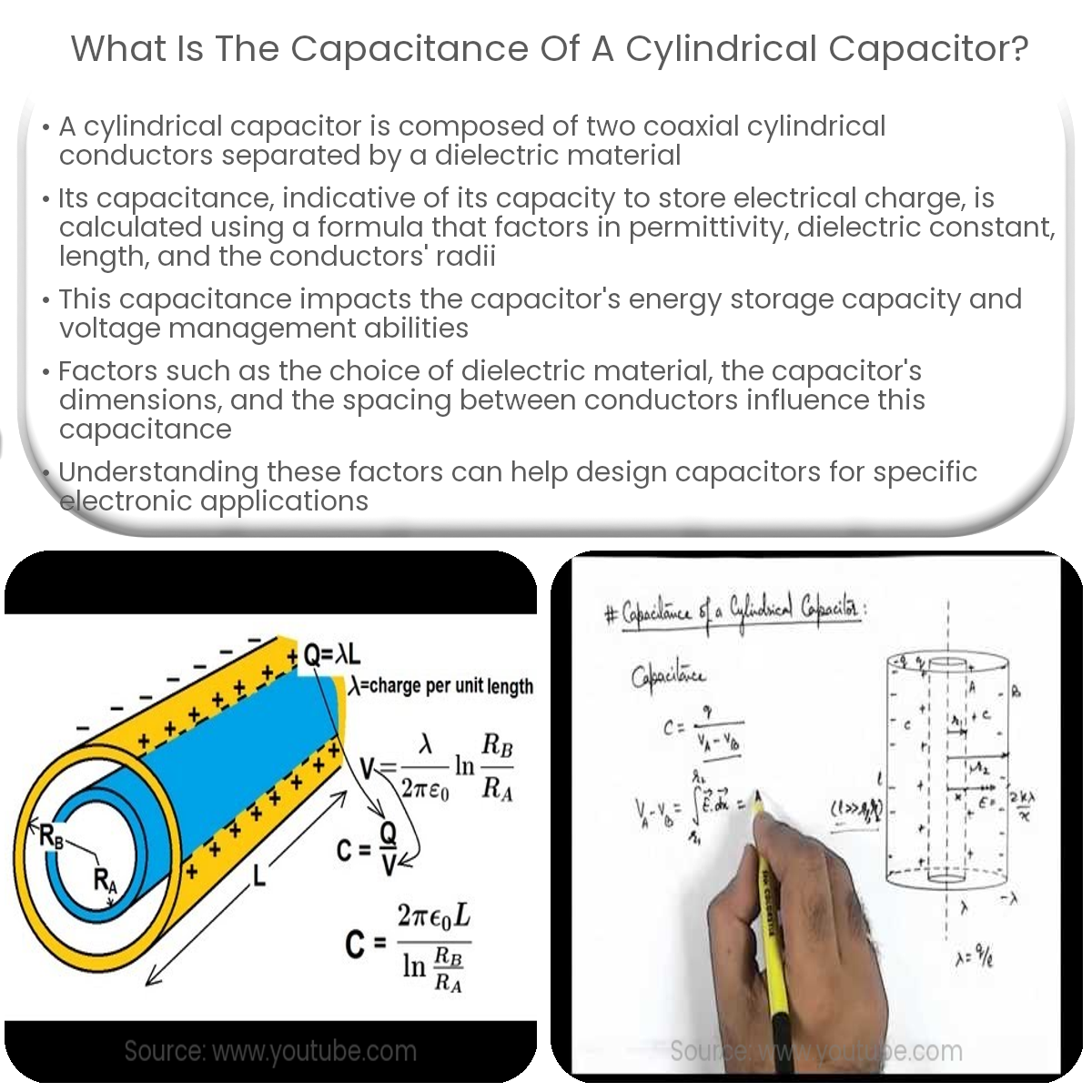
A cylindrical capacitor is a type of capacitor consisting of two coaxial cylindrical conductors separated by a dielectric material. The capacitance of a capacitor is a measure of its ability to store electrical charge, and it plays a crucial role in determining the performance of electronic circuits. This article explains the capacitance of a cylindrical capacitor, its significance, and the factors affecting it.
Calculating the Capacitance
The capacitance (C) of a cylindrical capacitor can be calculated using the following formula:
C = (2 * π * ε0 * εr * L) / ln(b / a)
Where:
- C is the capacitance in farads (F)
- ε0 is the vacuum permittivity (8.854 x 10-12 F/m)
- εr is the relative permittivity (dielectric constant) of the material between the conductors
- L is the length of the cylindrical capacitor in meters (m)
- a is the inner radius of the outer conductor in meters (m)
- b is the outer radius of the inner conductor in meters (m)
- ln denotes the natural logarithm
Significance of Capacitance
The capacitance of a cylindrical capacitor directly affects its ability to store electrical energy and manage voltage changes in a circuit. A higher capacitance value allows the capacitor to store more energy and respond more effectively to voltage fluctuations, making it suitable for applications like filtering, energy storage, and coupling or decoupling signals.
Factors Affecting Capacitance
Several factors influence the capacitance of a cylindrical capacitor, including:
- Dielectric Material: The choice of dielectric material affects the relative permittivity (εr), which directly impacts the capacitance. Different materials have varying dielectric constants, influencing the capacitor’s performance.
- Dimensions: The length (L) and radii (a and b) of the cylindrical capacitor also determine its capacitance. Longer capacitors or capacitors with smaller radii will have higher capacitance values.
- Spacing: The distance between the inner and outer conductors, represented by the ratio (b / a), affects the capacitance. A smaller spacing will result in higher capacitance.
In conclusion, the capacitance of a cylindrical capacitor depends on the dielectric material, dimensions, and spacing between its conductors. By understanding the factors affecting capacitance, engineers can design cylindrical capacitors with the desired properties for various electronic applications, such as filtering, energy storage, and signal coupling.