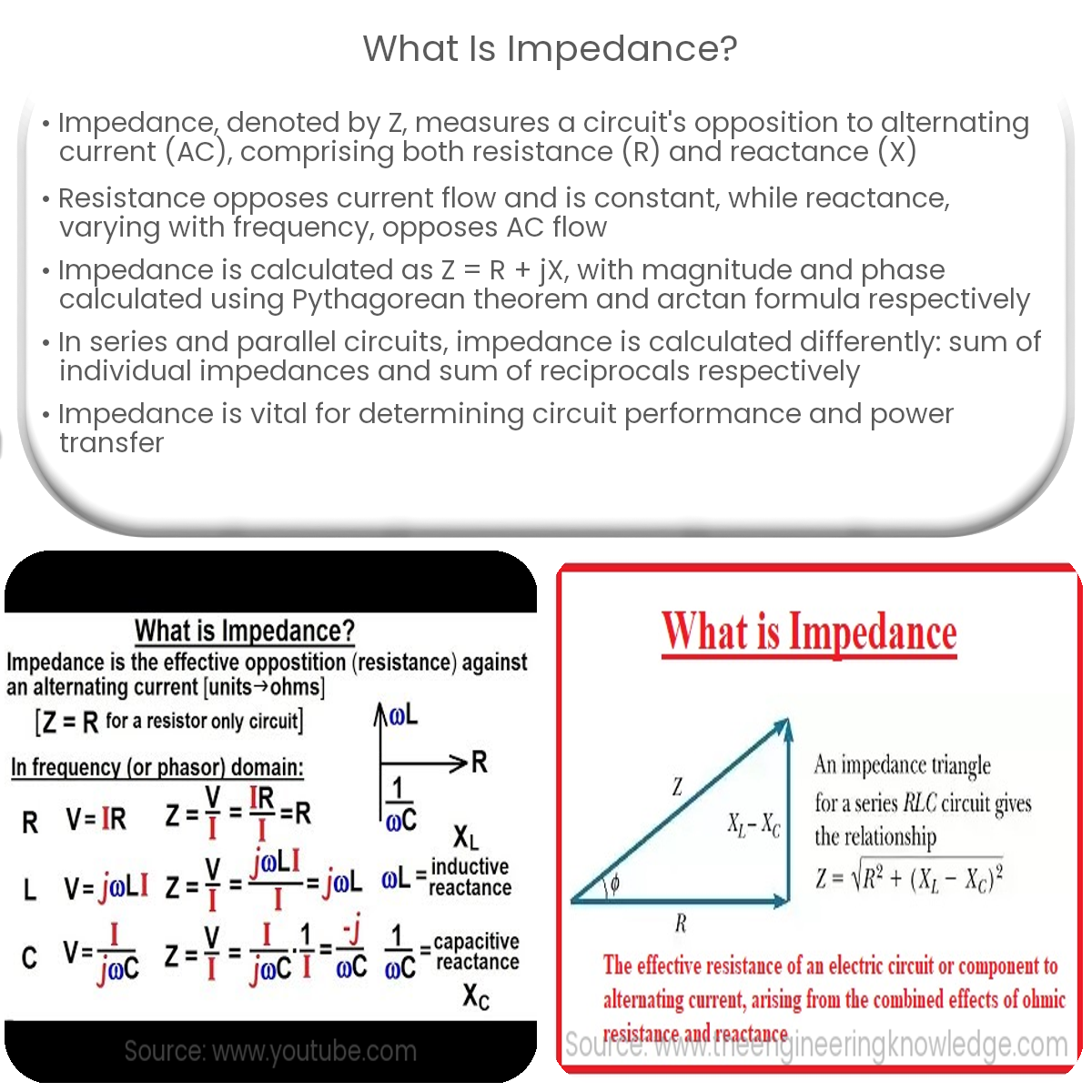
Impedance is a complex value representing the opposition a circuit element presents to the flow of AC or complex voltage, including resistance and reactance.
Understanding Impedance
Impedance is a fundamental concept in electrical and electronic engineering, describing the opposition a circuit element presents to the flow of alternating current (AC) or complex voltage. It is a complex quantity that encompasses both resistance and reactance, providing a comprehensive measure of how a circuit element impacts the AC signal. This article offers a deeper understanding of impedance and its significance.
Components of Impedance
Impedance (Z) is a complex value composed of two parts: resistance (R) and reactance (X). Resistance represents the opposition to current flow in a conductor, while reactance describes the opposition due to capacitive or inductive effects in a circuit. Reactance can be further divided into capacitive reactance (XC) and inductive reactance (XL).
Impedance in Resistors, Capacitors, and Inductors
Impedance is relevant to all passive components in a circuit, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors. The impedance of these elements is as follows:
- Resistors: In resistors, impedance is equal to the resistance itself (Z = R).
- Capacitors: The impedance of capacitors is inversely proportional to the capacitance value and the frequency of the AC signal (Z = 1/jωC), where ω is the angular frequency and C is the capacitance.
- Inductors: For inductors, impedance is directly proportional to the inductance value and the frequency of the AC signal (Z = jωL), where ω is the angular frequency and L is the inductance.
Impedance in AC Circuits
In AC circuits, the impedance plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of the circuit, including the voltage and current relationships. The impedance affects the amplitude and phase of the voltage and current waveforms, with the phase difference between voltage and current being the phase angle of the impedance.
Impedance Matching
Impedance matching is an essential concept in electronics, particularly in communication systems and power transfer applications. The goal of impedance matching is to minimize signal reflection and maximize power transfer between circuit elements, such as between a source and a load. This is achieved by making the input impedance of the load equal to the output impedance of the source.
Conclusion
Impedance is a vital concept in understanding the behavior of electrical circuits, particularly AC circuits. By considering the impedance of various circuit elements, engineers can design circuits that perform optimally and efficiently transfer power between components. Knowledge of impedance is crucial for various applications, such as communication systems and power electronics.