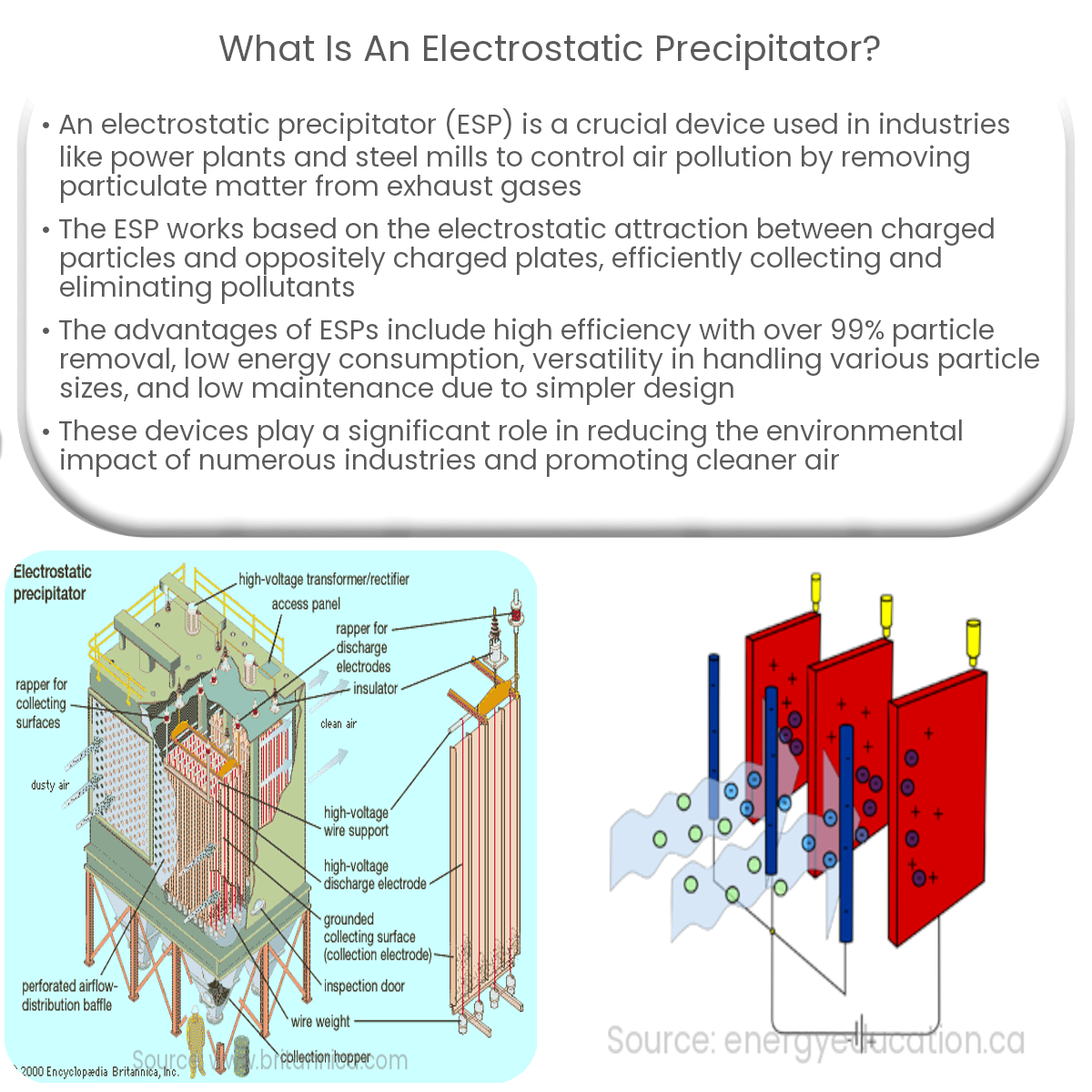
An electrostatic precipitator removes particles from exhaust gases using electrostatic attraction, significantly reducing air pollution in industries.
Introduction to Electrostatic Precipitators
An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is a device commonly used to remove particles from industrial exhaust gases, especially in power plants, cement industries, and steel mills. The main goal of an ESP is to reduce air pollution by collecting and eliminating particulate matter, including dust, smoke, and other fine particles suspended in the air.
Working Principle
The fundamental principle behind the operation of an ESP is the electrostatic attraction between charged particles and oppositely charged electrodes. The device consists of a series of parallel plates, where one set is positively charged (anode) and the other is negatively charged (cathode). As the polluted air passes through the ESP, the particles become ionized by the high-voltage electric field created between the plates.
Once the particles are charged, they are attracted to the oppositely charged plates and adhere to their surface. This process effectively removes the particles from the air, allowing clean air to flow through the system. The collected particles are then periodically removed from the plates, typically by a mechanical rapping system or by washing the plates with water.
Advantages and Applications
There are several advantages of using an ESP in industrial processes:
Electrostatic precipitators find applications in a wide range of industries, including power generation, cement production, steel manufacturing, and waste incineration. They also play a crucial role in controlling emissions from diesel engines and other combustion processes.
Conclusion
An electrostatic precipitator is a vital device for controlling air pollution in industrial settings. By leveraging the electrostatic attraction between charged particles and oppositely charged plates, ESPs efficiently remove particulate matter from exhaust gases, significantly reducing the environmental impact of various industries and contributing to cleaner air for all.