A smart grid is an advanced electrical grid that uses innovative technologies to improve efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity distribution.
Introduction to Smart Grids
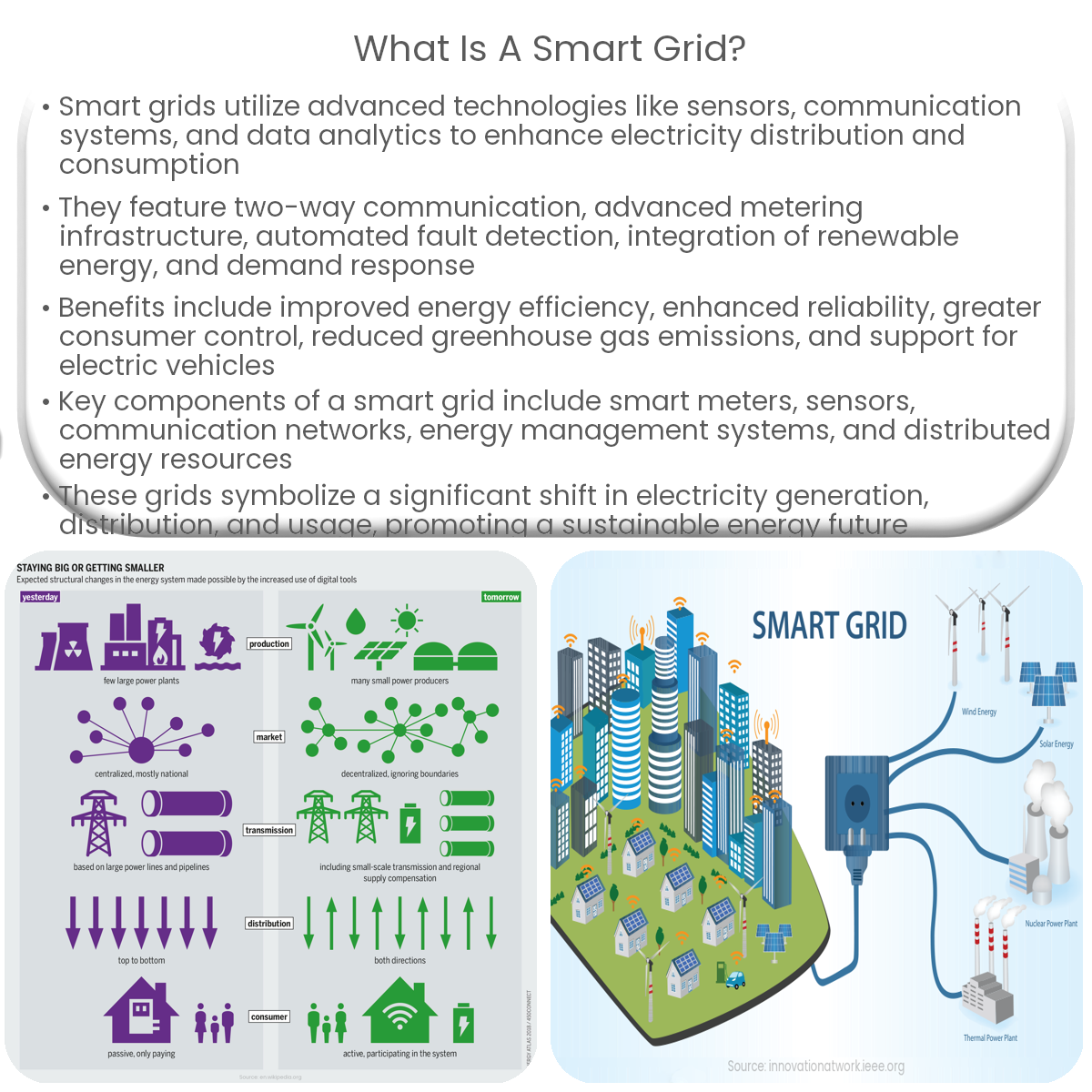
A smart grid is an advanced electrical grid that uses innovative technologies, such as sensors, communication systems, and data analytics, to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity distribution and consumption. This article will discuss the key features, benefits, and components of a smart grid.
Key Features of a Smart Grid
Smart grids incorporate several key features to improve the overall functioning of the electrical grid:
- Two-way communication: Smart grids enable real-time communication between utilities and consumers, allowing for better demand management and grid optimization.
- Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI): AMI includes smart meters that collect detailed energy usage data and transmit it to utilities for monitoring and billing purposes.
- Automated fault detection and isolation: Smart grids can quickly identify and isolate faults in the grid, reducing outage times and improving service reliability.
- Integration of renewable energy sources: Smart grids can seamlessly integrate various renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to diversify the energy mix and reduce carbon emissions.
- Demand response: Smart grids facilitate demand response programs that incentivize consumers to reduce energy consumption during peak periods or shift their usage to off-peak hours.
Benefits of a Smart Grid
Smart grids offer numerous benefits for utilities, consumers, and the environment:
- Improved energy efficiency: Smart grids help optimize energy usage, minimize losses, and reduce overall energy consumption, leading to cost savings for consumers and utilities.
- Enhanced reliability: By rapidly detecting and resolving issues, smart grids can minimize power outages and improve service quality for consumers.
- Greater consumer control: With access to real-time energy usage data, consumers can make informed decisions about their energy consumption, potentially lowering their energy bills.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: By integrating renewable energy sources and promoting energy efficiency, smart grids can significantly reduce carbon emissions and contribute to a cleaner environment.
- Support for electric vehicles (EVs): Smart grids can accommodate the growing number of EVs and their charging infrastructure, encouraging further adoption of cleaner transportation options.
Components of a Smart Grid
A smart grid consists of various interconnected components that work together to optimize the electrical grid:
- Smart meters: Collect and transmit energy usage data to utilities and consumers.
- Sensors and monitoring equipment: Monitor grid performance and detect issues in real-time.
- Communication networks: Facilitate data exchange between grid components, utilities, and consumers.
- Energy management systems: Analyze and manage energy usage to optimize grid performance.
- Distributed energy resources (DERs): Include renewable energy sources, energy storage devices, and demand response programs that contribute to grid flexibility and resilience.
Conclusion
Smart grids represent a significant evolution in the way electricity is generated, distributed, and consumed. By incorporating advanced technologies and promoting clean energy, smart grids can create a more sustainable, efficient, and reliable energy future.