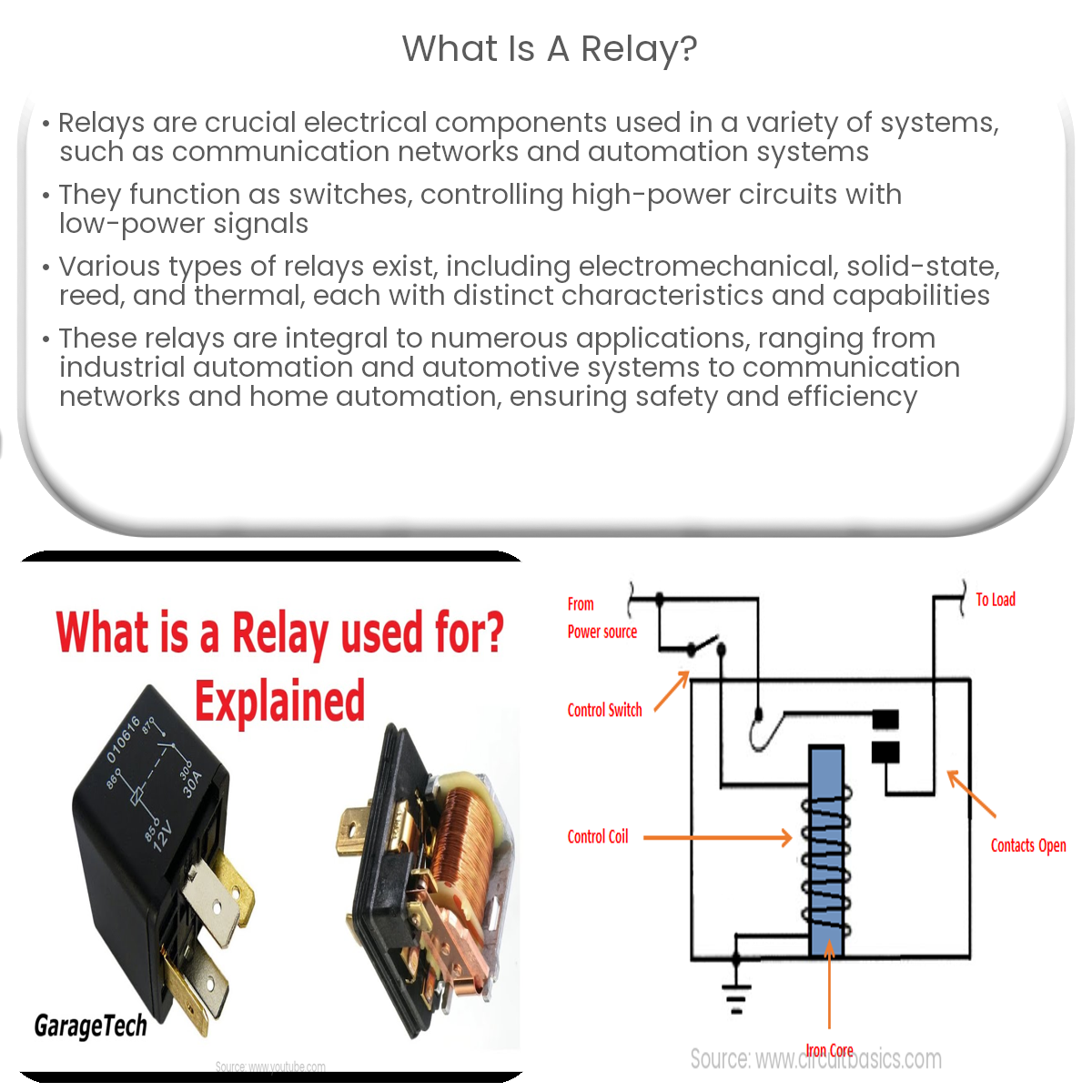
A relay is an electrical component that functions as a switch, controlling high-power circuits using low-power signals in various systems.
What is a Relay?
A relay is an essential electrical component in various systems, such as communication networks, control circuits, and automation systems. It functions as a switch, allowing users to control a high-power circuit using a low-power signal. This article delves into the workings, types, and applications of relays.
How Does a Relay Work?
Relays comprise an electromagnet, a set of contacts, and a spring. When a low-power electrical signal flows through the electromagnet’s coil, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field attracts the movable contact, causing it to touch the stationary contact and complete the high-power circuit. When the low-power signal is removed, the magnetic field collapses, and the spring returns the movable contact to its original position, breaking the high-power circuit.
Types of Relays
- Electromechanical Relays: These are the most common type of relay, consisting of an electromagnet, contacts, and a spring. They can handle high currents and voltages but have limited switching speeds.
- Solid-State Relays: These relays have no moving parts, using electronic components such as transistors or thyristors to control the high-power circuit. They have faster switching speeds and longer lifespans but may have limited current handling capabilities.
- Reed Relays: These relays contain magnetic reed switches that are actuated by an external magnetic field. They are compact, fast, and reliable but may have lower current handling capabilities.
- Thermal Relays: These relays respond to temperature changes, typically employing a bimetallic strip or thermistor. They are often used for thermal protection in motors and other electrical devices.
Applications of Relays
- Industrial Automation: Relays are used to control motors, lights, and other high-power devices in various industries, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
- Automotive Systems: They are utilized in vehicles for controlling headlights, wipers, air conditioning, and other electrical systems.
- Communication Networks: Relays are an integral part of telecommunication systems, allowing the routing and control of signals between devices.
- Home Automation: In smart homes, relays are employed to control lighting, HVAC systems, and security devices, contributing to energy efficiency and convenience.
In conclusion, relays are vital electrical components that enable the control of high-power circuits using low-power signals. They are found in numerous applications, including industrial automation, automotive systems, communication networks, and home automation, ensuring safe and efficient operations.