A photoresistor is an electronic component that changes its resistance based on the amount of light it’s exposed to, often used in light sensing.
Introduction to Photoresistors
A photoresistor, also known as a light-dependent resistor (LDR), is an electronic component that varies its resistance based on the amount of light it is exposed to. In essence, it is a light-sensitive resistor, and its primary application is in sensing and responding to varying light conditions.
How Photoresistors Work
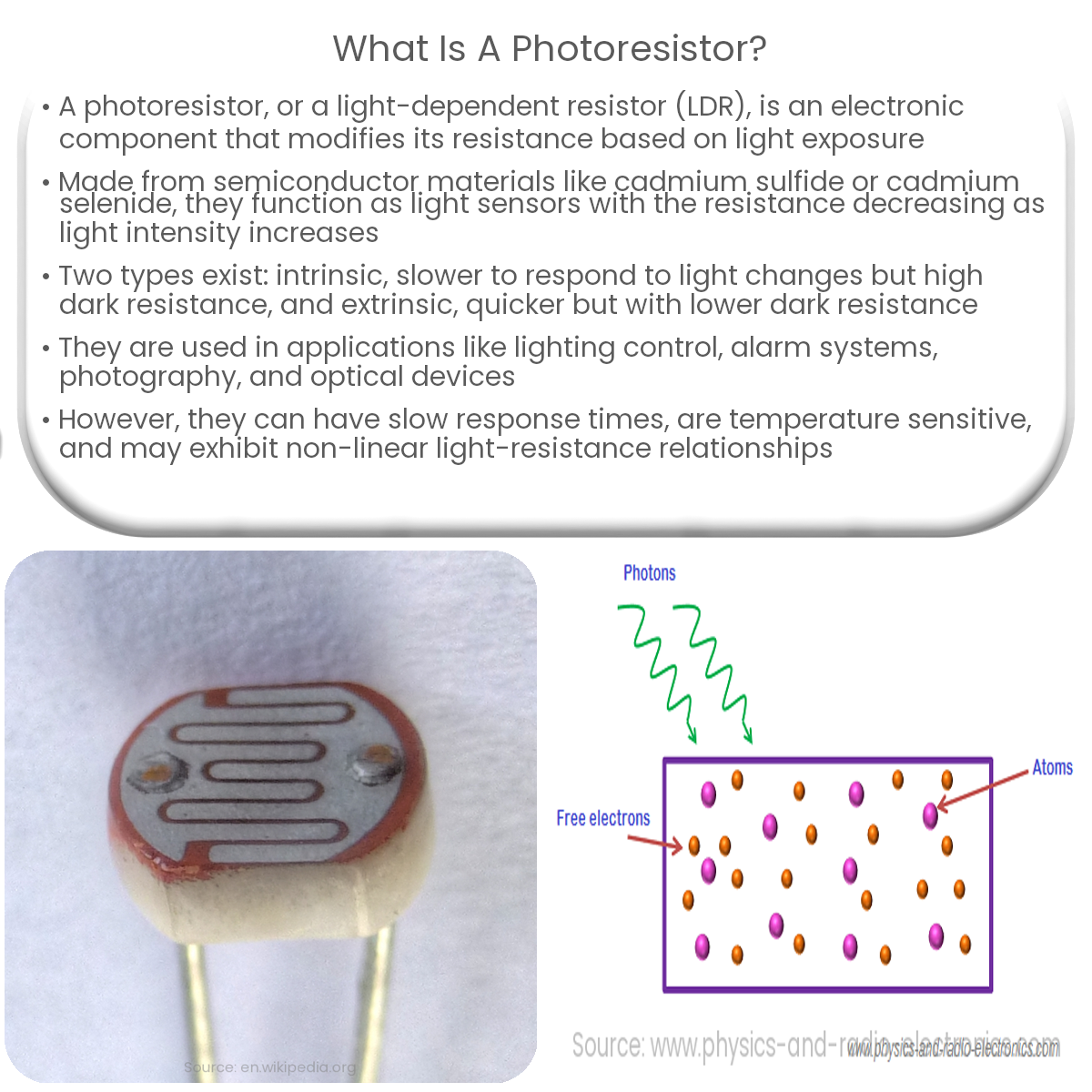
Photoresistors are made of semiconductor materials, such as cadmium sulfide (CdS) or cadmium selenide (CdSe). When these materials are exposed to light, photons with sufficient energy cause electrons to jump from the valence band to the conduction band. This increases the number of free electrons available for conduction, thus reducing the resistance of the material.
Conversely, when the intensity of light decreases, fewer electrons are available for conduction, resulting in an increase in resistance. This property allows photoresistors to function as light sensors in various applications.
Types of Photoresistors
There are two primary types of photoresistors:
- Intrinsic photoresistors: These are made from pure semiconductor materials and have a high resistance in the dark. They are typically slower to respond to changes in light intensity.
- Extrinsic photoresistors: These are made by adding impurities to the semiconductor material to create additional energy levels within the bandgap. This results in faster response times and a lower dark resistance.
Applications of Photoresistors
Photoresistors are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Lighting control systems: Photoresistors are often used to automatically switch on or off lights based on the ambient light level.
- Alarm systems: By detecting changes in light levels, photoresistors can be used as part of intrusion detection systems.
- Photography: In cameras, photoresistors help determine the correct exposure settings based on the available light.
- Optical devices: They can be used in various devices, such as optocouplers, to enable the transfer of electrical signals through light.
Limitations and Considerations
While photoresistors offer several benefits, they also have some limitations:
- Response time: Photoresistors can have relatively slow response times, which may not be suitable for certain high-speed applications.
- Temperature sensitivity: Changes in temperature can affect the resistance of a photoresistor, leading to variations in its performance.
- Non-linearity: The relationship between light intensity and resistance is not always linear, which may require additional calibration or processing in some applications.