A Hall effect sensor is a device that detects magnetic fields and produces an output voltage proportional to the field strength, used in various applications.
Introduction to Hall Effect Sensors
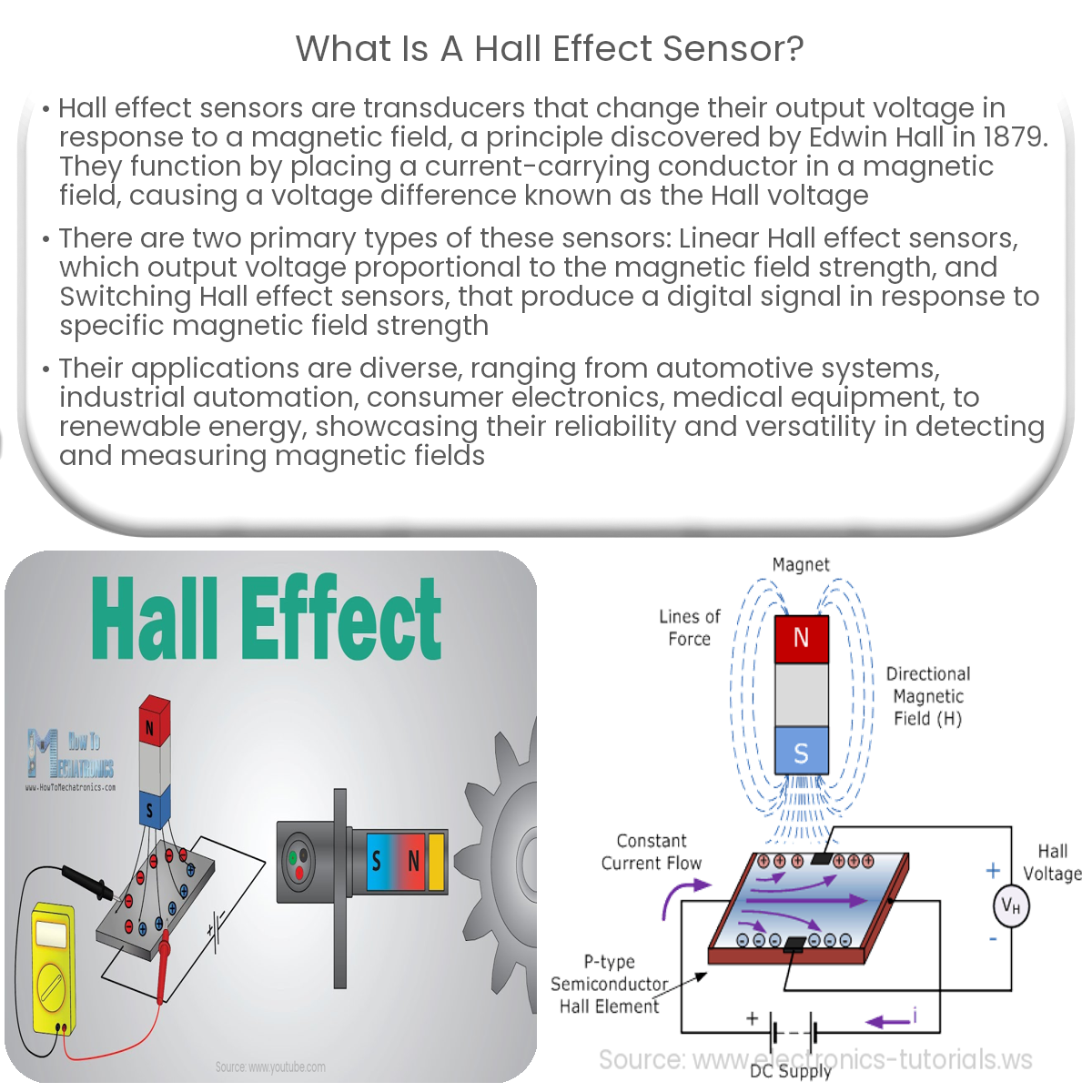
A Hall effect sensor is a transducer that detects the presence and magnitude of magnetic fields. Named after Edwin Hall, who discovered the Hall effect in 1879, these sensors produce an output voltage proportional to the magnetic field strength, making them ideal for various applications.
Working Principle of Hall Effect Sensors
Hall effect sensors function based on the Hall effect, a phenomenon that occurs when a current-carrying conductor is subjected to a magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of current flow. The magnetic field causes a deflection of the charge carriers (electrons or holes), resulting in a voltage difference across the conductor. This voltage, known as the Hall voltage, is directly proportional to the magnetic field strength and current.
Types of Hall Effect Sensors
There are two primary types of Hall effect sensors:
Applications of Hall Effect Sensors
Hall effect sensors are versatile and find applications in various industries, including:
In summary, Hall effect sensors are essential components in many modern devices, providing accurate magnetic field sensing for a wide range of applications.