A dielectric is an insulating material that doesn’t conduct electric charge but supports an electric field. It is used in capacitors and insulators.
What is a Dielectric?
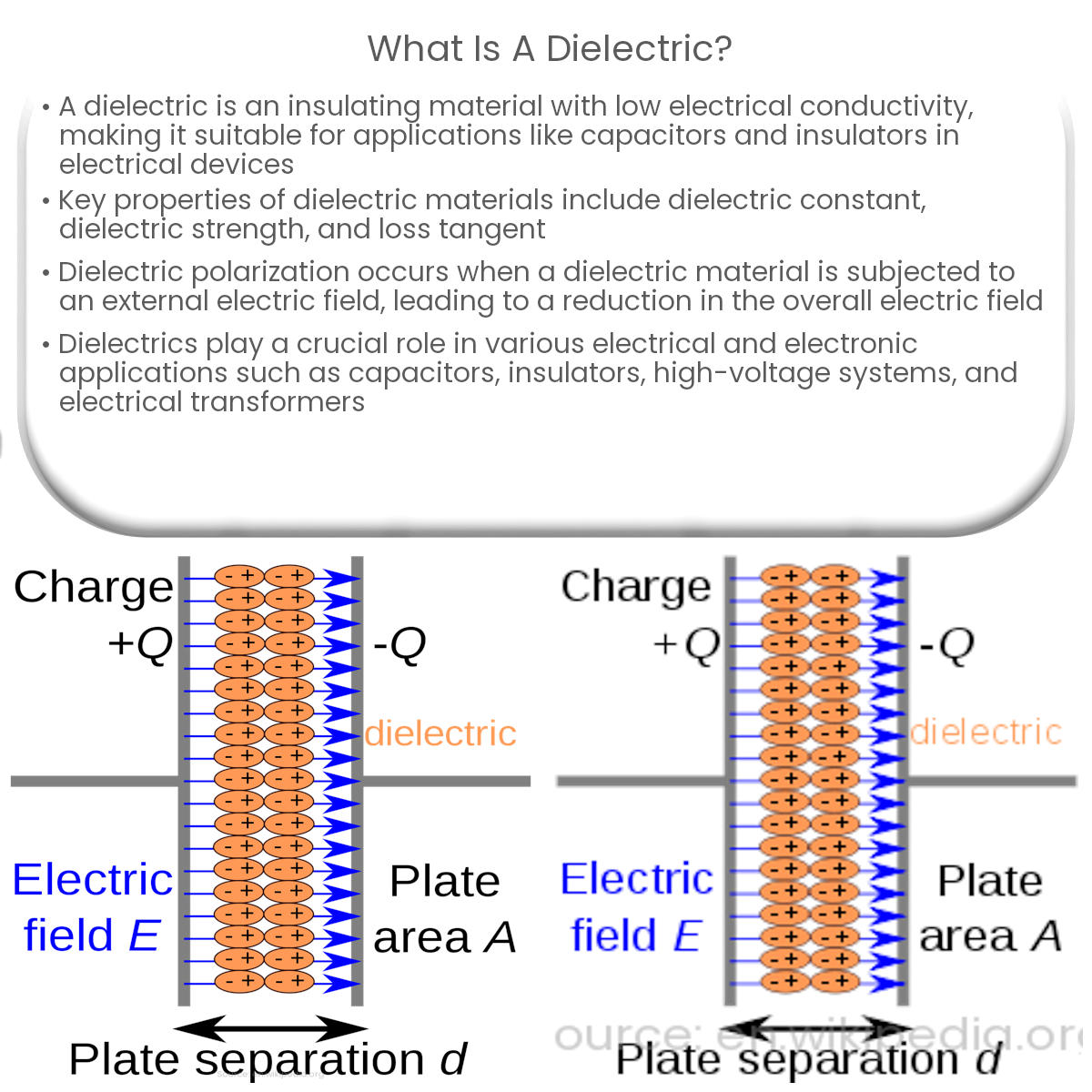
A dielectric is an insulating material that does not allow the flow of electric charge, but can support an electric field. These materials have low electrical conductivity and high resistance to electric current, making them suitable for various applications, such as capacitors and insulators in electrical and electronic devices.
Dielectric Properties
Dielectric materials exhibit several important properties, including:
Dielectric Polarization
When a dielectric material is subjected to an external electric field, its molecules or atoms become polarized, creating electric dipoles. These dipoles align themselves with the external electric field, resulting in a net internal electric field that opposes the external field. This phenomenon is known as dielectric polarization and leads to the reduction of the overall electric field within the material.
Applications of Dielectrics
Dielectrics have numerous applications in electrical and electronic systems, such as:
In summary, dielectrics are insulating materials that play a crucial role in various electrical and electronic applications. They exhibit unique properties, such as dielectric constant, dielectric strength, and loss tangent, which make them indispensable components in capacitors, insulators, and other devices.