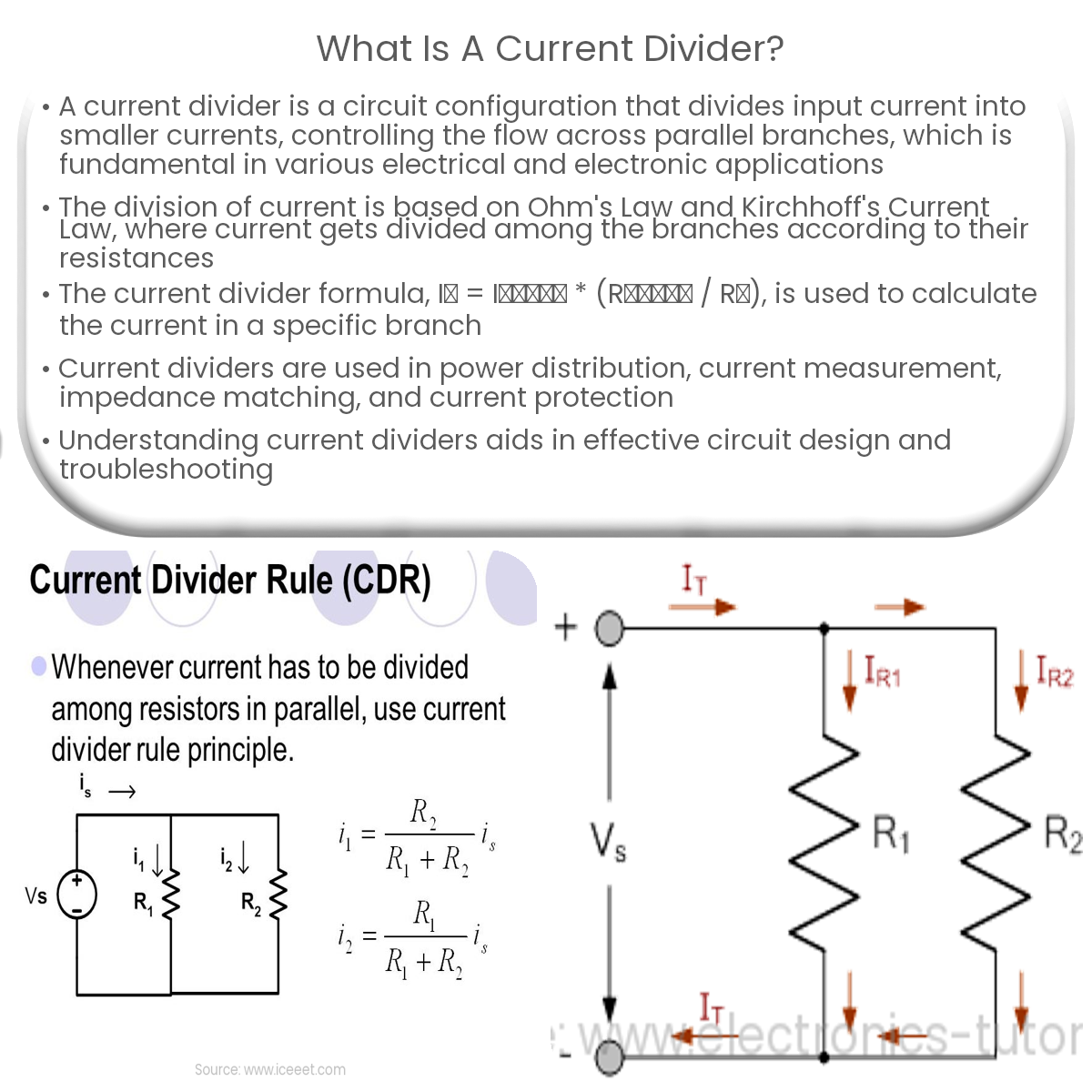
A current divider is a circuit that divides input current among parallel branches based on their resistances, controlling current flow in components.
Introduction to Current Dividers
A current divider is a simple circuit configuration that divides the input current into smaller currents, distributing them across parallel branches. This concept is essential in various electrical and electronic applications, as it enables control and management of current flow through different components or devices.
Working Principle
The working principle of a current divider relies on Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Current Law. In a parallel circuit, the voltage across all components remains the same, while the current gets divided among the branches based on their resistances. The sum of the currents in all branches equals the total input current.
Current Divider Formula
To calculate the current flowing through a specific branch in a parallel circuit, the current divider formula is used:
In = Itotal * (Rtotal / Rn)
where In is the current in the nth branch, Itotal is the total input current, Rtotal is the total resistance of the parallel circuit, and Rn is the resistance of the nth branch.
Applications
Current dividers have a wide range of applications in electrical and electronic systems, including:
- Power distribution: In power supply systems, current dividers help distribute the available current among different devices or circuits.
- Current measurement: Current dividers can be used with measuring instruments, such as ammeters, to measure high currents indirectly by measuring the current in a smaller parallel branch.
- Impedance matching: In communication systems, current dividers can help match impedance between the source and load, ensuring maximum power transfer.
- Current protection: By dividing the current across multiple parallel branches, current dividers can protect sensitive components from excessive current.
Conclusion
Current dividers play a crucial role in managing current distribution in electrical and electronic circuits. By understanding the principles behind current dividers, engineers and technicians can design and troubleshoot circuits more effectively, ensuring optimal performance and protection of components.