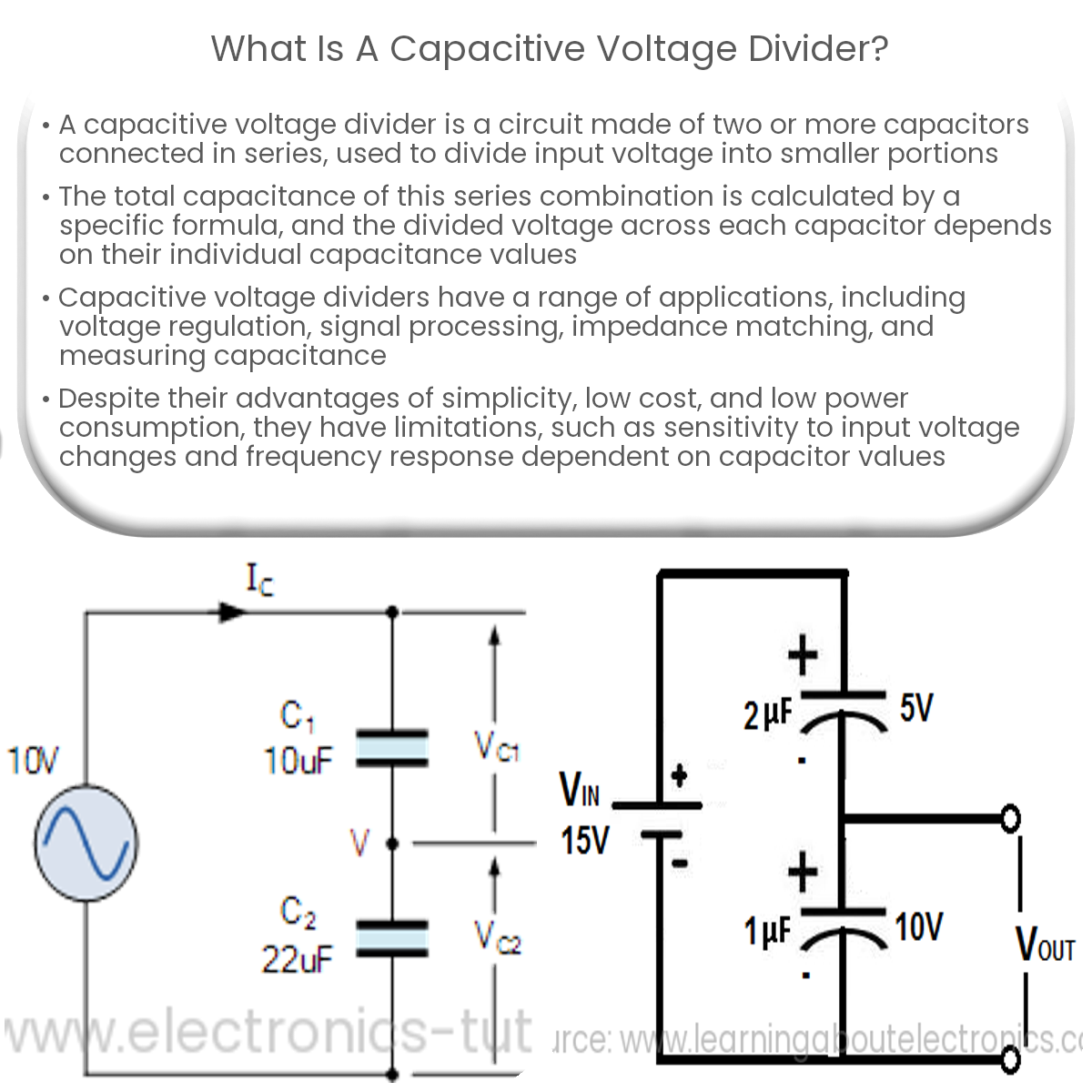
A capacitive voltage divider is a circuit with capacitors connected in series, dividing input voltage into smaller portions based on capacitance values.
Introduction to Capacitive Voltage Dividers
A capacitive voltage divider is a circuit configuration consisting of two or more capacitors connected in series. It is used to divide the input voltage, which is applied across the series-connected capacitors, into smaller voltage portions. These voltage portions are then available at the junctions between the capacitors, and can be utilized for various purposes such as voltage regulation or signal processing.
How Capacitive Voltage Dividers Work
When capacitors are connected in series, the total capacitance (Ctotal) of the series combination is determined by the formula:
1/Ctotal = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + … + 1/Cn
Where C1, C2, …, Cn are the capacitances of the individual capacitors.
In a capacitive voltage divider, the input voltage (Vin) is divided between the capacitors according to their capacitance values. The voltage across each capacitor (V1, V2, …, Vn) can be calculated using the following formula:
Vi = Vin * (Ctotal / Ci)
Where Vi is the voltage across capacitor Ci.
Applications of Capacitive Voltage Dividers
- Voltage regulation: Capacitive voltage dividers are used in voltage regulation circuits to reduce the input voltage to a desired level, which is then used to power other electronic components.
- Signal processing: In signal processing applications, capacitive voltage dividers can be used to filter out high-frequency noise and provide a stable, clean voltage output.
- Impedance matching: Capacitive voltage dividers can be employed in impedance matching circuits to optimize the transfer of energy between different components within an electronic system.
- Measuring capacitance: Capacitive voltage dividers can be used in conjunction with an AC voltage source to measure unknown capacitance values by comparing the output voltage to a known reference capacitor.
Advantages and Limitations
Capacitive voltage dividers offer some advantages, including simplicity, low cost, and low power consumption. However, they have a few limitations:
- The output voltage is sensitive to changes in the input voltage, which can lead to fluctuations in the output if the input is unstable.
- The capacitive voltage divider’s frequency response is dependent on the capacitors’ values, which may affect the accuracy of the output voltage in certain applications.