A band-pass filter is an electronic circuit that allows signals within a specific frequency range to pass while attenuating signals outside that range.
Introduction to Band-Pass Filters
A band-pass filter is an electronic circuit designed to allow signals within a specific frequency range to pass through while attenuating signals outside that range. It combines the characteristics of both high-pass and low-pass filters, making it useful in various applications, such as audio processing, communication systems, and signal processing.
Components and Design
Band-pass filters can be designed using passive or active components. Passive filters are made up of resistors, capacitors, and inductors, while active filters employ operational amplifiers in addition to the passive components. Both types can be realized in different topologies like Butterworth, Chebyshev, or Bessel, each with its unique frequency response characteristics.
Types of Band-Pass Filters
- Narrow Band-Pass Filter: These filters have a narrow frequency range or bandwidth. They are often used in applications that require precise frequency selection, such as in radio frequency (RF) communication.
- Wide Band-Pass Filter: In contrast, wide band-pass filters have a broader frequency range. They are commonly used in audio processing applications to adjust the tone or equalization of a sound signal.
Frequency Response
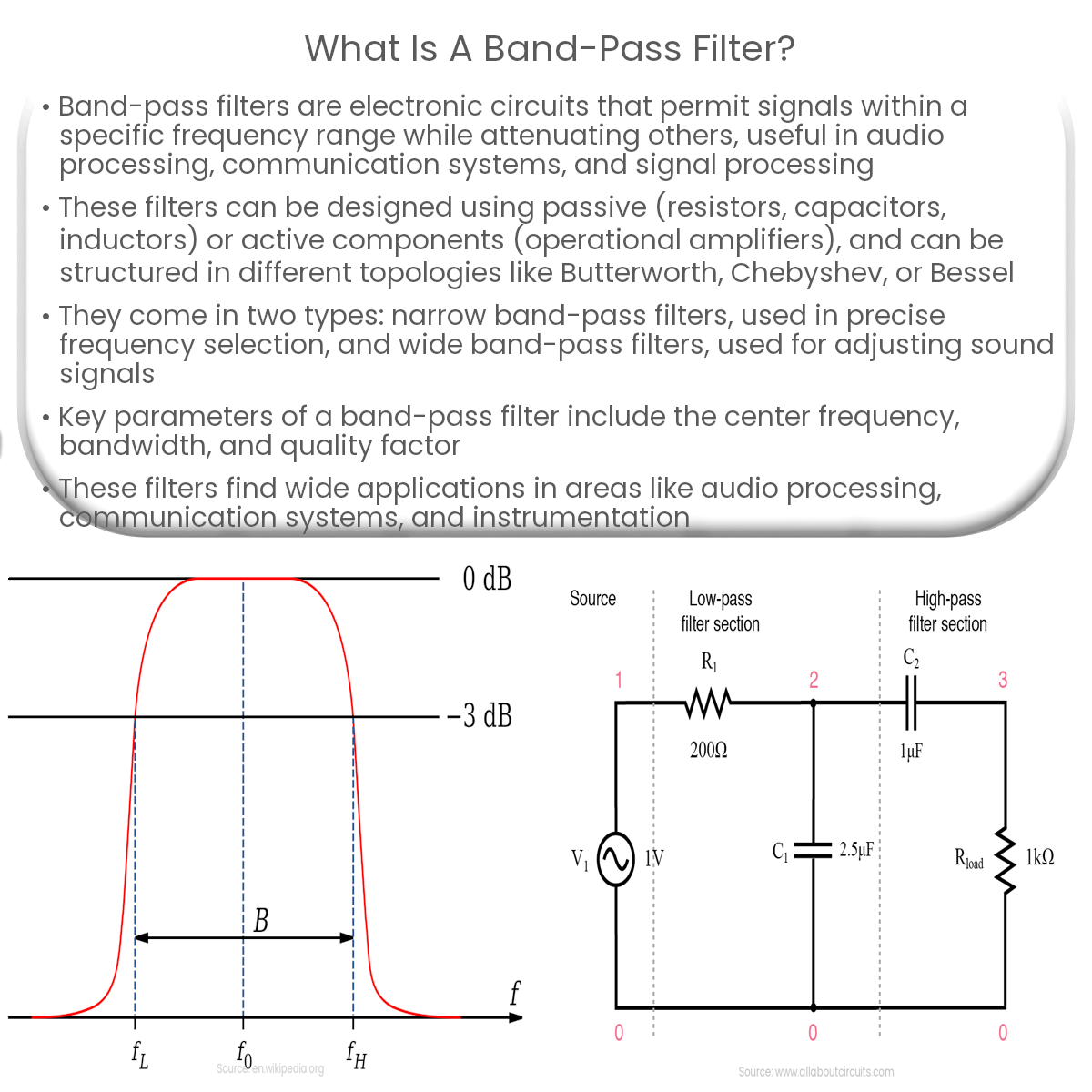
The frequency response of a band-pass filter consists of three key parameters:
- Center Frequency (fc): The frequency at which the filter’s output is at its maximum or, in other words, the midpoint of the passband.
- Bandwidth (BW): The difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies, representing the range of frequencies that pass through the filter with minimal attenuation.
- Quality Factor (Q): The ratio of the center frequency to the bandwidth, which is a measure of the selectivity or sharpness of the filter’s frequency response.
Applications of Band-Pass Filters
Band-pass filters are widely used in various fields, including:
- Audio Processing: They can be utilized in equalizers to adjust specific frequency bands of an audio signal, enhancing or attenuating certain frequencies to improve sound quality.
- Communication Systems: Band-pass filters help in isolating desired signals from a mix of frequencies, allowing for more efficient transmission and reception of data.
- Instrumentation: In test and measurement applications, band-pass filters can isolate specific frequency components from a complex signal, making it easier to analyze and characterize the signal.