Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces between neutral atoms or molecules, influencing properties like adhesion, boiling points, and surface tension.
Van der Waals Forces
Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that exist between neutral molecules or atoms. They play a crucial role in various phenomena, such as molecular adhesion, condensation, and the properties of liquids and solids. These forces arise from temporary fluctuations in electron distribution around atoms and molecules, leading to the formation of instantaneous dipoles that interact with one another.
Types of Van der Waals Forces
There are three main types of Van der Waals forces:
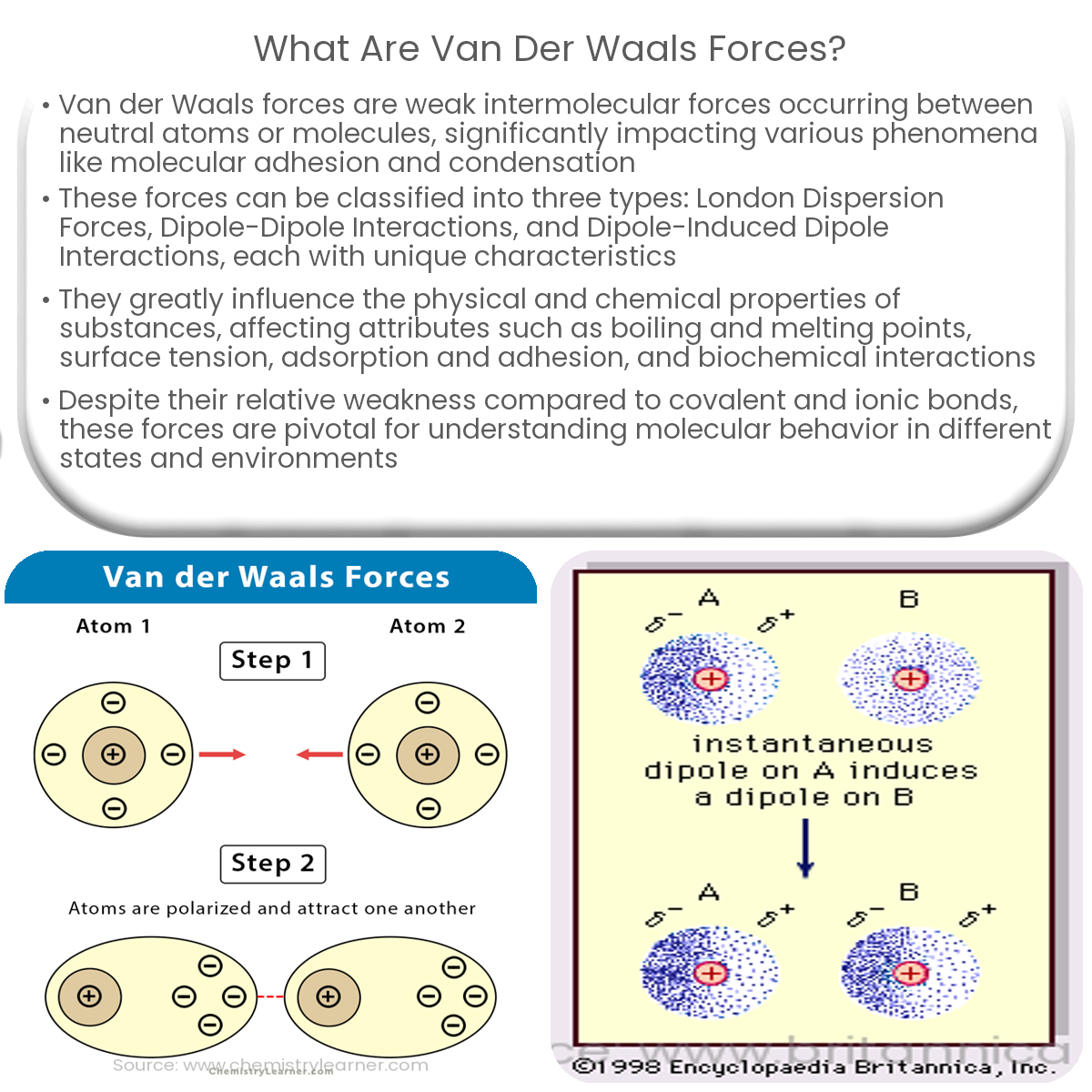
- London Dispersion Forces: Also known as instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces, these are the weakest form of Van der Waals forces. They occur between all atoms and molecules, including nonpolar ones, due to temporary fluctuations in electron distribution around the particles.
- Dipole-Dipole Interactions: These forces arise between polar molecules that possess permanent dipoles. The positively charged end of one molecule is attracted to the negatively charged end of another molecule, resulting in an attractive force.
- Dipole-Induced Dipole Interactions: These forces occur between a polar molecule with a permanent dipole and a nonpolar molecule. The permanent dipole induces a temporary dipole in the nonpolar molecule, leading to an attractive force between the two.
Significance of Van der Waals Forces
Van der Waals forces significantly influence the physical and chemical properties of substances. Some examples include:
- Boiling and Melting Points: Van der Waals forces are responsible for holding molecules together in the liquid and solid states. As these forces increase, boiling and melting points also increase.
- Surface Tension: The cohesion between molecules due to Van der Waals forces contributes to surface tension in liquids.
- Adsorption and Adhesion: Van der Waals forces play a role in the adsorption of gases onto surfaces and the adhesion of molecules to one another or to surfaces.
- Biochemical Interactions: In biological systems, Van der Waals forces contribute to the stability of macromolecular structures such as proteins and nucleic acids.
In conclusion, Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that are crucial in determining various physical and chemical properties of substances. Despite their weakness compared to covalent and ionic bonds, they are vital in understanding and predicting the behavior of molecules in different states and environments.