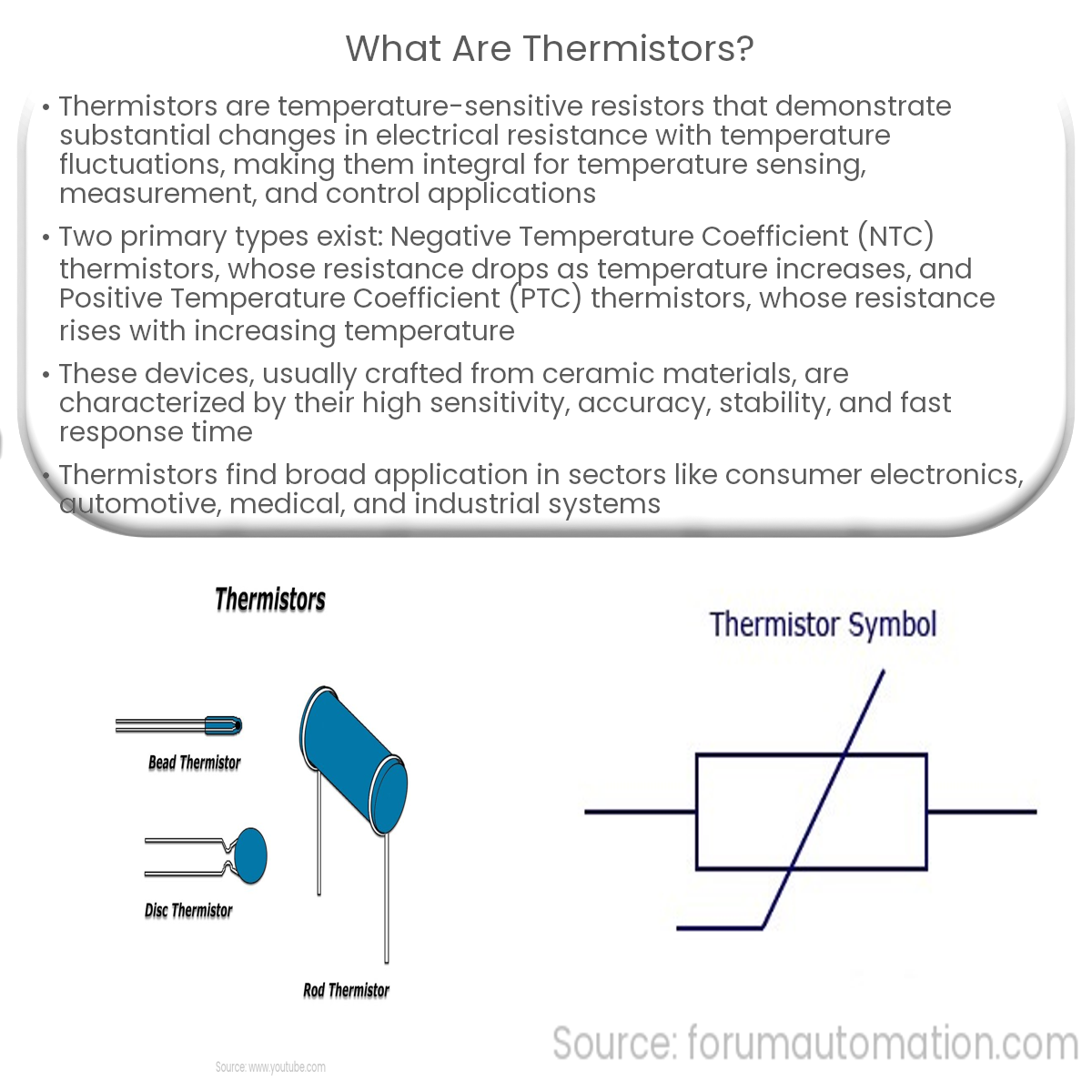
Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors used for sensing, measuring, and controlling temperature, due to their high sensitivity and accuracy.
What are Thermistors?
Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors that exhibit a significant change in electrical resistance with temperature variations. They are widely used in temperature sensing, measurement, and control applications, owing to their high sensitivity and accuracy.
Types of Thermistors
Thermistors are classified into two main types based on their temperature-resistance relationship:
- Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Thermistors: NTC thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient, meaning their resistance decreases as temperature increases. They are commonly used in temperature sensing applications due to their high sensitivity and wide temperature range.
- Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) Thermistors: PTC thermistors have a positive temperature coefficient, meaning their resistance increases as temperature increases. They are often used as self-regulating heating elements or overcurrent protection devices.
Construction
Thermistors are typically constructed using ceramic materials such as metal oxides, which exhibit a predictable change in resistance with temperature. The most common materials used include nickel, manganese, and cobalt oxides. The ceramic material is formed into a small bead, disk, or rod, which is then coated with a protective material like epoxy or glass to ensure stability and durability.
Characteristics
Thermistors have several key characteristics that make them suitable for a variety of temperature-related applications:
- High Sensitivity: Thermistors are highly sensitive to temperature changes, making them ideal for precise temperature measurements.
- Accuracy: They can provide accurate temperature measurements within a specific temperature range, typically within 0.1°C to 1°C.
- Stability: Thermistors exhibit long-term stability, ensuring consistent performance over time.
- Fast Response Time: Due to their small size, thermistors can respond quickly to changes in temperature.
Applications
Thermistors are utilized in a wide range of applications, including:
- Temperature sensing and control in consumer electronics, such as smartphones and computers
- Temperature compensation in electronic circuits
- Automotive applications, including engine temperature monitoring and climate control systems
- Medical devices, such as patient monitoring systems and incubators
- Industrial process control and HVAC systems
Conclusion
Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors that play a crucial role in various temperature measurement and control applications. With their high sensitivity, accuracy, stability, and fast response time, thermistors provide reliable performance in a wide array of industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, medical, and industrial sectors.