Magnetic sensors detect and measure magnetic fields, used in position sensing, current sensing, speed measurement, navigation systems, and more.
Introduction to Magnetic Sensors
Magnetic sensors are devices that detect and measure magnetic fields, playing a vital role in numerous applications. This article discusses various types of magnetic sensors and their applications.
Types of Magnetic Sensors
Applications of Magnetic Sensors
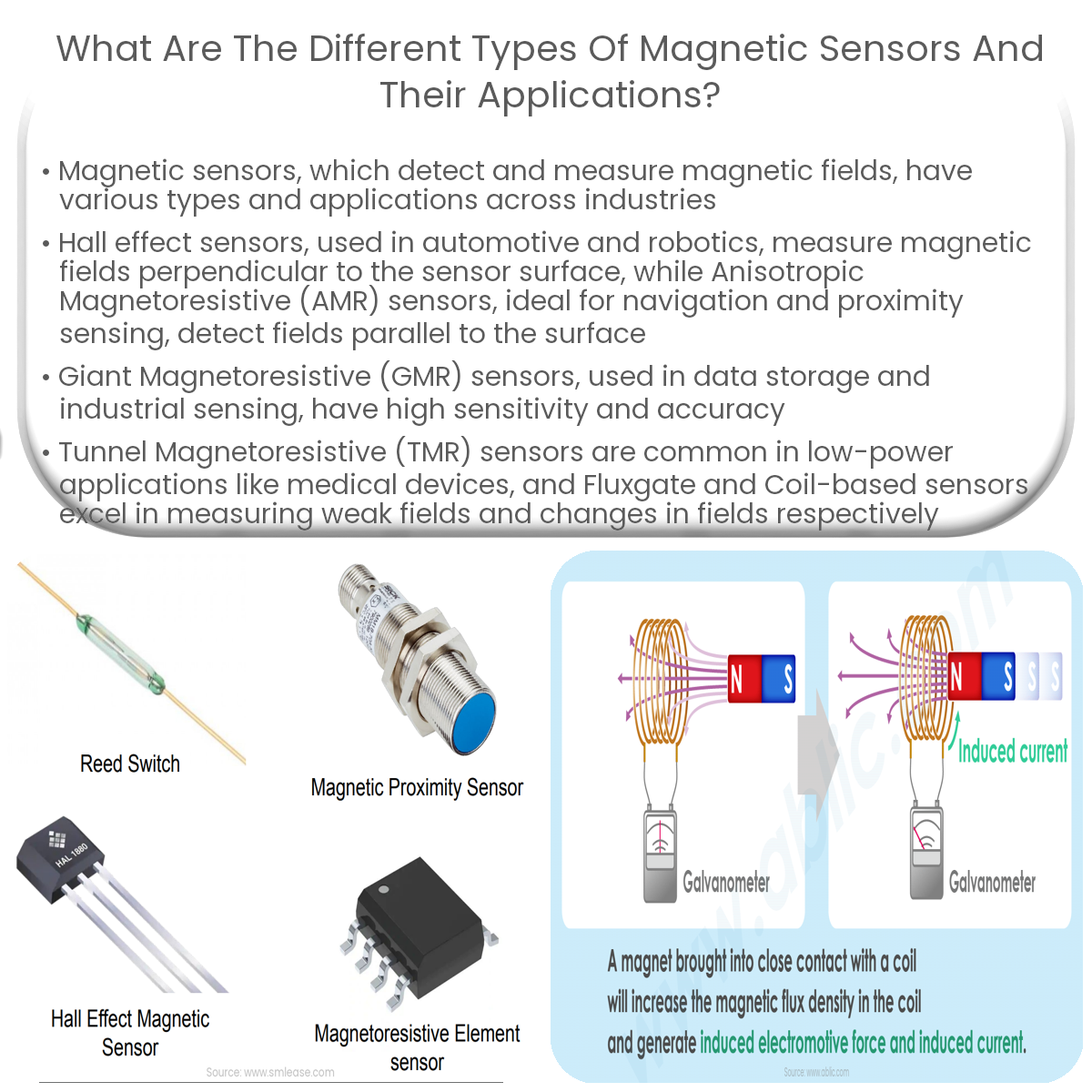
Hall Effect Sensors
Hall effect sensors measure magnetic fields perpendicular to the sensor surface. Applications include position sensing, current sensing, and speed measurement in industries such as automotive, robotics, and consumer electronics.
Anisotropic Magnetoresistive (AMR) Sensors
AMR sensors detect magnetic fields parallel to the sensor surface. They offer high sensitivity and low power consumption, making them suitable for applications like navigation systems, electronic compasses, and proximity sensing.
Giant Magnetoresistive (GMR) Sensors
GMR sensors exhibit a strong change in resistance when exposed to magnetic fields. They are widely used in data storage devices, automotive sensors, and industrial position sensing due to their high sensitivity and accuracy.
Tunnel Magnetoresistive (TMR) Sensors
TMR sensors offer the highest sensitivity among magnetoresistive sensors. They are commonly used in low-power applications, such as medical devices, wearables, and IoT devices for position, angle, and magnetic field detection.
Fluxgate Sensors
Fluxgate sensors are ideal for measuring weak magnetic fields. Their applications include geophysical surveys, space exploration, and underwater navigation systems.
Coil-based Sensors
Coil-based sensors, such as search coils and Rogowski coils, detect changes in magnetic fields by measuring induced voltage. They are often used in power systems, industrial automation, and non-destructive testing.
Conclusion
Magnetic sensors play a crucial role in various industries, offering accurate and reliable detection and measurement of magnetic fields. By understanding the different types of sensors and their applications, designers can select the most suitable technology for their specific needs.