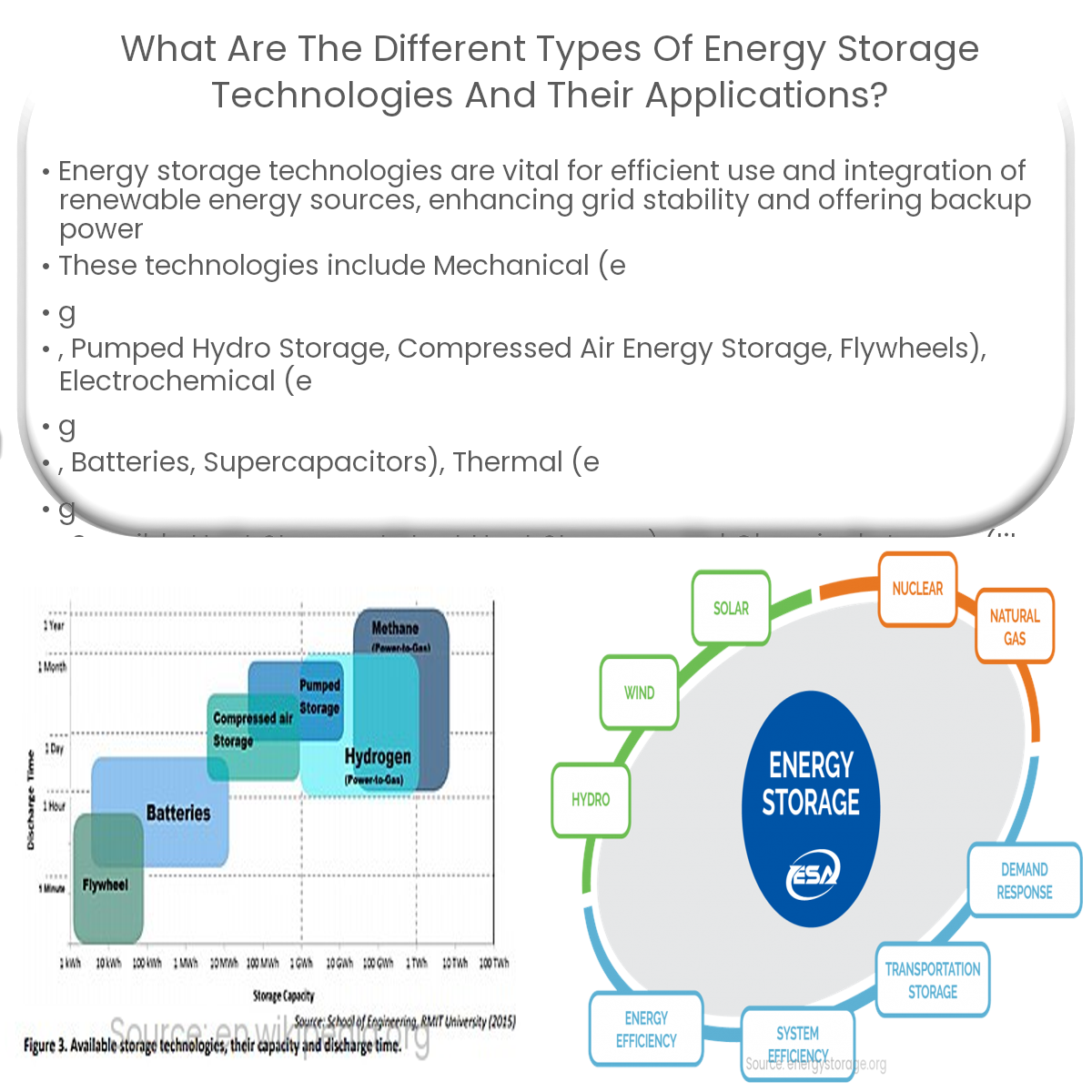
Energy storage technologies include pumped hydro storage, compressed air, flywheels, batteries, supercapacitors, thermal storage, and hydrogen storage.
Introduction to Energy Storage Technologies
Energy storage technologies play a crucial role in promoting the integration and efficient use of renewable energy sources. They can help manage energy demand, improve grid stability, and provide backup power during outages. This article explores the different types of energy storage technologies and their applications.
Mechanical Energy Storage
- Pumped Hydro Storage (PHS): PHS involves storing energy by pumping water from a lower reservoir to a higher one. During periods of high energy demand, the water is released back to the lower reservoir, generating electricity via turbines.
- Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES): CAES stores energy by compressing air in underground caverns. The compressed air is later released, driving turbines to generate electricity.
- Flywheels: Flywheels store energy in a rotating mass. When power is needed, the kinetic energy of the spinning flywheel is converted back into electricity.
Electrochemical Energy Storage
- Batteries: Batteries store energy through electrochemical reactions. Different types of batteries include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and flow batteries, each with varying energy densities and lifespans.
- Supercapacitors: Supercapacitors store energy in an electric field, allowing for rapid charge and discharge cycles. They have a longer lifespan than batteries but lower energy density.
Thermal Energy Storage
- Sensible Heat Storage: Sensible heat storage involves storing energy in a medium, such as water or rocks, by raising its temperature. The stored heat is later extracted and converted into electricity.
- Latent Heat Storage: Latent heat storage systems use phase change materials (PCMs) that absorb or release energy during a phase transition, such as melting or solidification.
Hydrogen and Other Chemical Energy Storage
Hydrogen can be produced through electrolysis using excess renewable energy and stored for later use in fuel cells or gas turbines. Additionally, other chemical energy storage technologies involve converting electricity into chemical bonds and vice versa.
Applications of Energy Storage Technologies
Energy storage technologies find applications in various sectors, including:
- Grid stabilization and peak shaving
- Renewable energy integration
- Backup power for critical systems
- Electric vehicle charging infrastructure
- Load leveling and demand response
As renewable energy sources continue to expand, the importance of energy storage technologies will only grow, helping to create a more resilient and sustainable energy future.