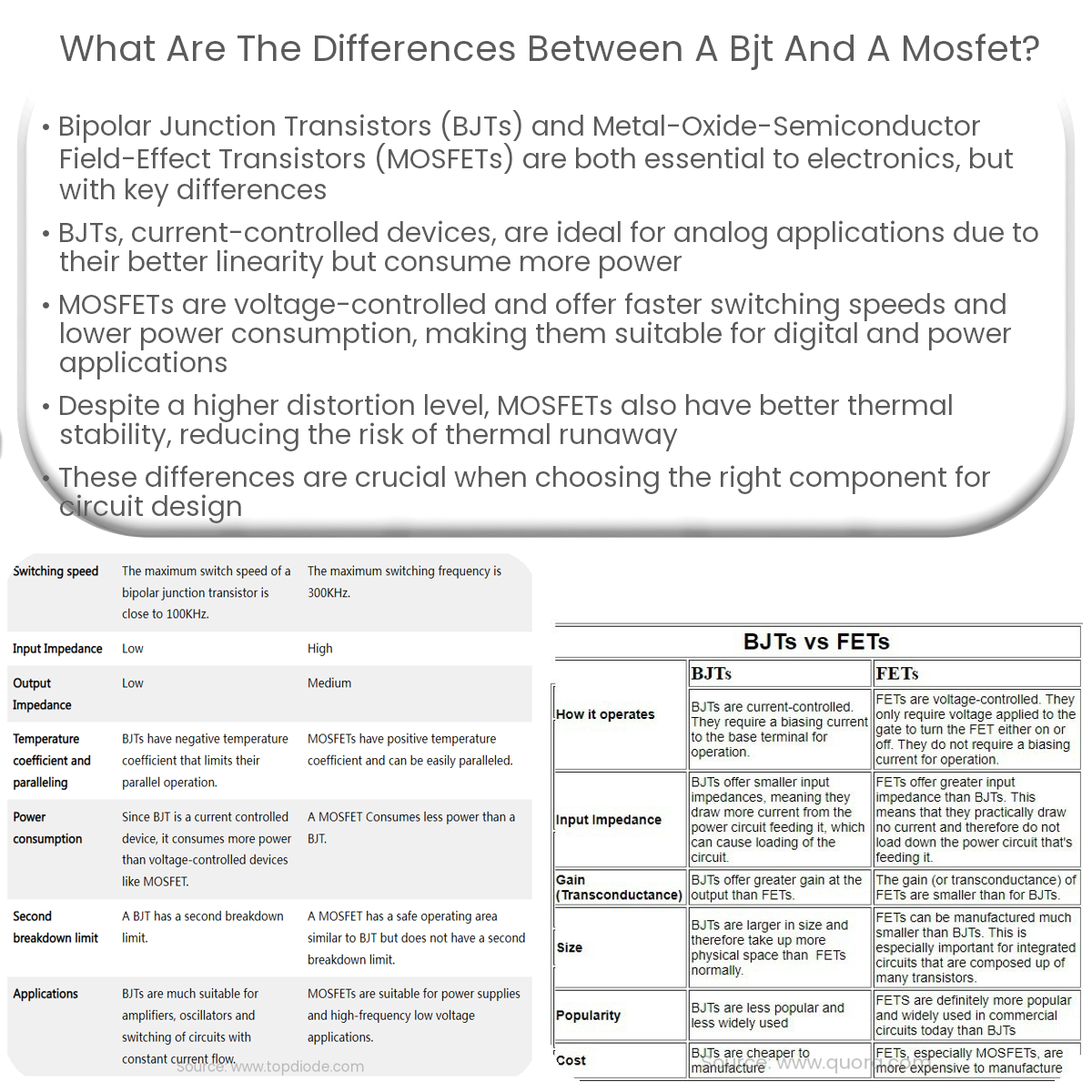
BJTs are current-controlled, better for analog applications, and can suffer thermal runaway. MOSFETs are voltage-controlled, faster, and more energy-efficient.
Introduction
Transistors play a vital role in the world of electronics as they are the building blocks of many circuits. Two widely used transistor types are Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) and Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFET). In this article, we will discuss the key differences between these two types of transistors.
Structure and Operation
BJTs are formed by combining two types of semiconductors, N-type and P-type, in either NPN or PNP configurations. They have three terminals: the emitter, base, and collector. BJTs are current-controlled devices, meaning that a small current flowing through the base-emitter junction controls a larger current flowing between the collector and emitter.
MOSFETs, on the other hand, consist of a gate, source, and drain terminal. They are voltage-controlled devices where the voltage applied to the gate controls the current flow between the source and drain terminals. The gate is electrically insulated from the channel by a thin oxide layer, leading to a high input impedance.
Power Consumption
BJTs have lower input impedance, which results in higher power consumption when used in amplifying circuits. MOSFETs, with their high input impedance, consume less power, making them more energy-efficient in certain applications.
Switching Speed
MOSFETs generally have faster switching speeds compared to BJTs. This is due to the absence of minority charge carriers, which results in reduced storage and transit times. However, high-frequency BJTs are also available, but they may have lower power handling capabilities.
Linearity
BJTs exhibit better linearity than MOSFETs, making them more suitable for analog applications, such as audio amplifiers. MOSFETs tend to have higher distortion levels, but they are still widely used in various applications, including digital circuits.
Thermal Stability
BJTs can suffer from thermal runaway, a condition where an increase in temperature causes the transistor to conduct more current, which in turn increases its temperature. This can lead to device failure. MOSFETs are less susceptible to thermal runaway due to their positive temperature coefficient, which helps stabilize the device at higher temperatures.
Conclusion
BJTs and MOSFETs are both essential components in electronic circuits, but their properties make them better suited for specific applications. BJT’s linearity and current-controlled operation make them ideal for analog applications, while MOSFET’s fast switching speeds, low power consumption, and voltage-controlled operation make them suitable for digital and power applications. Understanding the differences between these two types of transistors is crucial for selecting the right component for your circuit design.