Explore the fundamentals of Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), its types, benefits, challenges, and future prospects in our detailed guide.
Introduction to Wavelength Division Multiplexers (WDM)
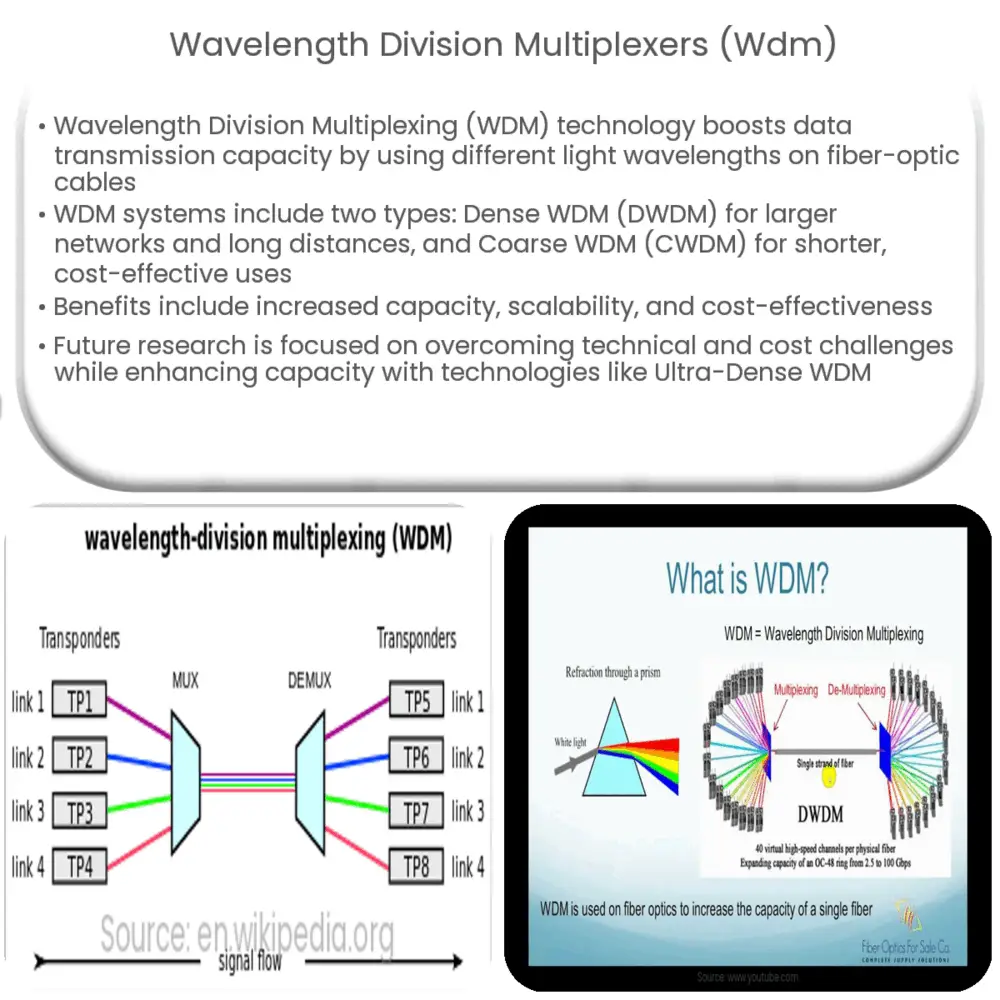
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a technology that has played a crucial role in the evolution and advancement of telecommunications and networking systems. It is designed to maximize the capacity of fiber-optic cables by simultaneously transmitting multiple data signals on the same fiber using different light wavelengths.
Working Principle of WDM
The fundamental principle of WDM is rooted in the properties of light and fiber-optic cables. As light of different wavelengths (colors) can travel along the same fiber without interfering with each other, WDM technology utilizes this characteristic to increase the data transmission capacity of the fiber.
Types of Wavelength Division Multiplexing
There are two primary types of WDM:
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM): DWDM works with a greater number of channels than the traditional WDM. It can transmit over longer distances and is primarily used in large-scale networks such as those found in internet service providers and telecommunication companies.
- Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM): CWDM is a more cost-effective version of WDM. It offers fewer channels and is best suited for short distances. It is commonly used in metropolitan area networks (MANs) and enterprise networks.
Components of a WDM System
A WDM system comprises several key components, and among them, the Wavelength Division Multiplexer holds a critical role. This component is designed to merge light signals with different wavelengths coming from different fibers into a single fiber. Other major components include:
- Transmitter: It generates the light signal and injects it into the fiber.
- Fiber-optic cables: These are the medium for the light signal transmission.
- Optical amplifiers: They boost the light signals to cover long distances without significant loss of signal strength.
Benefits of Wavelength Division Multiplexing
WDM technology offers a multitude of benefits, which have led to its widespread adoption in modern communication systems:
- Increased capacity: By utilizing multiple wavelengths, WDM significantly increases the data-carrying capacity of fiber-optic cables.
- Scalability: The system can be easily scaled up by adding new wavelengths to accommodate growing data requirements without laying additional fiber.
- Cost-effectiveness: WDM reduces costs by maximizing the use of each fiber strand, thereby minimizing the need for installing additional infrastructure.
Future Prospects and Challenges of WDM
Despite its advantages, WDM technology also presents some challenges. Designing and managing complex WDM systems requires sophisticated and often expensive equipment. Moreover, the need for precise light wavelengths necessitates high-quality lasers that are stable and tunable, adding to the overall cost. Nevertheless, research is ongoing to mitigate these challenges and further advance the technology.
In the future, we can expect to see the advent of technologies such as Ultra-Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (UDWDM), which aims to further increase the number of channels and overall capacity. Moreover, integrated photonics technology could potentially lead to more compact and cost-efficient WDM systems.
Conclusion
Wavelength Division Multiplexing is a critical technology that has revolutionized the telecommunications industry, making it possible to transmit vast amounts of data over large distances. Its ability to maximize the usage of fiber-optic cables has been instrumental in meeting the rising demand for data transmission in today’s digital age. Despite the challenges it presents, the future of WDM looks promising, with continual advancements expected to further enhance its capabilities. Understanding WDM technology is thus key to understanding the past, present, and future of telecommunications and networking.

