Explore the potential of triboelectric generators (TENGs) as a clean energy source, converting mechanical energy into electricity through the triboelectric effect.
Triboelectric Generator: A Promising Source of Clean Energy
Introduction
As the world faces an increasing demand for clean and renewable energy, researchers and engineers continue to explore innovative solutions to generate power. One such promising technology is the triboelectric generator (TENG). This article will provide an overview of the triboelectric generator, discuss its working principle, and delve into its potential applications and benefits.
What is a Triboelectric Generator?
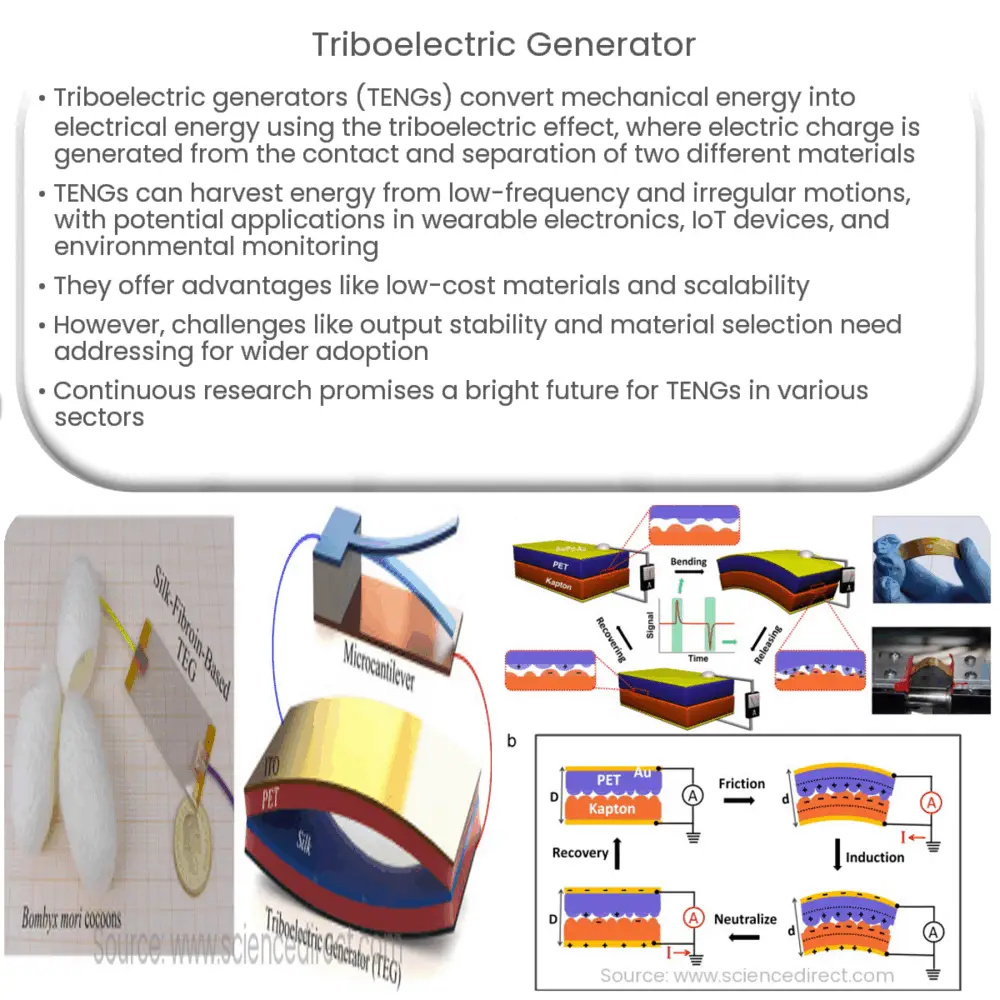
A triboelectric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through the triboelectric effect. The triboelectric effect refers to the generation of electric charge due to the contact and separation of two dissimilar materials. This phenomenon is commonly observed in everyday life, such as when rubbing a balloon against one’s hair or shuffling one’s feet on a carpeted floor. In the case of TENGs, the generated charge is harnessed and converted into usable electrical energy.
Working Principle of TENGs
The basic operation of a triboelectric generator involves the following steps: contact, separation, charge transfer, and charge collection. When two materials with different triboelectric affinities come into contact, electrons transfer from one material to the other, resulting in a charge imbalance. Upon separation, an electric potential difference is generated between the two materials, which can be utilized to drive current flow in an external circuit.
There are various designs and configurations of TENGs, such as vertical contact-separation mode, lateral-sliding mode, single-electrode mode, and freestanding triboelectric-layer mode. Each mode offers unique advantages and can be tailored to specific applications and environments.
Potential Applications and Benefits
Triboelectric generators hold immense potential in a wide range of applications, particularly in energy harvesting and self-powered systems. Some examples of TENG applications include:
- Wearable electronics: TENGs can be integrated into clothing, shoes, or accessories to harvest energy from human motion and power wearable devices such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical sensors.
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices: TENGs can serve as a sustainable energy source for wireless sensors and IoT devices, eliminating the need for battery replacement and reducing maintenance costs.
- Environmental monitoring: By harvesting energy from natural sources like wind, rain, or ocean waves, TENGs can power remote sensing equipment for monitoring environmental conditions and natural disasters.
One of the key benefits of triboelectric generators is their ability to harvest energy from low-frequency and irregular mechanical motions, which are often difficult to harness using traditional energy harvesting technologies. Additionally, TENGs offer advantages such as low-cost materials, simple fabrication, and scalability, making them an attractive option for various applications.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the numerous advantages and potential applications of triboelectric generators, there are also several challenges to be addressed. Some of these challenges include:
- Output stability: The output power of TENGs can be affected by environmental factors such as humidity and temperature, leading to fluctuations in performance. Researchers are working to develop strategies to improve the stability and reliability of TENGs under various conditions.
- Material selection: Identifying the optimal combination of materials with appropriate triboelectric properties is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of TENGs. Ongoing research aims to discover and develop new materials with superior performance.
- System integration: Integrating TENGs with other energy harvesting technologies and electronic devices requires the development of efficient power management systems and energy storage solutions.
Despite these challenges, the future of triboelectric generators looks promising. Continuous research and development efforts are expected to result in technological breakthroughs and novel applications for TENGs in various industries.
Conclusion
Triboelectric generators offer a promising solution for clean and sustainable energy generation by harnessing the power of the triboelectric effect. With their ability to convert mechanical energy from a wide range of sources into electrical energy, TENGs have the potential to revolutionize the fields of energy harvesting and self-powered systems. As research continues to address the challenges associated with TENGs and explore new materials and designs, we can expect to see a growing adoption of this technology in various applications, from wearable electronics and IoT devices to environmental monitoring and beyond.
References
- Wang, Z. L. (2012). Triboelectric Nanogenerators as New Energy Technology for Self-Powered Systems and as Active Mechanical and Chemical Sensors. ACS Nano, 6(10), 9533-9557.
- Wang, Z. L. (2017). On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Materials Today, 20(2), 74-82.
- Chen, J., Huang, Y., Zhang, N., Zou, H., Liu, R., Tao, C., Fan, X., & Wang, Z. L. (2020). Micro-cable structured textile for simultaneously harvesting solar and mechanical energy. Nature Energy, 1(10), 809-817.

