Explore the world of transistor voltage regulators, their working principles, types, applications, and their role in maintaining a stable voltage supply.
Introduction to Transistor Voltage Regulators
Transistor voltage regulators play a vital role in power electronics, where maintaining a stable voltage supply is essential for optimal functionality. As the name suggests, a transistor voltage regulator is a device that uses transistors, semiconductor devices with the ability to amplify or switch electronic signals, to maintain a constant voltage level.
Understanding the Basics
Voltage regulation is a process by which an electrical system maintains a constant voltage level despite changes in load conditions or input voltage. Voltage regulators are essential in many electronics, as they ensure that the devices receive the correct voltage to operate optimally and prevent damage from voltage spikes or drops.
How Transistor Voltage Regulators Work
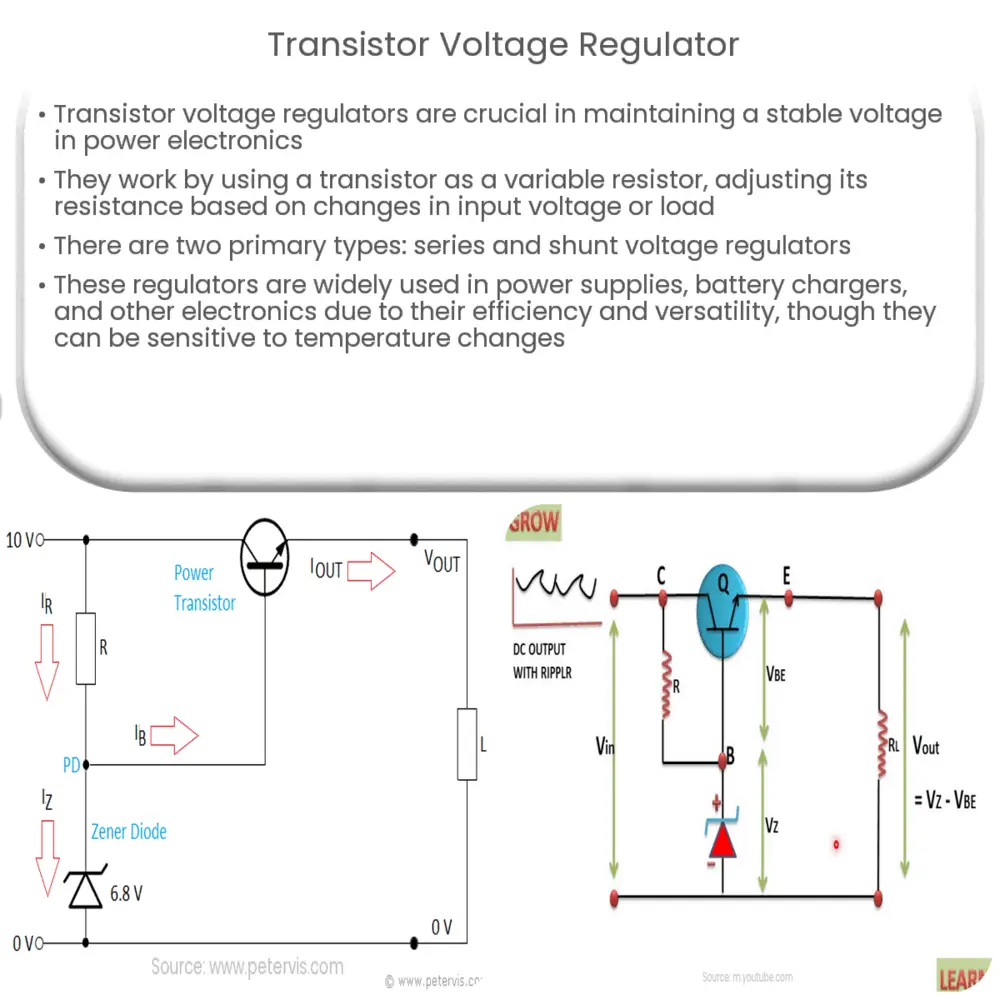
The transistor voltage regulator works based on the principle of using a variable resistor in the form of a transistor. This transistor adjusts its resistance in response to changes in input voltage or load conditions, thus maintaining a steady output voltage. When the input voltage or load changes, the transistor changes its resistance to keep the output voltage constant.
- Input Voltage: The input voltage, often referred to as the unregulated voltage, is the initial voltage supplied to the regulator. This voltage can fluctuate based on different factors, such as the supply source or environmental conditions.
- Output Voltage: This is the stabilized voltage that comes out of the regulator. The regulator’s purpose is to ensure that this voltage remains constant regardless of changes in the input voltage or load.
- Load Conditions: Load conditions refer to the electrical demand of the device or circuit connected to the output of the regulator. As the load changes, the current demand changes, which could potentially affect the output voltage if not for the action of the regulator.
The Role of Transistors in Voltage Regulation
Transistors are semiconductor devices that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. They are the main component in a transistor voltage regulator, acting as a variable resistor. When the input voltage increases, the transistor increases its resistance to maintain the output voltage constant, and vice versa. The resistance of the transistor can be controlled by the base current, making it an ideal component for maintaining a constant output voltage in a wide range of input voltages and load conditions.
Types of Transistor Voltage Regulators
There are primarily two types of transistor voltage regulators: series voltage regulators and shunt voltage regulators. Each type has a specific configuration and characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
- Series Voltage Regulator: In a series voltage regulator, the transistor is placed in series with the load. The transistor’s base-emitter junction functions as a variable resistor. As the input voltage changes, the base current is adjusted accordingly, changing the resistance to maintain a constant output voltage.
- Shunt Voltage Regulator: The shunt voltage regulator configuration places the transistor in parallel with the load. Here, the transistor acts as a variable shunt across the load. It absorbs the excess input voltage to protect the load and maintain a stable output voltage.
Applications of Transistor Voltage Regulators
Transistor voltage regulators find extensive use in power supply circuits, where maintaining a stable output voltage is crucial. They are also widely used in battery chargers, automobile alternators, computer power supplies, and other electronic devices that require a constant voltage supply. In addition, they can be found in power converters and power amplifiers, where they help to ensure the devices’ stability and reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Transistor Voltage Regulators
Transistor voltage regulators offer several advantages, such as their ability to provide a stable output voltage, their high efficiency, and their ability to handle a wide range of input voltages and load conditions. However, they also have certain disadvantages, such as their susceptibility to temperature changes and their requirement for a consistent base current to function correctly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, transistor voltage regulators are essential devices in the field of electronics, providing a stable voltage supply for a multitude of devices and circuits. They operate based on the variable resistance of a transistor, adjusting according to input voltage and load changes to maintain a consistent output voltage. While they come with their challenges, such as sensitivity to temperature changes, their benefits, including versatility and efficiency, make them indispensable in modern electronics.

