A thermal fuse is a one-time-use, temperature-sensitive safety device that interrupts an electrical circuit when a predetermined heat threshold is reached.
Understanding Thermal Fuses: Function, Applications, and How They Work
Introduction
A thermal fuse is a critical safety component in many electrical and electronic devices, designed to protect them from overheating and potential fire hazards. In this article, we will delve into the working mechanism of a thermal fuse, its various applications, and how it can save your appliances from potential damage.
What is a Thermal Fuse?
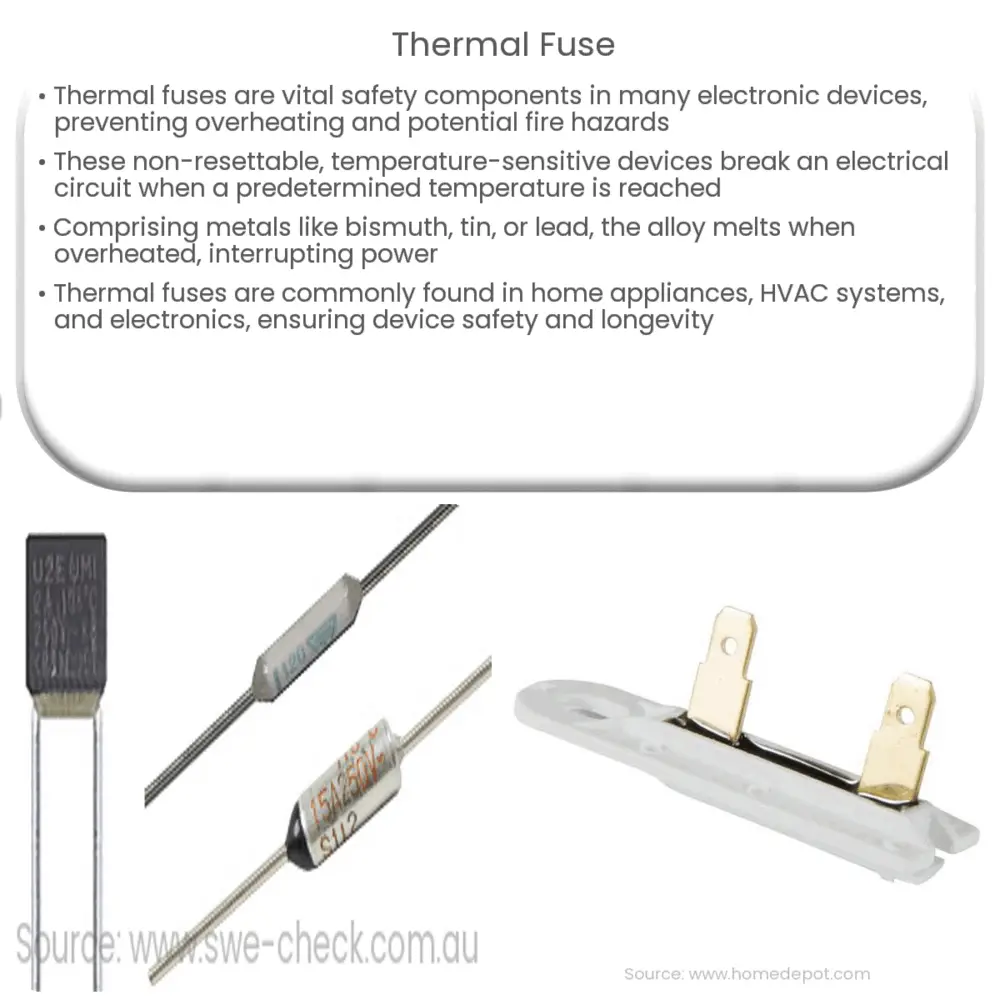
A thermal fuse is a small, non-resettable temperature-sensitive device that interrupts an electrical circuit when the temperature reaches a predetermined threshold. It is a one-time-use component, which means that once it has activated, it must be replaced. This feature ensures the utmost safety, as the device will not function again until the underlying issue causing the overheating is resolved.
How Does a Thermal Fuse Work?
A thermal fuse contains a temperature-sensitive alloy that melts when exposed to excessive heat. This alloy, typically composed of metals such as bismuth, tin, or lead, is designed to have a low melting point. When the temperature rises above the fuse’s rated threshold, the alloy melts, breaking the electrical circuit and shutting off the power to the device. This process prevents further overheating and potential damage to the appliance or even a fire.
Applications of Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses are found in various household and industrial appliances, where they provide an essential layer of protection against overheating. Some common applications of thermal fuses include:
- Home appliances: Thermal fuses are used in devices such as hairdryers, toasters, microwave ovens, and coffee makers. They prevent overheating and minimize the risk of fires caused by electrical malfunctions or component failures.
- Heating and cooling systems: HVAC systems and space heaters also employ thermal fuses to safeguard against the hazards of overheating, ensuring that the system shuts down if temperatures reach unsafe levels.
- Electronics: Power supplies, chargers, and other electronic devices utilize thermal fuses to protect sensitive components from heat damage, maintaining both safety and longevity.
Types of Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses come in various designs, each suited to different applications and temperature ranges. The two primary types of thermal fuses are:
- Axial thermal fuses: These cylindrical fuses are designed for direct mounting on printed circuit boards (PCBs) or in-line mounting within a cable or wire assembly. Axial thermal fuses are compact and versatile, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Radial thermal fuses: Radial fuses have a disc-like shape and are typically used in devices where space is limited. Their compact design allows for easy integration into appliances and electronic systems.
Selecting the Right Thermal Fuse
When choosing a thermal fuse for a specific application, several factors must be taken into consideration:
- Temperature rating: The fuse’s temperature rating should be set slightly higher than the device’s normal operating temperature to avoid nuisance tripping. The rating should also be lower than the temperature at which the appliance or component may be damaged or become hazardous.
- Current rating: The fuse must be able to handle the current flowing through the circuit without causing a voltage drop. Selecting a fuse with an appropriate current rating ensures proper device performance and reliable protection.
- Physical size and shape: The thermal fuse should fit within the designated space in the device without obstructing other components or impeding airflow.
Replacing a Thermal Fuse
Once a thermal fuse has been activated, it cannot be reset and must be replaced. To replace a thermal fuse, follow these steps:
- Disconnect the device from the power source and allow it to cool down.
- Locate the thermal fuse within the device. Consult the user manual or search for information online if you are unsure of its location.
- Remove the damaged thermal fuse and take note of its specifications, including temperature and current ratings.
- Purchase a replacement fuse with the same specifications from an authorized retailer or online store.
- Install the new thermal fuse and reassemble the device.
- Power up the device and test its functionality. If the thermal fuse activates again, consult a professional technician to diagnose and repair the underlying issue causing the overheating.
Conclusion
Thermal fuses play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of various electrical and electronic devices. By understanding their function and applications, you can better appreciate the importance of these components and make informed decisions when selecting, replacing, or troubleshooting thermal fuses in your appliances and systems.




